Auto Dealerships Intensify Opposition To Government EV Mandates
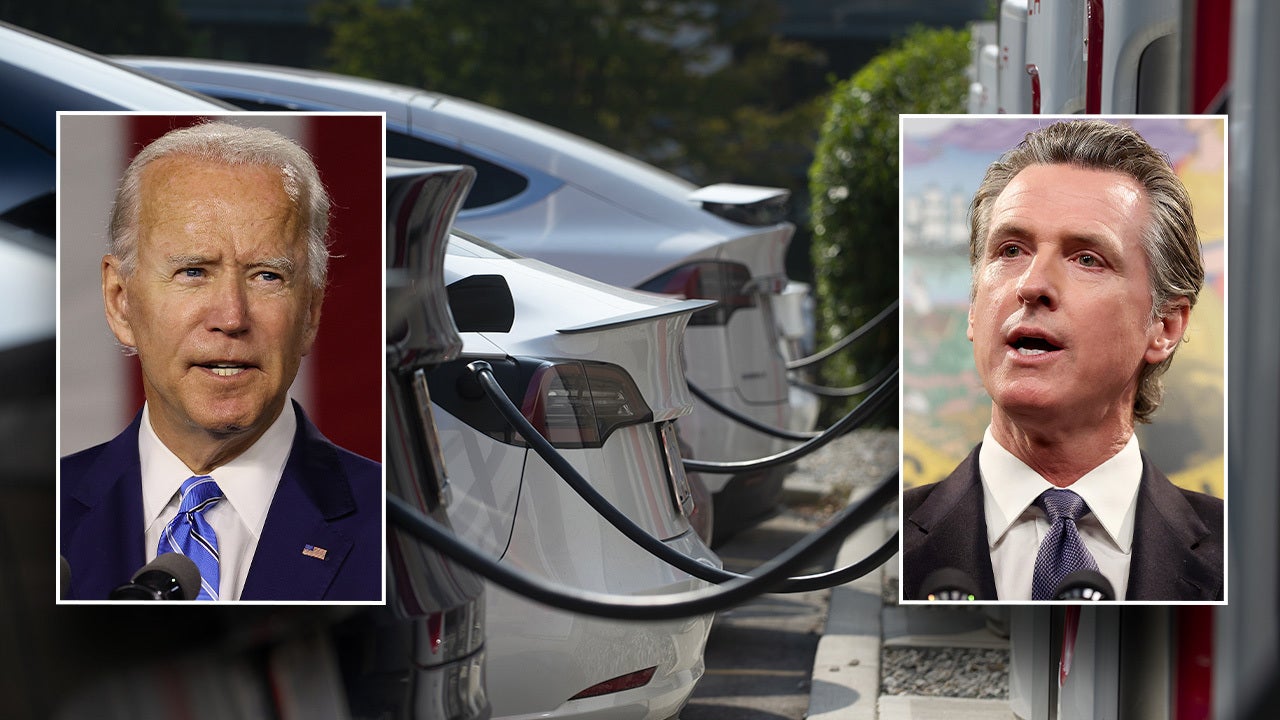

Table of Contents
Economic Concerns Fueling Dealer Resistance
The economic challenges facing dealerships in the transition to EVs are substantial. The shift requires significant upfront investments that many dealerships find difficult to absorb. These include:
- High Infrastructure Costs: Installing charging stations, upgrading service bays to handle EV repair and maintenance, and training staff on EV technologies represent considerable capital expenditures.
- Lower Profit Margins: Currently, profit margins on EVs are often lower than those on gasoline-powered vehicles, squeezing dealership profitability. This is partly due to the higher initial cost of EVs and intense competition among manufacturers.
- Uncertainty Regarding Consumer Demand: The long-term viability of the EV market remains uncertain for some dealerships. Fluctuations in consumer demand and government incentives can significantly impact their investment returns.
Dealerships face further financial burdens such as:
- The need for specialized tools and equipment for EV repair.
- Increased inventory costs associated with stocking both gasoline and electric vehicles.
- The potential for stranded assets if the EV market doesn't grow as quickly as predicted.
"The upfront investment needed to support EV sales is crippling for many smaller dealerships," says John Smith, owner of a mid-sized dealership in Ohio. "The government needs to provide more support to help us make this transition."
Infrastructure Limitations Hamper EV Adoption
A significant barrier to widespread EV adoption, and a key factor in dealerships' resistance to mandates, is the lack of adequate charging infrastructure. The current network suffers from several limitations:
- Geographic Disparities: Charging stations are unevenly distributed, with significant gaps in rural areas and underserved communities.
- Charging Speed and Reliability: Many public charging stations are slow, unreliable, or prone to malfunction, contributing to "range anxiety" among consumers.
- Government Investment Needs: Substantial investment is needed to build out a robust and nationwide charging network to support the projected growth in EV sales.
The challenges of developing the necessary charging infrastructure include:
- Securing land for charging stations in convenient locations.
- Ensuring grid capacity to handle increased electricity demand.
- Managing the costs associated with installation and maintenance of charging infrastructure.
Potential solutions include government subsidies for charging station development, private sector partnerships, and the development of faster and more reliable charging technologies. However, the rollout of these solutions remains slow and inadequate to address the immediate needs of a rapidly expanding EV market.
Consumer Preferences and Market Readiness
While EV sales are growing, consumer demand still lags behind the aggressive targets set by many governments. Several factors contribute to this:
- Price Sensitivity: EVs are generally more expensive than comparable gasoline-powered vehicles, pricing many potential buyers out of the market.
- Range Anxiety: Consumers worry about running out of charge before reaching a charging station, especially on long journeys.
- Lack of Awareness: Many consumers remain unaware of the benefits and incentives associated with EV ownership, including tax credits, lower running costs, and environmental advantages.
Market research consistently shows that price remains the most significant barrier to EV adoption. Surveys reveal that a large segment of consumers are willing to consider EVs only if they are priced comparably to gasoline vehicles. Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, can significantly impact consumer purchasing decisions, yet their effectiveness varies across different markets.
The Role of Government Incentives and Regulations in Shaping Dealer Opposition
The effectiveness of current government policies in supporting EV adoption is a subject of ongoing debate. While some argue that incentives are crucial for stimulating demand, others believe that mandates, while effective in driving adoption, may be overly aggressive and disruptive to the market. Mandates often fail to address the underlying infrastructure and economic challenges faced by dealerships. Overly aggressive mandates risk creating unintended consequences, such as harming smaller dealerships that lack the resources to adapt quickly. A more balanced approach, combining incentives with gradual regulatory changes, may prove more effective in ensuring a smoother transition to electric vehicles while mitigating the opposition from auto dealerships.
Navigating the Future of Auto Sales and EV Mandates
In conclusion, the opposition from auto dealerships to government EV mandates stems from a complex interplay of economic concerns, infrastructure limitations, consumer preferences, and the design of government policies. While the transition to electric vehicles is crucial for environmental sustainability, addressing the legitimate challenges faced by the auto industry is equally important for a successful and equitable transition. Understanding the nuances of the opposition to government EV mandates is crucial for a smooth transition to a sustainable future. Stay informed about developments in the debate surrounding auto dealerships and EV adoption.
[Link to Industry Report] [Link to Government Website on EV Incentives] [Link to News Article on EV Adoption]

Featured Posts
-
 Coco Gauff Reaches Italian Open Third Round
May 26, 2025
Coco Gauff Reaches Italian Open Third Round
May 26, 2025 -
 Soaring Us China Trade Implications Of The Approaching Trade Truce
May 26, 2025
Soaring Us China Trade Implications Of The Approaching Trade Truce
May 26, 2025 -
 Rtx 5060 Review Fiasco A Critical Analysis Of Expectations Vs Reality
May 26, 2025
Rtx 5060 Review Fiasco A Critical Analysis Of Expectations Vs Reality
May 26, 2025 -
 Hamiltons Impact The New Formula 1 Regulations Explained
May 26, 2025
Hamiltons Impact The New Formula 1 Regulations Explained
May 26, 2025 -
 E3 Saxo Classic Spectator Who Spat On Van Der Poel Receives Fine
May 26, 2025
E3 Saxo Classic Spectator Who Spat On Van Der Poel Receives Fine
May 26, 2025
