Auto Dealers Double Down On Opposition To EV Sales Quotas

Table of Contents
Financial Concerns and Infrastructure Readiness
The core of auto dealers' opposition to EV sales quotas lies in significant financial hurdles and the lack of supporting infrastructure. The transition to a predominantly electric vehicle market requires substantial investment and carries considerable risk.
High Upfront Investment Costs for Dealerships
Adapting to an EV-centric sales model demands significant capital investment. Dealerships face substantial expenses related to infrastructure upgrades, specialized tools, and employee training.
- Charging Station Installation: Installing Level 2 and DC fast chargers requires considerable upfront costs, varying based on the number of chargers, power requirements, and installation complexity. The cost can range from several thousand dollars per charger to tens of thousands for a comprehensive network.
- Employee Training Programs: Sales staff and technicians need specialized training to understand and service EVs. This includes training on EV batteries, charging systems, and specialized diagnostic tools, adding to the overall expense.
- Inventory Adjustments: Dealerships must adjust their inventory to accommodate the increased demand for EVs, potentially requiring significant upfront investment in EV stock while managing the decline in sales of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. This shift in inventory can lead to losses if EV sales don't meet projections.
- Statistics: A recent study by the National Automobile Dealers Association (NADA – replace with actual association if different) indicates that smaller dealerships face a disproportionate burden, with some estimating upfront costs exceeding $100,000 (replace with actual statistic if available). This financial strain could force some smaller dealerships out of business.
Lack of Consumer Demand and Charging Infrastructure
Dealers argue that current consumer demand for EVs doesn't justify the immediate imposition of aggressive sales quotas. The insufficient availability of public and private charging infrastructure further hinders widespread EV adoption.
- Market Share: Currently, EVs represent a relatively small percentage of total vehicle sales (insert actual statistic here). This suggests that mandating high EV sales quotas would artificially inflate demand, potentially leading to unsold inventory and financial losses for dealerships.
- Charging Station Availability: The density of public charging stations, especially fast-charging stations, remains inadequate in many areas. This "range anxiety" among potential EV buyers significantly impacts consumer confidence and adoption rates. Data on charging station availability (insert relevant data here) highlights this crucial infrastructure gap.
Uncertainty and Risk in the Rapidly Evolving EV Market
The EV market is dynamic and highly susceptible to rapid technological change. This inherent uncertainty makes it difficult for dealers to accurately forecast future demand and manage their investments effectively.
- Technological Advancements: Battery technology, charging infrastructure, and even vehicle design are constantly evolving. Investments in current technology may quickly become obsolete, leading to significant financial losses for dealerships.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in battery prices, government incentives, and consumer preferences introduce significant market volatility, adding to the risks associated with large-scale investments in the EV sector.
Concerns Regarding Consumer Choice and Market Competition
Beyond financial concerns, auto dealers express deep concerns about the impact of EV sales quotas on consumer choice and market competition.
Quotas Limiting Consumer Vehicle Selection
Mandated quotas could artificially restrict consumer choice by potentially limiting the availability of gasoline-powered vehicles. This raises concerns about consumer sovereignty and the right to choose the vehicle best suited to their individual needs and preferences.
- Consumer Preference Data: (Insert data on consumer preferences for vehicle types. Include sources). This data could demonstrate that a significant portion of the market still prefers gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Government Intervention: The argument against government intervention in consumer choices emphasizes the importance of market forces in determining consumer preferences and vehicle availability.
Impact on Smaller Dealerships and Independent Repair Shops
The transition to EVs poses a disproportionate challenge for smaller dealerships and independent repair shops, which often lack the resources to quickly adapt to the new technology.
- Market Statistics: (Insert statistics comparing the number of small vs. large dealerships). This data could illustrate the vulnerability of smaller businesses to the financial pressures of transitioning to EV sales.
- Job Losses: The shift away from gasoline vehicles could lead to job losses in the automotive repair sector, as the skills required to maintain EVs differ significantly from those needed for traditional vehicles.
Unfair Competition Concerns and Potential Market Distortions
Dealers fear that mandated quotas might create an uneven playing field, favoring larger corporations with greater resources to adapt to the changing market landscape.
- Corporate Investments: (Provide examples of large automotive companies' substantial investments in EV technology). This illustrates the disparity in resources available to large corporations compared to smaller dealerships.
- Impact on Independent Automakers: Smaller, independent automakers might be particularly disadvantaged by aggressive quotas, potentially hindering innovation and competition in the EV market.
Alternative Approaches and Policy Recommendations
Instead of imposing rigid EV sales quotas, dealers advocate for alternative approaches that promote a gradual and sustainable transition to electric vehicles.
Phased Implementation of EV Sales Targets
A phased approach to EV sales quotas would allow dealerships ample time to adapt to the changing market, invest in necessary infrastructure, and manage the transition without significant financial distress.
- Phased Implementation Models: (Provide examples of successful phased implementation models from other industries or regions).
- Advantages: A phased approach allows for continuous monitoring and adjustment, mitigating risks and fostering a more balanced transition.
Government Support for Infrastructure Development
Significant government investment in EV charging infrastructure is crucial to supporting greater EV adoption. This includes both public and private charging networks.
- Government Incentives: (Discuss specific government incentives, such as tax credits, grants, and subsidies for charging infrastructure development).
- Accessibility: Strategies to improve the accessibility of charging infrastructure, such as expanding charging networks in underserved areas, are essential for widespread EV adoption.
Consumer Education and Incentives for EV Adoption
Boosting consumer demand for EVs requires comprehensive educational campaigns and attractive purchase incentives.
- Successful Campaigns: (Provide examples of successful EV promotion campaigns from other countries or regions).
- Consumer Incentives: (Discuss government tax credits, rebates, and other incentives designed to encourage EV purchases).
Conclusion
This article highlighted the significant opposition from auto dealers regarding mandated EV sales quotas, focusing on their financial concerns, worries about consumer choice, and concerns about fair competition. Dealers are pushing for alternative approaches such as phased implementation, substantial infrastructure investment, and targeted consumer incentives. Understanding the multifaceted issues surrounding EV sales quotas is crucial. Continued dialogue involving all stakeholders – government, manufacturers, and dealers – is essential to finding a balanced solution that promotes the transition to electric vehicles while ensuring a fair and sustainable automotive market. Further research on the impact of EV sales quotas and their alternatives is needed to inform future policy decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 90s Fashion Trends And More Our Photo Gallery
Apr 25, 2025
90s Fashion Trends And More Our Photo Gallery
Apr 25, 2025 -
 How Election Promises Lead To Budget Deficits An Economic Analysis
Apr 25, 2025
How Election Promises Lead To Budget Deficits An Economic Analysis
Apr 25, 2025 -
 69th Eurovision Song Contest Betting Odds And Expert Predictions
Apr 25, 2025
69th Eurovision Song Contest Betting Odds And Expert Predictions
Apr 25, 2025 -
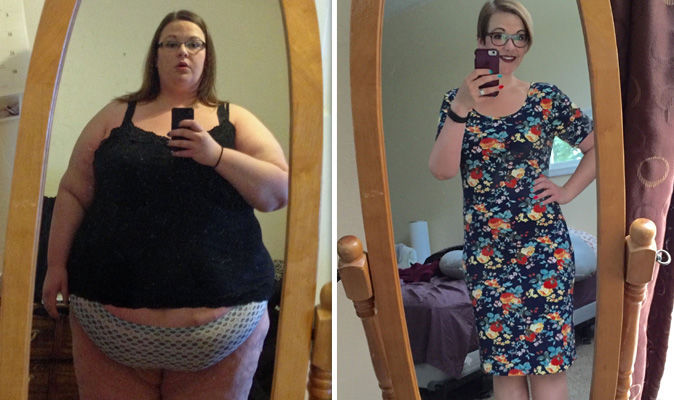 30 Stone Weight Loss The Power Of Motivation And A Friends Honest Feedback
Apr 25, 2025
30 Stone Weight Loss The Power Of Motivation And A Friends Honest Feedback
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Taylors Of Harrogate Wins Gold
Apr 25, 2025
Taylors Of Harrogate Wins Gold
Apr 25, 2025
