China's Economic Stimulus: Rate Cuts And Easier Access To Bank Loans
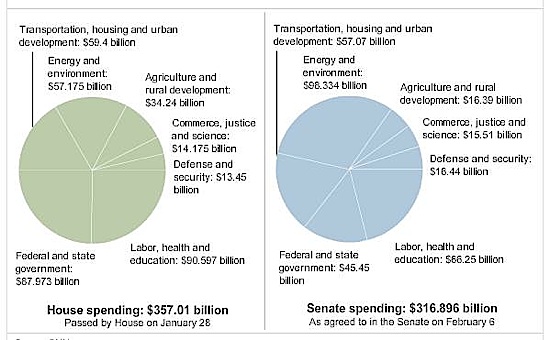
Table of Contents
Interest Rate Cuts: A Key Component of China's Economic Stimulus
The rationale behind China's interest rate cuts is straightforward: stimulate borrowing and investment. By lowering borrowing costs, the government aims to incentivize businesses and consumers to increase spending and investment, thereby injecting much-needed momentum into the economy.
- Recent Rate Cut Announcements:
- In [Month, Year], the People's Bank of China (PBOC) announced a [percentage]% cut in the [specific interest rate].
- A further reduction of [percentage]% was implemented in [Month, Year] impacting the [specific interest rate].
- These cuts represent a significant shift in monetary policy, signaling the government's commitment to stimulating economic growth.
Lower interest rates translate to reduced borrowing costs for businesses, making expansion and investment more attractive. Consumers also benefit from cheaper loans, potentially boosting consumption. However, rate cuts are not without potential drawbacks. One significant risk is increased inflation, as cheaper credit could fuel higher demand and put upward pressure on prices. The PBOC must carefully balance the need for economic stimulus with the risk of runaway inflation.
Easing Access to Bank Loans: Fueling Investment and Consumption
In tandem with interest rate cuts, the Chinese government is actively working to improve access to bank loans, particularly for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). SMEs are the backbone of China's economy, and their ability to secure financing is critical for overall economic health.
- Government Initiatives:
- The government has encouraged state-owned banks to loosen lending standards for SMEs.
- Several targeted programs offer subsidized loans and reduced collateral requirements for SMEs.
- Measures to streamline loan application processes have been introduced to speed up access to credit.
State-owned banks play a crucial role in implementing these policies. Their lending decisions directly impact the availability of credit for businesses and influence investment levels in infrastructure projects and the private sector. This increased lending, while crucial for economic growth, also carries risks. The potential for a rise in non-performing loans (NPLs) needs careful monitoring and management to prevent systemic instability.
The Impact on Economic Growth and Key Sectors
The projected impact of this economic stimulus on China's GDP growth is a subject of ongoing debate among economists. While many predict a positive effect, the magnitude remains uncertain. The stimulus is expected to have varying impacts across different sectors:
- Real Estate: Easing credit conditions may temporarily boost the real estate market, though government regulations aim to curb excessive speculation.
- Manufacturing: Improved access to credit could support production and investment within the manufacturing sector.
- Technology: The tech sector is likely to benefit from the improved financing environment, facilitating innovation and growth.
However, challenges remain. The effectiveness of the stimulus hinges on several factors, including the speed of implementation, the absorption capacity of the economy, and the global economic climate. Data on investment, consumption, and production will be crucial in assessing the actual effectiveness of the policy.
Challenges and Risks Associated with China's Economic Stimulus
While the stimulus package aims to boost economic growth, several challenges and risks must be considered:
- Inflationary Pressures: The increased money supply resulting from rate cuts and expanded lending could lead to significant inflationary pressures.
- Asset Bubbles: Increased credit availability may fuel asset bubbles, especially in the already volatile real estate market.
- Equitable Distribution: Ensuring the benefits of the stimulus reach all segments of the population and regions equally presents a significant challenge.
Conclusion
China's economic stimulus plan centers on strategic interest rate cuts and enhanced access to bank loans. While these measures aim to boost GDP growth and stimulate investment, potential risks, including inflation and asset bubbles, must be carefully managed. The success of the stimulus will depend on effective implementation, careful monitoring, and addressing the challenges associated with equitable distribution of benefits. Stay informed about the unfolding effects of China's economic stimulus and its implications for the global economy. Follow our updates on future developments related to China's interest rate cuts and easier access to bank loans for a comprehensive understanding of this significant economic policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Neymar Podria Volver A La Seleccion Brasilena Prelista Para Argentina
May 08, 2025
Neymar Podria Volver A La Seleccion Brasilena Prelista Para Argentina
May 08, 2025 -
 Dont Miss It Superman And Krypto Team Up In Next Weeks Special
May 08, 2025
Dont Miss It Superman And Krypto Team Up In Next Weeks Special
May 08, 2025 -
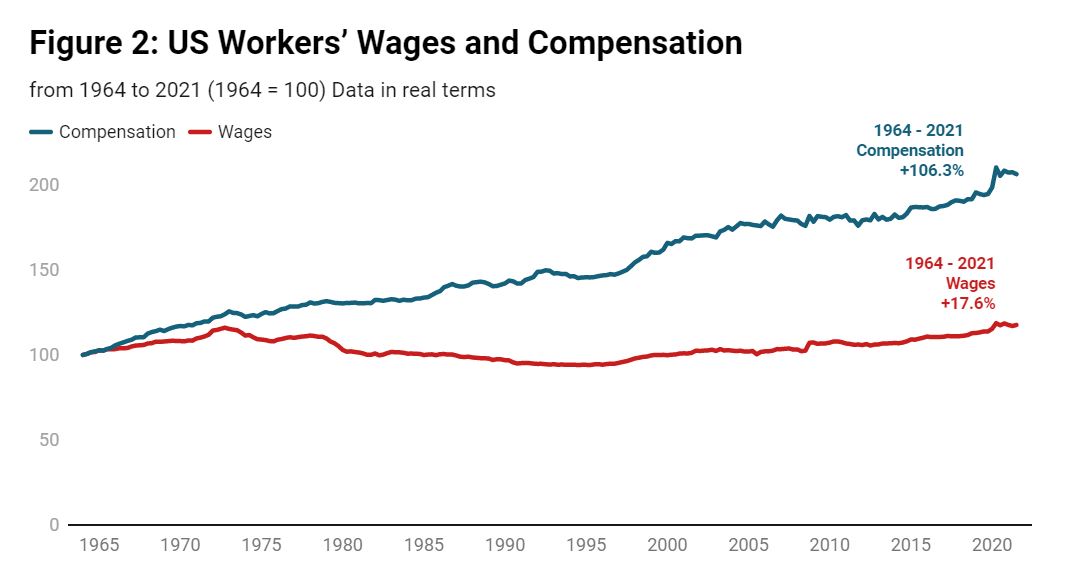 Analyzing The Great Decoupling Trends And Forecasts
May 08, 2025
Analyzing The Great Decoupling Trends And Forecasts
May 08, 2025 -
 Major Xrp Whale Transaction Analysis And Market Outlook
May 08, 2025
Major Xrp Whale Transaction Analysis And Market Outlook
May 08, 2025 -
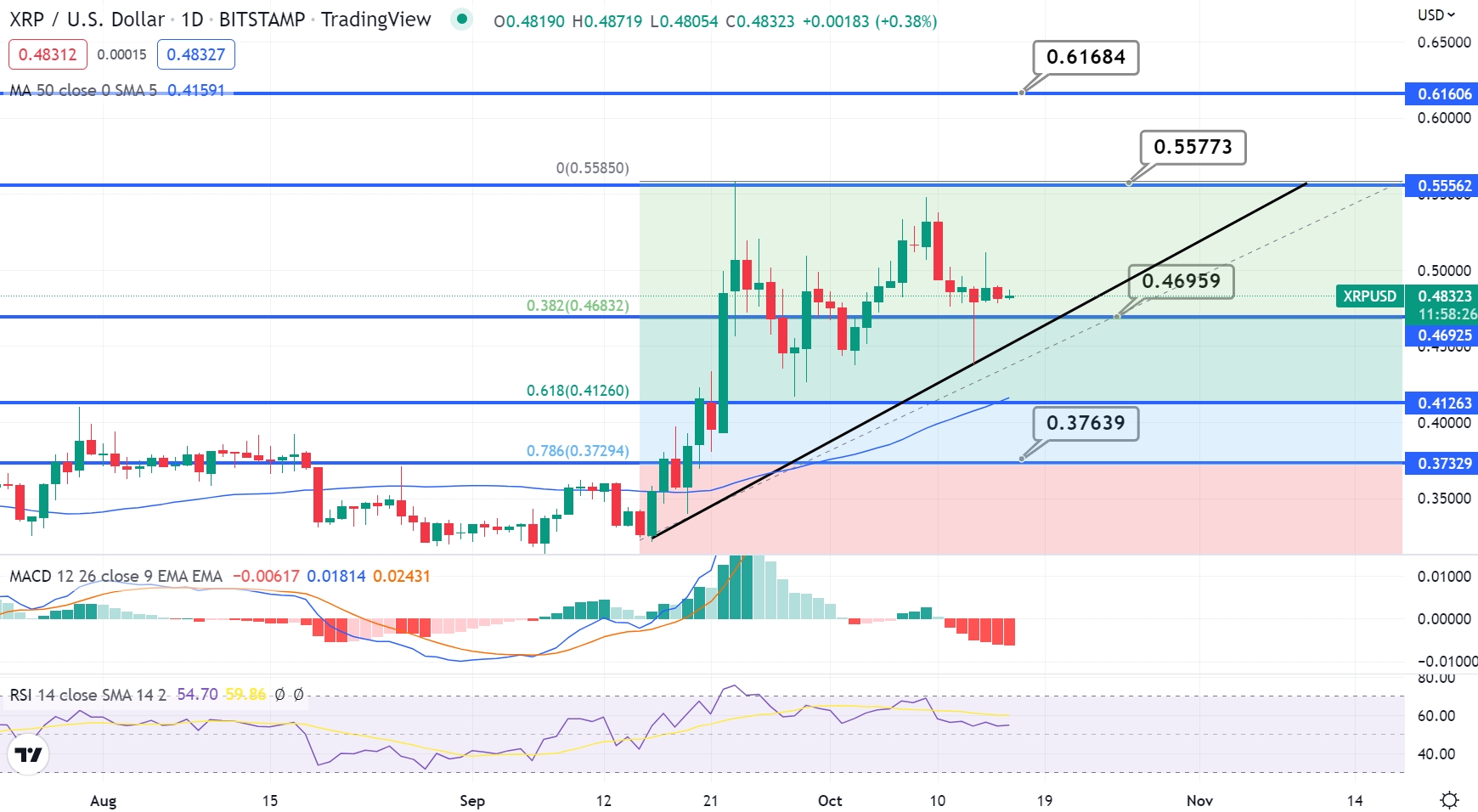 Xrp Price Prediction Can Xrp Rise Further After A 400 Surge
May 08, 2025
Xrp Price Prediction Can Xrp Rise Further After A 400 Surge
May 08, 2025
