Falling Profits At Westpac (WBC): The Role Of Shrinking Margins
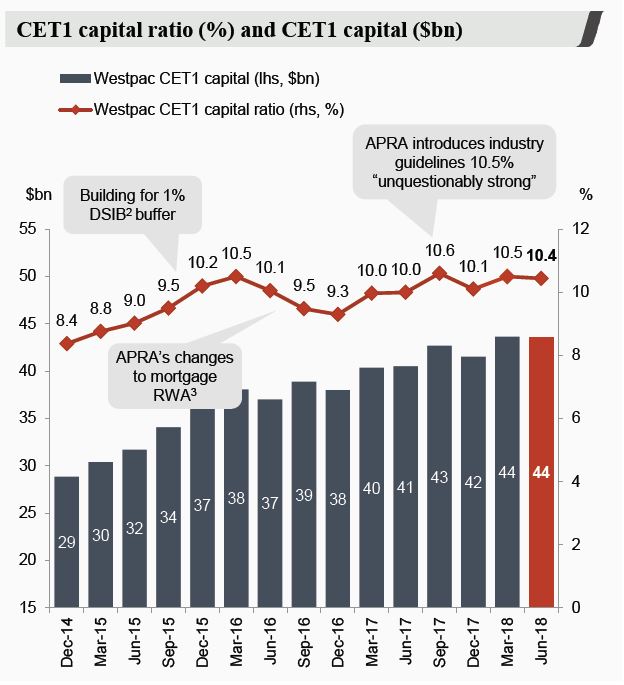
Table of Contents
Increased Competition in the Australian Banking Sector
The Australian banking sector is experiencing a period of unprecedented competition, directly impacting Westpac's profitability and leading to Westpac shrinking margins. This heightened competition comes from two primary sources: the rise of fintech disruptors and the continued pressure from established competitors.
The Rise of Fintech and Challenger Banks
The emergence of innovative fintech companies and digital-first challenger banks is significantly reshaping the financial landscape. These agile newcomers are aggressively competing for market share, particularly in areas such as mortgages, personal loans, and business banking services.
- Increased competition for mortgages: Fintech lenders are offering streamlined processes and competitive interest rates, attracting customers away from traditional institutions.
- Aggressive pricing strategies: Smaller banks and fintechs are employing aggressive pricing strategies, undercutting established players like Westpac and putting downward pressure on lending margins.
- Erosion of market dominance: The dominance once enjoyed by major Australian banks is eroding as customers embrace the convenience and competitive offerings provided by newer entrants. This direct competition is a significant contributor to Westpac shrinking margins.
Pressure from Established Competitors
Westpac also faces intense pressure from established competitors such as the Commonwealth Bank, ANZ, and NAB. This competition manifests in several ways:
- Price wars and promotional offers: The major banks are engaged in a fierce battle for customers, leading to price wars and promotional offers that drive down lending rates and compress margins.
- Increased investment in technology and customer service: To maintain competitiveness, these banks are investing heavily in technology and customer service, increasing operational costs and further impacting profitability.
- Pressure on net interest margins (NIMs): The intense competition directly translates into pressure on net interest margins (NIMs), a crucial indicator of a bank's profitability. These shrinking NIMs directly reflect the challenge of Westpac shrinking margins.
Rising Operational Costs
Beyond competitive pressures, Westpac is facing increased operational costs that are further contributing to Westpac shrinking margins. These costs stem from two primary sources: regulatory compliance and necessary technological investments.
Regulatory Compliance and Compliance Costs
The Australian financial services industry is subject to increasingly stringent regulations and heightened scrutiny from regulatory bodies like APRA (Australian Prudential Regulation Authority). This increased regulatory burden translates into significantly higher operational costs for Westpac.
- Higher compliance staffing costs: Banks need to employ specialized staff to ensure compliance with complex regulations, adding to personnel expenses.
- Investment in new technologies for regulatory reporting: Meeting regulatory reporting requirements often involves significant investments in new technologies and systems.
- Increased legal and advisory fees: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape often necessitates engaging external legal and advisory services, adding to operational costs.
Technological Investments
While essential for remaining competitive, significant investments in digital banking infrastructure and technology upgrades put a strain on Westpac's short-term profitability.
- Upgrades to online and mobile banking platforms: Maintaining a state-of-the-art digital banking experience requires continuous investment in platform upgrades and maintenance.
- Investment in cybersecurity to protect against fraud: Protecting customer data and preventing fraud necessitates substantial investment in cybersecurity measures.
- Development of new digital products and services: The need to innovate and develop new digital products and services adds to the already substantial investment burden.
Economic Headwinds and Low Interest Rate Environment
The broader economic climate also plays a significant role in the pressure on Westpac shrinking margins. The prolonged period of low interest rates and economic uncertainty have created several challenges.
Low Interest Rate Cycle
The global low interest rate environment has significantly impacted Westpac's profitability, particularly its net interest income, a key driver of earnings.
- Reduced return on lending activities: Lower interest rates directly reduce the return on lending activities, impacting the bank’s profitability.
- Difficulty in passing on lower interest rates to customers: Banks face challenges in passing on lower interest rates to customers, reducing their ability to maintain margins.
- Impact on profitability from lower yields on investments: Lower interest rates also reduce yields on the bank's investments, further impacting profitability.
Economic Uncertainty and Consumer Sentiment
A subdued economic outlook and cautious consumer sentiment negatively impact loan demand and increase the provision for bad debts.
- Lower demand for loans and mortgages impacting loan growth: Economic uncertainty leads to reduced demand for loans and mortgages, affecting loan growth and revenue.
- Increased risk of loan defaults and non-performing assets: Economic hardship increases the risk of loan defaults and non-performing assets, leading to higher provisions for credit losses.
- Impact on profitability through higher provisions for credit losses: These higher provisions directly reduce profitability, adding to the pressure of Westpac shrinking margins.
Conclusion
Westpac's shrinking margins are a multifaceted problem arising from a confluence of factors: intensified competition, increasing operational costs, and a challenging economic environment. Understanding these pressures is crucial for investors, stakeholders, and anyone interested in the Australian banking sector. To stay informed about the ongoing impact of these factors on Westpac’s performance, continue monitoring financial news and reports on Westpac shrinking margins. Regularly analyzing Westpac's financial statements and industry analyses will provide a clearer picture of the bank’s financial health and its ability to navigate this period of margin pressure. Staying abreast of developments related to Westpac shrinking margins is essential for making informed financial decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Celtics Vs Knicks Game Where To Watch Live Stream Options
May 06, 2025
Celtics Vs Knicks Game Where To Watch Live Stream Options
May 06, 2025 -
 Apple Tv Casts Ayo Edebiri And Will Sharpe In New Series On Former Child Stars
May 06, 2025
Apple Tv Casts Ayo Edebiri And Will Sharpe In New Series On Former Child Stars
May 06, 2025 -
 Gypsy Rose Blanchards 25 Pound Weight Loss Health And Fitness Update
May 06, 2025
Gypsy Rose Blanchards 25 Pound Weight Loss Health And Fitness Update
May 06, 2025 -
 Gypsy Rose Blanchard Challenging The Narrative On Loose Women
May 06, 2025
Gypsy Rose Blanchard Challenging The Narrative On Loose Women
May 06, 2025 -
 Arnold Schwarzenegger Supports Son Patricks Nude Role
May 06, 2025
Arnold Schwarzenegger Supports Son Patricks Nude Role
May 06, 2025
