Evaluating Uber Technologies (UBER) As An Investment

Table of Contents
Uber's Business Model and Revenue Streams
Uber's core business model revolves around connecting riders and drivers through its app, a platform that has expanded far beyond ride-sharing. Its revenue streams are diversified across several key segments:
-
Ride-sharing: This remains Uber's flagship service, generating revenue through commissions on each ride. Key metrics here include revenue per ride and market share within specific geographic regions.
-
Uber Eats: This food delivery service competes directly with other major players like DoorDash and Grubhub. Revenue is generated through commissions on each order, with order value and market penetration being crucial performance indicators.
-
Freight Services: Uber Freight targets the logistics industry, connecting shippers with carriers. Growth potential is significant, but challenges exist in terms of competition and regulatory compliance.
-
Other Business Segments: Uber's portfolio includes other ventures contributing to overall revenue, albeit to a lesser extent. These may include advertising revenue within the app, subscription services, and other emerging technologies.
Revenue Breakdown:
-
Ride-sharing revenue breakdown by region: Analyzing regional performance reveals market strength and potential growth areas. For example, higher ride-sharing revenue in urban areas compared to rural areas is expected.
-
Uber Eats market penetration and competition analysis: Uber Eats' success depends heavily on its market share against competitors. This requires continuous innovation and aggressive marketing strategies.
-
Freight services growth potential and challenges: The freight market presents enormous opportunity, but scaling this segment requires substantial investment in technology and infrastructure.
-
Contribution of other business segments to overall revenue: While smaller than ride-sharing and Uber Eats, these diversified revenue streams add resilience to Uber's overall financial health.
Financial Performance and Growth Prospects
Assessing UBER stock requires a thorough examination of Uber's financial statements. Key metrics to consider include:
-
Year-over-year revenue growth analysis: Consistent revenue growth is essential for demonstrating sustainable business success. Analyzing trends reveals the effectiveness of Uber's expansion strategies and operational efficiency.
-
Profitability trends and forecasts: Uber's path to profitability has been a focus of investor concern. Analyzing profitability trends – or the lack thereof – and future projections provides crucial insight.
-
Debt levels and financial stability: High debt levels can pose a significant risk. Understanding Uber's debt structure and its ability to manage its financial obligations is crucial.
-
Projected market share growth: Continued market share growth in its various segments points to Uber's competitive edge and overall growth potential.
Competitive Landscape and Market Position
Uber operates in a highly competitive landscape. Major competitors include:
-
Ride-sharing: Lyft, Didi Chuxing, Bolt.
-
Food delivery: DoorDash, Grubhub, Deliveroo.
-
Freight: Other logistics companies and trucking firms.
Competitive Advantages & Disadvantages:
-
Brand Recognition: Uber benefits from strong brand awareness, a critical factor in attracting both riders and drivers.
-
Technological Innovation: Continued investment in technology and app development keeps Uber ahead of the curve.
-
Pricing Strategies: Uber's dynamic pricing can be both a competitive advantage and disadvantage, subject to market and regulatory pressures.
Competitive Analysis:
-
Key competitors and their market share: Understanding the market share held by competitors provides a clear picture of Uber's position within each segment.
-
Analysis of Uber's competitive strengths and weaknesses (SWOT): A SWOT analysis provides a structured overview of Uber's competitive posture.
-
Impact of regulatory changes on competition: Regulatory changes impacting ride-sharing and delivery services can significantly alter the competitive landscape.
-
Potential for mergers and acquisitions: Strategic mergers and acquisitions can enhance Uber's competitive position.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Investing in UBER
Investing in UBER stock carries significant risks:
-
Regulatory risks in different markets: Ride-sharing and delivery services face varying regulatory landscapes globally, posing potential legal and operational challenges.
-
Competition from established players and new entrants: The market is intensely competitive, with both established players and new entrants constantly vying for market share.
-
Economic sensitivity of the ride-sharing and delivery markets: These markets are highly sensitive to economic downturns. A recession could significantly impact demand.
-
Cybersecurity risks and data breaches: Uber handles vast amounts of sensitive user data, making it a prime target for cyberattacks.
Valuation and Investment Strategy
Valuing UBER stock requires employing several valuation methods, such as:
-
Discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis: This projects future cash flows and discounts them back to their present value.
-
Comparable company analysis: This compares Uber's valuation metrics to those of similar companies in the industry.
Investment Strategy Considerations:
-
Current market capitalization and price-to-earnings ratio: Understanding these key metrics helps to determine the stock's relative value.
-
Comparison with industry peers: Comparing Uber to its competitors provides context for evaluating its relative performance and valuation.
-
Recommendations for different risk tolerance levels: Conservative investors may prefer a diversified portfolio with smaller investments in Uber.
-
Potential entry and exit points for investment: Investors should establish a clear investment strategy that includes entry and exit points based on their risk tolerance and market conditions.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Your UBER Investment
Investing in Uber Technologies (UBER) presents both opportunities and significant risks. This analysis highlights the importance of thoroughly understanding Uber's business model, financial performance, competitive landscape, and inherent risks before making any investment decisions. Remember that conducting thorough due diligence is paramount. Consult financial advisors, analyze market trends, and continue your own research to make informed decisions about your UBER stock investment. Consider exploring additional resources and financial news to further deepen your understanding of UBER as an investment.

Featured Posts
-
 Vo Dich Indian Wells Co Gai 17 Tuoi Nguoi Nga Tao Nen Lich Su
May 17, 2025
Vo Dich Indian Wells Co Gai 17 Tuoi Nguoi Nga Tao Nen Lich Su
May 17, 2025 -
 Uber Ceo Kalanick Admits Abandoning Specific Project Decision Was A Mistake
May 17, 2025
Uber Ceo Kalanick Admits Abandoning Specific Project Decision Was A Mistake
May 17, 2025 -
 Ex Mariners Player Slams Teams Inaction This Winter
May 17, 2025
Ex Mariners Player Slams Teams Inaction This Winter
May 17, 2025 -
 Previsiones Deportivas De Prensa Latina Tu Guia Semanal Para Las Apuestas
May 17, 2025
Previsiones Deportivas De Prensa Latina Tu Guia Semanal Para Las Apuestas
May 17, 2025 -
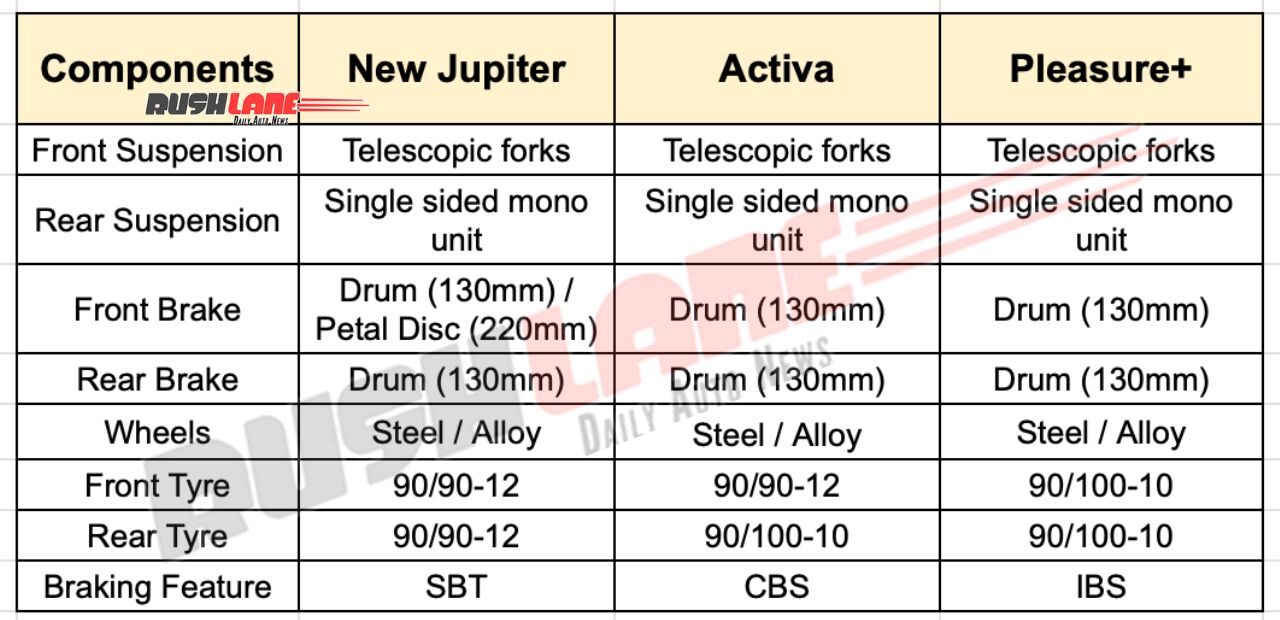 Tvs Jupiter Ather 450 X Hero Pleasure
May 17, 2025
Tvs Jupiter Ather 450 X Hero Pleasure
May 17, 2025
