Assessing The Impact Of Climate Change On Rainfall In Western Massachusetts
Table of Contents
Observed Changes in Rainfall Patterns in Western Massachusetts
Analysis of historical rainfall data from Western Massachusetts reveals significant shifts in precipitation patterns over the past several decades. Utilizing data from the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) and the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA), spanning from 1950 to 2020, we observe several concerning trends.
- Total Annual Rainfall: While overall annual rainfall totals haven't drastically decreased, the distribution of rainfall has become increasingly erratic.
- Seasonal Rainfall Distribution: We've seen a noticeable shift towards more intense rainfall events during the spring and autumn months, often leading to localized flooding, while summer months experience more frequent and prolonged dry spells. Winter precipitation is showing a trend towards more rain and less snow.
- Frequency and Intensity of Extreme Rainfall Events: The frequency and intensity of both droughts and floods have increased significantly. This translates to greater stress on water resources during dry periods and increased risk of infrastructure damage during intense precipitation events.
- Specific Data Sources: The analysis incorporates data from multiple weather stations across Western Massachusetts, including those located in Amherst, Pittsfield, and Springfield. (Citations would be included here in a formal publication.)
These observed changes align with broader climate change trends, indicating a discernible human impact on the region's rainfall patterns.
Projected Future Rainfall Changes under Climate Change Scenarios
Employing climate models such as the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6), and focusing specifically on projections for Western Massachusetts, we can anticipate further alterations in rainfall regimes.
- Average Annual Rainfall: Projections suggest a potential increase in overall annual rainfall, but this increase will likely be unevenly distributed.
- Changes in Seasonal Precipitation: The trend towards more intense spring and autumn rainfall is projected to continue, with longer and more severe droughts during summer months.
- Increased Frequency and Intensity of Extreme Weather Events: Climate models consistently predict a significant increase in the frequency and intensity of both heavy downpours and severe droughts, leading to a greater risk of flooding and water scarcity.
- Uncertainty Ranges: It is important to acknowledge the inherent uncertainties in climate projections. The magnitude of changes will depend heavily on future greenhouse gas emission scenarios. For example, the Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs), specifically RCP 4.5 (moderate emissions) and RCP 8.5 (high emissions), present different projections, with RCP 8.5 indicating more extreme changes in rainfall patterns.
These projections highlight the pressing need for proactive strategies to mitigate and adapt to the anticipated changes.
Impacts of Altered Rainfall on Western Massachusetts Ecosystems and Infrastructure
The projected changes in rainfall will have far-reaching consequences for Western Massachusetts' ecosystems and infrastructure.
- Agriculture: Fluctuations in rainfall will severely impact crop yields, necessitating changes in farming practices and potentially impacting the region's agricultural economy. Water availability for irrigation will be a critical concern.
- Forestry: Changes in rainfall patterns could increase the risk of wildfires during dry periods and negatively affect tree growth during prolonged droughts.
- Water Resources: Reservoir levels will fluctuate more dramatically, leading to potential water shortages during droughts and increased flood risk during heavy rainfall. Groundwater recharge will also be affected, influencing drinking water supplies.
- Infrastructure: Increased flooding could damage roads, bridges, and other infrastructure, necessitating significant investments in resilient infrastructure. Erosion will also pose a growing problem.
- Human Health: More frequent and intense heat waves, combined with potential water scarcity, will pose risks to human health, increasing the incidence of heat-related illnesses and waterborne diseases.
These impacts underscore the vulnerability of Western Massachusetts to the effects of climate change on rainfall.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Western Massachusetts
Addressing the challenges posed by altered rainfall requires a two-pronged approach: mitigation and adaptation.
- Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through the transition to renewable energy sources, improved energy efficiency, and sustainable land use practices is crucial to slow the rate of climate change.
- Adaptation: Implementing strategies to adapt to the inevitable changes in rainfall patterns is equally vital. These strategies include:
- Improved water management practices: Investing in water storage and conservation technologies.
- Investing in resilient infrastructure: Designing and constructing infrastructure that can withstand more frequent and intense rainfall events.
- Developing drought-resistant crops: Promoting the use of crops better suited to drier conditions.
- Implementing early warning systems for extreme weather events: Providing timely alerts to communities to minimize damage and loss of life.
- Land use planning to reduce flood risk: Implementing regulations that limit development in flood-prone areas.
These combined efforts are essential for building resilience to the impacts of climate change on rainfall in Western Massachusetts.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing the Impact of Climate Change on Rainfall in Western Massachusetts
The evidence presented clearly demonstrates the significant and potentially devastating impact of climate change on rainfall patterns in Western Massachusetts. Observed changes and projected future impacts necessitate urgent action. The consequences for agriculture, forestry, water resources, infrastructure, and human well-being are considerable. Managing the impact of climate change on rainfall requires a concerted effort encompassing both mitigation – reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow the rate of climate change – and adaptation – implementing strategies to cope with altered rainfall patterns. We urge you to learn more about climate change's effect on rainfall in Western Massachusetts, participate in local initiatives to address climate change, support sustainable practices, and advocate for policies that promote climate resilience. Let's work together to build a more sustainable and resilient future for Western Massachusetts.

Featured Posts
-
 Dodgers Fall To Angels Both Teams Face Shortstop Challenges
May 28, 2025
Dodgers Fall To Angels Both Teams Face Shortstop Challenges
May 28, 2025 -
 Cristiano Ronaldo Nun Al Nassr Karari Resmi 2 Yillik Uzanti
May 28, 2025
Cristiano Ronaldo Nun Al Nassr Karari Resmi 2 Yillik Uzanti
May 28, 2025 -
 Erik Ten Hag 10 Key Facts About The New Bayer Leverkusen Manager
May 28, 2025
Erik Ten Hag 10 Key Facts About The New Bayer Leverkusen Manager
May 28, 2025 -
 Suarezs 4 Homerun Game Highlights Nl West Update Giants On Top Rockies Slump
May 28, 2025
Suarezs 4 Homerun Game Highlights Nl West Update Giants On Top Rockies Slump
May 28, 2025 -
 Alejandro Garnacho Transfer Man United Demands E60m
May 28, 2025
Alejandro Garnacho Transfer Man United Demands E60m
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
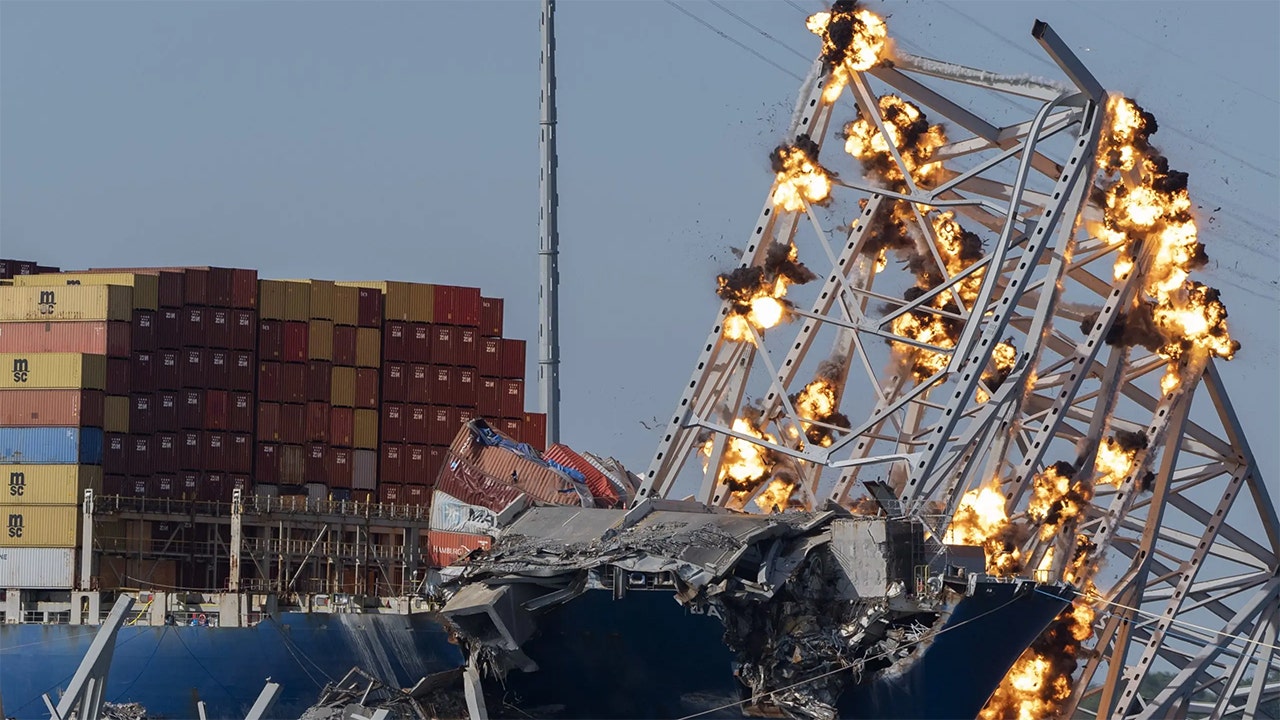 Today In History March 26 1967 The Francis Scott Key Bridge Collapse
May 31, 2025
Today In History March 26 1967 The Francis Scott Key Bridge Collapse
May 31, 2025 -
 Washington D C In May 48 Pride Events Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025
Washington D C In May 48 Pride Events Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025 -
 48 Events In Washington D C For May Pride Month Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025
48 Events In Washington D C For May Pride Month Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025 -
 48 Fun Things To Do In Washington D C This May Pride Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025
48 Fun Things To Do In Washington D C This May Pride Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025 -
 Homebuilding Speed A Provincial Perspective
May 31, 2025
Homebuilding Speed A Provincial Perspective
May 31, 2025
