China And US Trade: A Race Against Time To Meet Trade Agreement Goals
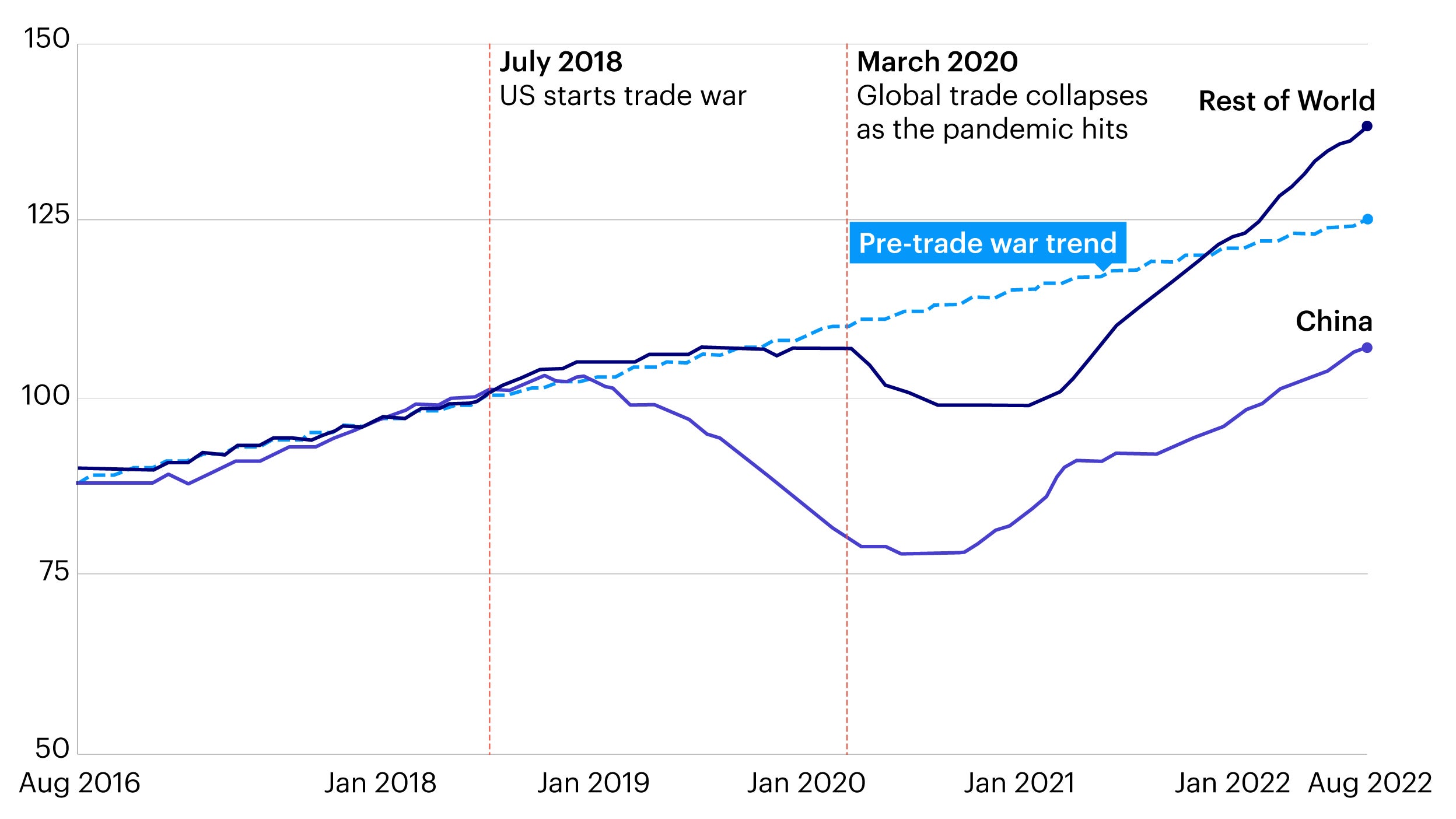
Table of Contents
Phase One Deal Implementation Challenges and Progress
The Phase One trade deal, signed in January 2020, aimed to address longstanding trade imbalances and concerns between the US and China. This agreement involved significant Chinese purchase commitments for American agricultural products and manufactured goods, alongside commitments on intellectual property protection and market access.
While some progress has been made, significant challenges persist. China has increased its purchases of certain American goods, particularly soybeans, contributing to a boost in US agricultural exports. However, other targets remain unmet, particularly concerning technology transfer and certain manufactured goods.
- Successful Implementation: Increased soybean exports to China have benefited US farmers.
- Unmet Targets: Delays in achieving promised purchases of manufactured goods and technology transfers have hindered progress.
- Industry Impact: The US agricultural sector has seen a positive impact, while some manufacturing sectors face ongoing challenges in accessing the Chinese market. The impact on Chinese industries is complex, with some sectors benefiting from increased imports while others face increased competition.
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) Protection and Enforcement
Robust intellectual property rights (IPR) protection is crucial for fostering innovation and fair competition. The Phase One deal included commitments from China to strengthen IPR protection and enforcement. However, challenges remain, particularly in effectively enforcing these rights against counterfeiting and forced technology transfer.
Weak IPR protection in China continues to impact US businesses, hindering their ability to compete and protect their innovations. This necessitates further cooperation and consistent pressure to ensure meaningful implementation of IPR provisions.
- Successful Enforcement: While specific examples are often confidential due to legal reasons, improved transparency and reporting on IPR enforcement is needed to demonstrate progress.
- Ongoing Violations: Counterfeiting of US brands and intellectual property theft remain prevalent issues requiring persistent attention.
- Recommendations: Strengthening cooperation through joint investigations and improved mechanisms for dispute resolution are crucial for effective IPR protection.
Market Access and Non-Tariff Barriers in China
Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs) present significant hurdles to US businesses seeking access to the Chinese market. These barriers, often hidden behind regulations, licensing requirements, and complex bureaucratic processes, hinder market entry and competitiveness.
The Phase One deal addressed some NTBs, but many remain, posing considerable challenges for American companies seeking to export goods and services to China.
- Specific NTBs: Complex product certification processes, discriminatory regulations, and opaque licensing requirements are common examples.
- Impact on Competitiveness: NTBs increase costs, delay market entry, and reduce the competitiveness of US firms in China.
- Overcoming NTBs: Targeted negotiations, increased transparency in regulatory processes, and consistent engagement with Chinese authorities are vital for addressing these barriers.
The Role of Technology Transfer and Innovation
Technology transfer is a critical element in the China-US trade relationship. While collaborative technology transfer can benefit both countries, concerns remain about instances of forced technology transfer, where US companies are compelled to share their intellectual property as a condition for market access in China. This practice undermines US technological leadership and innovation.
- Successful Collaborations: Joint ventures and licensing agreements can facilitate beneficial technology transfer, leading to mutual innovation.
- Forced Technology Transfer Concerns: Pressure on US firms to share sensitive technology as a condition for operating in China remains a significant concern.
- Implications for Future Development: Addressing forced technology transfer is essential to safeguard US technological advantage and foster a fair and balanced trading environment.
Accelerating Progress Towards China and US Trade Agreement Goals
Meeting the China and US Trade Agreement Goals requires sustained effort and collaboration. While progress has been made in some areas, significant challenges remain in areas like intellectual property rights, market access, and technology transfer. The urgency to achieve these targets within the stipulated timeframe is paramount. Continued dialogue and cooperation between the two nations are essential to navigate the complexities and ensure a mutually beneficial outcome.
To stay informed about developments related to China and US Trade Agreement Goals and their impact on the global economy, follow reputable news sources and research institutions focusing on international trade. Understanding the dynamics of this crucial relationship is vital for businesses and policymakers alike.

Featured Posts
-
 How Jesse Eisenberg Cast Kieran Culkin In A Real Pain An Interview
May 23, 2025
How Jesse Eisenberg Cast Kieran Culkin In A Real Pain An Interview
May 23, 2025 -
 2027 Tour De France Race Starts In Edinburgh Uk
May 23, 2025
2027 Tour De France Race Starts In Edinburgh Uk
May 23, 2025 -
 Tu Horoscopo Semanal 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025
May 23, 2025
Tu Horoscopo Semanal 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025
May 23, 2025 -
 Kazakhstan Stuns Australia In Billie Jean King Cup Qualifying Tie
May 23, 2025
Kazakhstan Stuns Australia In Billie Jean King Cup Qualifying Tie
May 23, 2025 -
 Bangladeshs Lead Grows Thanks To Shantos Unbeaten Half Century
May 23, 2025
Bangladeshs Lead Grows Thanks To Shantos Unbeaten Half Century
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Wrestle Mania 41 Golden Championship Belts And Memorial Day Weekend Ticket Offer
May 23, 2025
Wrestle Mania 41 Golden Championship Belts And Memorial Day Weekend Ticket Offer
May 23, 2025 -
 Wwe Wrestle Mania 41 Golden Belts And Memorial Day Weekend Ticket Sales
May 23, 2025
Wwe Wrestle Mania 41 Golden Belts And Memorial Day Weekend Ticket Sales
May 23, 2025 -
 Lowest Gas Prices In Decades Expected For Memorial Day Weekend
May 23, 2025
Lowest Gas Prices In Decades Expected For Memorial Day Weekend
May 23, 2025 -
 Neal Mc Donough Rides The Wildest Bull In The Last Rodeo
May 23, 2025
Neal Mc Donough Rides The Wildest Bull In The Last Rodeo
May 23, 2025 -
 Exclusive Neal Mc Donough Discusses Damien Darhk And A Possible Dc Project
May 23, 2025
Exclusive Neal Mc Donough Discusses Damien Darhk And A Possible Dc Project
May 23, 2025
