Fed Holds Interest Rates: Balancing Inflation And Job Growth Risks
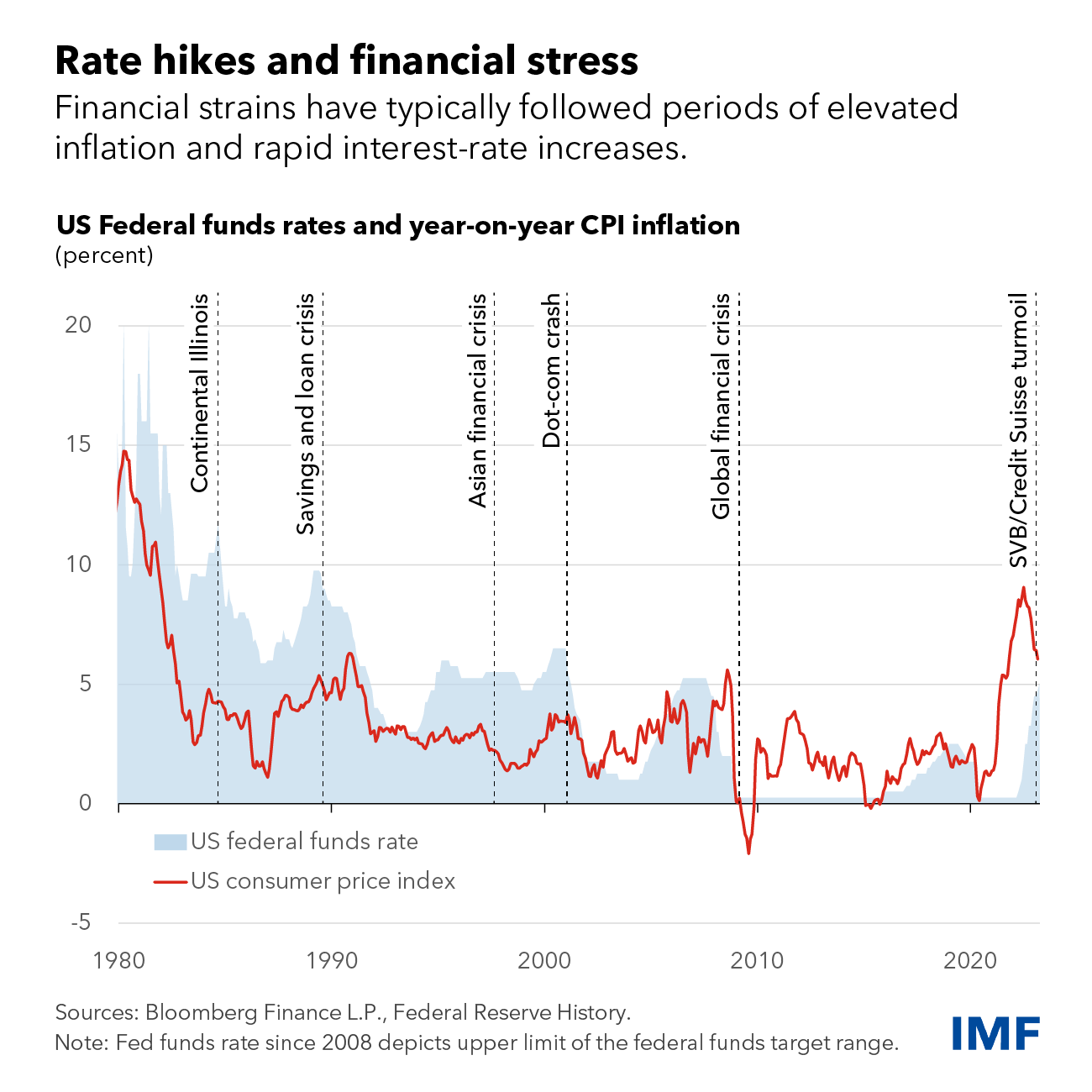
Table of Contents
The Federal Reserve's recent decision to hold interest rates unchanged marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing battle against inflation while simultaneously striving to maintain a healthy job market. This strategic pause reflects the complexities of navigating a turbulent economic landscape, presenting both opportunities and challenges for businesses and consumers alike. This article delves into the key factors influencing the Fed's decision, analyzing the risks associated with inflation and job growth, and exploring the potential implications for the future of the US economy.
Inflationary Pressures and the Fed's Response
Persistent Inflation
The current inflationary environment presents a significant challenge. Persistent inflation erodes purchasing power, impacting consumers' ability to afford essential goods and services. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial to formulating effective policy responses.
- Current CPI and PPI figures: Recent data shows the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) remaining elevated, although showing signs of slowing in some sectors. Specific numbers will need to be updated to reflect the most current data.
- Key contributing factors to inflation: Several factors contribute to persistent inflation, including supply chain disruptions, elevated energy prices driven by geopolitical factors, and robust consumer demand. The war in Ukraine, for example, significantly impacted energy costs globally.
- Impact on consumer purchasing power: Rising prices reduce the real value of wages, forcing consumers to make difficult choices about spending and saving. This can lead to decreased consumer confidence and potentially slower economic growth.
- Analysis of core inflation vs. headline inflation: While headline inflation (which includes volatile elements like food and energy) has shown some moderation, core inflation (excluding food and energy) remains stubbornly high, suggesting underlying inflationary pressures persist.
The Fed's Tools to Combat Inflation
The Federal Reserve employs various monetary policy tools to influence inflation. The primary tool is adjusting the federal funds rate, the target rate for overnight lending between banks.
- Explanation of the federal funds rate: Changes to the federal funds rate ripple through the financial system, impacting borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. A higher rate makes borrowing more expensive, potentially slowing down economic activity and reducing inflationary pressure.
- How interest rate adjustments impact borrowing costs: Higher interest rates increase the cost of mortgages, auto loans, and business loans, thus dampening spending and investment.
- The role of quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative tightening (QT): QE involves the Fed injecting liquidity into the market by purchasing assets, while QT is the reverse, reducing the money supply. QT is currently being employed to combat inflation.
- Potential impact of these tools on different sectors of the economy: The impact of these tools varies across sectors. Interest-rate-sensitive sectors like housing and automobiles are particularly affected by changes in borrowing costs.
Job Market Strength and Growth Concerns
Current Employment Situation
The US job market has shown remarkable resilience despite inflationary pressures. However, understanding the nuances is critical.
- Latest unemployment rate figures: The unemployment rate remains relatively low, indicating a strong labor market. Again, specific figures require updating to reflect the most recent data.
- Sector-specific job growth trends: Job growth has been uneven across sectors, with some experiencing robust growth while others face challenges.
- Wage growth and its contribution to inflationary pressures: Strong wage growth, while positive for workers, can contribute to inflationary pressures if businesses pass increased labor costs onto consumers.
- Discussion of labor force participation rate: Analyzing the labor force participation rate provides insights into the overall health of the labor market and potential future workforce dynamics.
Risks of Aggressive Rate Hikes on Employment
While controlling inflation is crucial, aggressively raising interest rates carries risks.
- Potential for a recession due to higher interest rates: Raising interest rates too quickly can trigger a recession by dampening economic activity and investment.
- Impact on business investment and expansion: Higher borrowing costs discourage businesses from investing in expansion and hiring, potentially leading to job losses.
- Effect on consumer spending and confidence: Reduced consumer spending due to higher borrowing costs and decreased confidence can further weaken economic growth.
- Potential for increased unemployment: A slowdown in economic activity caused by aggressive rate hikes can lead to increased unemployment.
Balancing Act: The Fed's Delicate Decision
The Trade-off Between Inflation and Growth
The Fed faces the difficult task of balancing the need to control inflation with the desire to maintain healthy economic growth and job creation.
- Explanation of the Phillips Curve and its relevance: The Phillips Curve illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. However, this relationship is not always stable and can be influenced by other factors.
- Analysis of the current economic data and its implications: A careful analysis of current economic data is crucial to guide the Fed's decisions.
- Discussion of potential scenarios depending on future Fed actions: Different policy choices will lead to varying outcomes, with potential trade-offs between inflation and employment.
Future Outlook and Potential Fed Moves
Predicting the Fed's future actions is challenging, but analyzing current trends offers insights.
- Predictions for future interest rate decisions: Future interest rate decisions will likely depend on incoming economic data, particularly inflation and employment figures.
- Anticipated impact on inflation and employment: Future Fed actions will significantly influence both inflation and employment levels.
- Consideration of geopolitical factors and their influence: Geopolitical events and global economic conditions can also impact the Fed's decision-making process.
Conclusion
The Fed's decision to hold interest rates reflects a careful assessment of the complex interplay between inflation and job growth. Maintaining economic stability requires a nuanced approach, balancing the risks of uncontrolled inflation with the potential harm of overly aggressive monetary policy. The ongoing economic data will play a crucial role in informing the Fed's future decisions.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest developments in monetary policy and their impact on your financial decisions. Keep up-to-date on the Fed's actions and their implications for interest rates and the overall economy by regularly checking reputable financial news sources and analyzing Fed Holds Interest Rates announcements.

Featured Posts
-
 Air Indias Response To Lisa Rays Complaint Full Story And Details
May 09, 2025
Air Indias Response To Lisa Rays Complaint Full Story And Details
May 09, 2025 -
 Nottingham Attack Survivors Break Silence Detail Ordeal
May 09, 2025
Nottingham Attack Survivors Break Silence Detail Ordeal
May 09, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Madenciligi Sonu Mu Baslangici Mi
May 09, 2025
Bitcoin Madenciligi Sonu Mu Baslangici Mi
May 09, 2025 -
 Bilateral Trade Agreement India And Us To Hold Key Discussions
May 09, 2025
Bilateral Trade Agreement India And Us To Hold Key Discussions
May 09, 2025 -
 Projections For The Wireless Mesh Networks Market 9 8 Cagr Growth
May 09, 2025
Projections For The Wireless Mesh Networks Market 9 8 Cagr Growth
May 09, 2025
