California's EV Mandate: Automakers' Aggressive Pushback
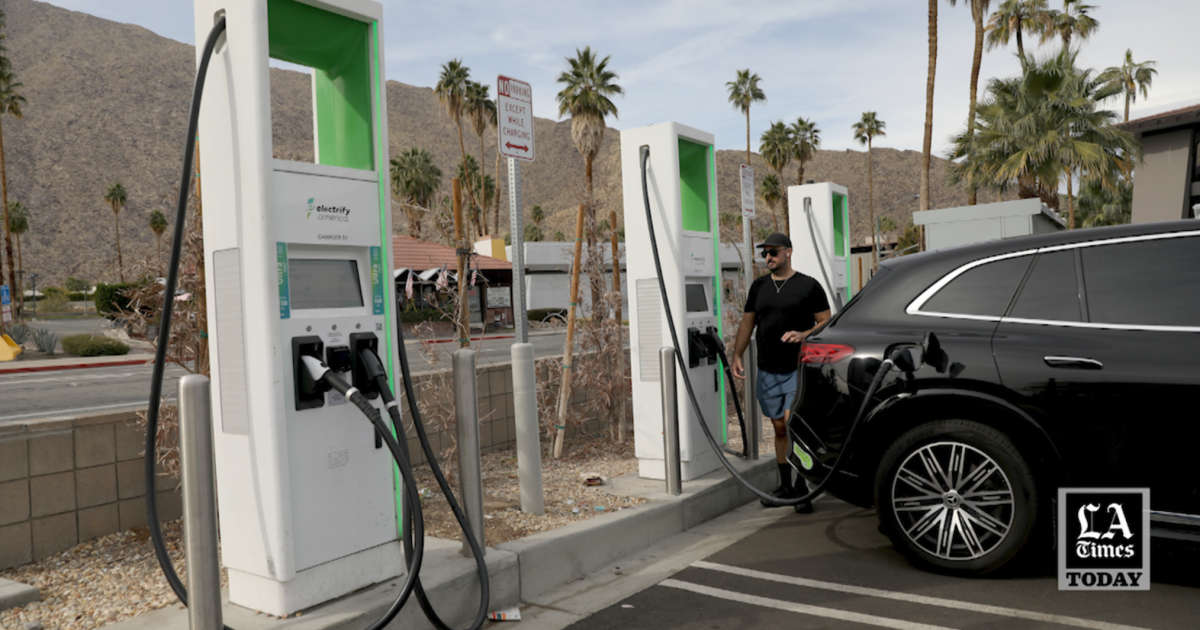

Table of Contents
Economic Challenges and Production Constraints
The core of automakers' resistance to California's EV mandate lies in the substantial economic hurdles associated with mass EV production. Meeting the mandate's aggressive timelines presents significant challenges, impacting profitability and potentially leading to job losses.
-
High battery costs and raw material scarcity: The cost of lithium-ion batteries, a critical component of EVs, remains a major obstacle. The scarcity of essential raw materials, coupled with fluctuating market prices, further exacerbates this issue. This directly impacts the final cost of the vehicle and makes it difficult for manufacturers to compete with gasoline-powered cars on price.
-
Lack of sufficient charging infrastructure: Widespread EV adoption requires a robust and readily accessible charging infrastructure. The current network, particularly in certain regions, is insufficient to support a large-scale shift to electric vehicles. This "range anxiety" deters potential buyers and presents a logistical challenge for automakers.
-
Investments needed in manufacturing and supply chains: Producing EVs demands significant investments in new manufacturing facilities, tooling, and revamped supply chains. This capital expenditure places a heavy burden on automakers, especially during periods of economic uncertainty.
-
Impact on profitability and potential job losses: The high upfront costs associated with EV production, coupled with the potential for lower profit margins compared to gasoline vehicles, threaten the profitability of automakers. Furthermore, there are concerns regarding potential job losses in traditional automotive manufacturing sectors if the transition is too rapid. Keywords: EV production costs, battery costs, charging infrastructure, supply chain issues, economic impact, profitability.
Concerns Regarding Consumer Demand and Market Readiness
Automakers contend that the current market isn't ready for the rapid shift mandated by California. They point to several factors highlighting insufficient consumer demand and a lack of preparedness.
-
Range anxiety and charging time concerns: Many consumers remain hesitant about EVs due to concerns about limited range and relatively long charging times compared to refueling gasoline vehicles. Addressing these anxieties requires significant technological advancements and infrastructure improvements.
-
High purchase prices compared to gasoline vehicles: The initial purchase price of EVs remains significantly higher than comparable gasoline-powered vehicles, making them inaccessible to many consumers. Government subsidies can partially mitigate this, but the price gap remains a considerable barrier to widespread adoption.
-
Limited model availability and variety: The current selection of EV models is still relatively limited compared to the diverse range of gasoline vehicles available. Expanding model availability and offering a wider variety of options will be essential for increased consumer adoption.
-
Consumer education and awareness gaps: Many consumers lack sufficient knowledge about the benefits, costs, and practicalities of owning an EV. Increased consumer education initiatives are needed to overcome these knowledge gaps and promote EV adoption. Keywords: consumer demand, market readiness, range anxiety, charging time, EV prices, consumer adoption, model availability.
Legal Challenges and Political Maneuvering
Faced with what they see as an overly aggressive mandate, automakers are deploying various legal and political strategies to oppose or modify the regulations.
-
Lawsuits challenging the legality of the mandate: Several automakers have filed lawsuits challenging the legality and feasibility of the California EV mandate, arguing that it exceeds the state's authority or is economically unachievable.
-
Lobbying efforts to influence state and federal policymakers: Intensive lobbying efforts are underway to influence policymakers at both the state and federal levels, aiming to delay, weaken, or repeal the mandate's stricter provisions.
-
Attempts to delay or modify the mandate's timeline: Automakers are actively seeking to extend the deadlines for meeting the mandate's targets, arguing that a more gradual transition is necessary for both economic and technological reasons.
-
Alliance-building with other states and industry groups: Automakers are forming alliances with other states and industry groups to present a unified front against the mandate, increasing their political leverage. Keywords: legal challenges, lobbying, political influence, policy changes, regulatory hurdles, legal battles.
Alternative Solutions and Technological Advancements
Automakers aren't simply resisting; they're also proposing alternative solutions and highlighting technological advancements that could potentially mitigate some of the concerns surrounding the mandate.
-
Focus on hybrid vehicles as a transition technology: Many manufacturers advocate for a more gradual transition, emphasizing the role of hybrid vehicles as an intermediary step towards full electrification. Hybrids offer a compromise, combining the benefits of electric motors with the convenience of gasoline engines.
-
Development of more efficient and affordable batteries: Significant progress is being made in battery technology, focusing on increasing energy density, extending range, and reducing costs. These advancements are key to making EVs more competitive with gasoline vehicles.
-
Improvements in charging infrastructure and technology: Innovations in charging technology, such as faster charging speeds and wireless charging, are crucial for addressing range anxiety and improving the overall EV ownership experience.
-
Government incentives and subsidies to support EV adoption: Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, play a significant role in making EVs more affordable and accessible to consumers. Keywords: hybrid vehicles, battery technology, charging technology, government incentives, technological advancements, alternative solutions.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of California's EV Mandate
The California EV mandate represents a significant challenge for automakers, sparking intense debate over economic feasibility, consumer demand, and the pace of technological advancement. The key points of contention center on the high costs of EV production, insufficient charging infrastructure, concerns about consumer acceptance, and the legal and political maneuvering surrounding the mandate. The mandate's significance for the future of transportation and the environment cannot be overstated, however. A collaborative approach is crucial to find a balance between ambitious environmental goals and economic realities. Further informed discussion on the California EV mandate and its impact is vital. To learn more about California's ZEV regulations and the ongoing debate, visit [link to relevant resource]. Keywords: California EV mandate, ZEV regulations, electric vehicle future, sustainable transportation.

Featured Posts
-
 Reduced Library Funding And Services Under Trumps Executive Order
May 19, 2025
Reduced Library Funding And Services Under Trumps Executive Order
May 19, 2025 -
 Cohep Y La Transparencia Electoral Un Analisis Del Proceso
May 19, 2025
Cohep Y La Transparencia Electoral Un Analisis Del Proceso
May 19, 2025 -
 Ny Mets Schedule 3 Crucial May Series That Will Define Their Season
May 19, 2025
Ny Mets Schedule 3 Crucial May Series That Will Define Their Season
May 19, 2025 -
 Ufc Vegas 106 Headliner Experts Weigh In On Michael Morales Real Deal Performance
May 19, 2025
Ufc Vegas 106 Headliner Experts Weigh In On Michael Morales Real Deal Performance
May 19, 2025 -
 Ufc Vegas 106 Michael Morales Back To Back Performance Bonuses
May 19, 2025
Ufc Vegas 106 Michael Morales Back To Back Performance Bonuses
May 19, 2025
