Europe's Exodus: Examining The Impact Of EU Policies

Table of Contents
Economic Factors Driving Europe's Exodus
High unemployment, stagnant wages, and widening income inequality are significant push factors contributing to Europe's Exodus. These economic hardships force many, particularly young people, to seek better opportunities abroad.
Youth Unemployment and Lack of Opportunities
High youth unemployment rates in several EU member states, particularly in Southern Europe, are a primary driver of emigration. Young, skilled individuals, facing bleak prospects at home, are drawn to countries with stronger economies and more job opportunities.
- Statistics on youth unemployment rates: Data from Eurostat consistently shows significantly higher youth unemployment rates (individuals aged 15-24) in countries like Spain, Italy, and Greece compared to Northern European nations. These discrepancies create a stark contrast in opportunities, fueling emigration.
- Examples of brain drain: The "brain drain" effect is evident, with highly educated young professionals from Southern Europe migrating to countries like Germany, the UK (pre-Brexit), and the Netherlands for better career prospects and higher salaries. This loss of human capital significantly harms the economic potential of the originating countries.
- EU initiatives tackling youth unemployment: The EU's Youth Guarantee initiative aims to provide young people with a quality job offer, traineeship, apprenticeship, or continued education within four months of leaving formal education or becoming unemployed. However, its effectiveness varies across member states, highlighting the need for more targeted and impactful interventions.
Wage Stagnation and Income Inequality
Slow wage growth and widening income inequality across the EU contribute to disillusionment and emigration, especially among the middle class. Austerity measures implemented in several countries following the 2008 financial crisis have further exacerbated this issue.
- Data comparing income levels: Data from the OECD reveals significant disparities in income levels and distribution across EU countries. This income inequality fuels social unrest and contributes to the decision of many to seek better living standards elsewhere.
- Impact of austerity measures: Austerity measures, while intended to stabilize economies, often led to wage freezes or reductions, impacting disposable income and further widening the gap between the rich and the poor. This has negatively affected living standards, contributing to Europe's Exodus.
- EU policies aimed at reducing income inequality: The EU has various initiatives to promote social inclusion and reduce income inequality, such as the European Social Fund Plus. However, the effectiveness of these programs in countering emigration remains a subject of ongoing debate.
Social and Political Factors Contributing to Europe's Exodus
Beyond economic factors, social and political issues also contribute to the outflow of population. The lack of affordable housing, increasing living costs, and political instability all play a role.
Lack of Affordable Housing and Increasing Living Costs
The rising cost of living, particularly housing, in major European cities is a significant deterrent, pushing many to seek more affordable options abroad. This is particularly relevant for younger generations struggling to enter the housing market.
- Statistics on housing affordability: Numerous reports highlight the decreasing affordability of housing in major European capitals, with rent and property prices significantly outpacing wage growth. This makes homeownership a distant dream for many, prompting them to consider emigration.
- Comparison with housing costs in other regions: Comparing housing costs in major European cities with those in other regions, particularly in North America or Australia, reveals significant differences, making emigration a more attractive option for some.
- Impact of immigration on housing markets: While immigration can contribute to demand, it doesn't automatically explain the high prices in many cities. Other factors like limited housing construction and speculative investment play a larger role in driving up costs.
Political Instability and Populism
The rise of right-wing populism and anti-EU sentiment in some member states creates an uncertain political climate, pushing some to leave in search of greater stability and inclusivity.
- Examples of political events influencing emigration: Events such as Brexit and the rise of nationalist movements in several countries have created uncertainty and fueled emigration, particularly among those who feel their values are not represented.
- Impact of Brexit on emigration patterns: Brexit has significantly impacted emigration patterns, with many EU citizens leaving the UK due to concerns about their future status and access to services.
- Analysis of the link between political polarization and emigration decisions: Increased political polarization and the erosion of trust in institutions can lead to feelings of alienation and insecurity, prompting some to seek a more stable and welcoming environment elsewhere.
The Impact of EU Policies on Europe's Exodus
EU policies have both facilitated and attempted to mitigate Europe's Exodus. Analyzing their impact is crucial to understanding the complexities of this trend.
The Schengen Agreement and Free Movement
The Schengen Agreement, while promoting economic integration and free movement of people, has also inadvertently facilitated emigration. While it offers opportunities, it also makes leaving easier.
- Discussion of the benefits and drawbacks of free movement: Free movement has fostered economic growth and cultural exchange but has also led to concerns about potential strains on resources and social services in certain regions.
- Case studies of countries significantly impacted by emigration due to Schengen: Countries with high unemployment and limited opportunities have experienced significant emigration flows due to the ease of movement within the Schengen area.
- Potential reforms to the Schengen system to address emigration concerns: Discussions about potential reforms to the Schengen system often involve strengthening border controls and addressing concerns about uncontrolled migration and potential security risks.
EU Agricultural Policies and Rural Depopulation
EU agricultural policies, while aimed at supporting farmers, may have inadvertently contributed to rural depopulation and emigration from rural areas.
- Discussion of the impact of agricultural subsidies on rural economies: While subsidies support farmers, they may not always translate into economic diversification and job creation in rural areas, leading to young people leaving for urban centers or other countries.
- Examples of regions experiencing significant rural depopulation: Many rural regions in Southern and Eastern Europe are experiencing significant population decline due to a lack of economic opportunities and limited access to services.
- Potential policy adjustments to support rural areas and curb emigration: Investing in rural infrastructure, supporting local businesses, and creating more diverse economic opportunities are crucial to counter rural depopulation and encourage people to stay.
Conclusion
Europe's Exodus is a multifaceted issue resulting from a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors. EU policies, while aiming for integration and prosperity, have both contributed to and attempted to mitigate this population outflow. Addressing youth unemployment, income inequality, affordable housing, and political instability is crucial to stem the tide of "Europe's Exodus." Further research and a comprehensive review of existing EU policies are necessary to combat this trend and build a more resilient and attractive Europe. We must work together to find solutions and reverse the trend of Europe's Exodus, creating a brighter future for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Alex Pereiras Future In The Ufc After Ufc 313 Loss
May 19, 2025
Alex Pereiras Future In The Ufc After Ufc 313 Loss
May 19, 2025 -
 Cooke Maroney And Jennifer Lawrence Couple Steps Out After Welcoming Second Child
May 19, 2025
Cooke Maroney And Jennifer Lawrence Couple Steps Out After Welcoming Second Child
May 19, 2025 -
 Ana Paola Hall Y El Cne Analisis De Su Independencia Y Caracter Colegiado
May 19, 2025
Ana Paola Hall Y El Cne Analisis De Su Independencia Y Caracter Colegiado
May 19, 2025 -
 Chateau Diy Your Guide To Stunning Castle Inspired Projects
May 19, 2025
Chateau Diy Your Guide To Stunning Castle Inspired Projects
May 19, 2025 -
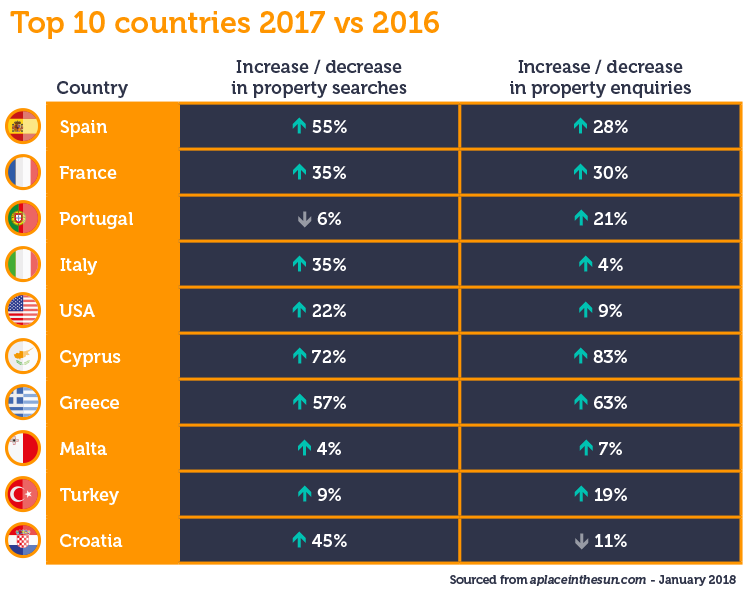 Your Place In The Sun Navigating The Overseas Property Market
May 19, 2025
Your Place In The Sun Navigating The Overseas Property Market
May 19, 2025
