Fed Holds Interest Rates: Balancing Inflation And Job Market Risks
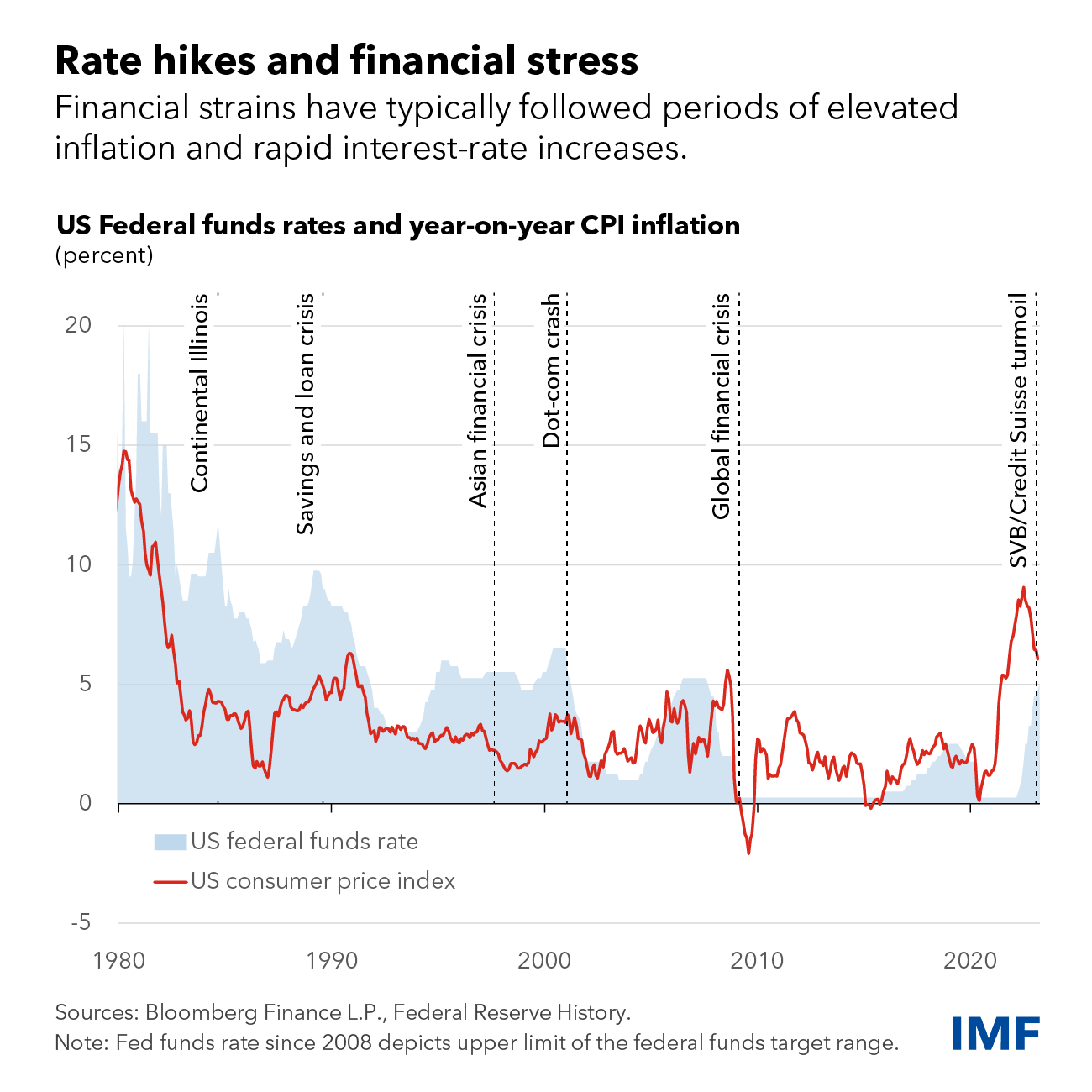
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures and the Fed's Response
Inflation remains a significant challenge for the US economy. Contributing factors include persistent supply chain disruptions, elevated energy prices fueled by geopolitical instability, and robust consumer demand. The Fed, tasked with maintaining price stability and maximum employment, faces the difficult task of cooling inflation without triggering a recession. Despite persistent inflationary pressures, the decision to hold interest rates reflects a cautious approach, prioritizing a nuanced assessment of the economic data.
- Current Inflation Figures: The latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) reports show inflation stubbornly high, although showing signs of slowing from its peak. Year-over-year comparisons reveal a gradual decrease, but the rate remains above the Fed's target.
- Specific Inflationary Pressures: Rising housing costs, persistent food price increases, and the lingering effects of supply chain bottlenecks continue to exert upward pressure on inflation.
- The Fed's Inflation Target: The Federal Reserve aims for a 2% annual inflation rate. The current rate, while declining, remains significantly above this target, necessitating a careful monitoring of economic indicators.
- Downsides of Aggressive Rate Hikes: Raising interest rates too aggressively risks triggering a sharp economic slowdown or even a recession, potentially leading to job losses and increased economic hardship.
The Strength of the Job Market and its Implications
The US job market continues to show remarkable resilience. Unemployment rates remain low, job creation is robust across various sectors, and wage growth, while moderating, remains noticeable. This strength, while positive for workers, presents a double-edged sword for the Fed. Strong wage growth can contribute to a wage-price spiral, exacerbating inflationary pressures. The Fed carefully weighs the benefits of a strong job market against the risk of fueling inflation.
- Current Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate is currently near historic lows, indicating a tight labor market.
- Recent Job Growth Figures: Recent job reports consistently show strong job creation, particularly in sectors like leisure and hospitality.
- Average Wage Growth: While wage growth has shown signs of cooling, it remains above pre-pandemic levels, contributing to inflationary pressures.
- Risks of Slowing Job Growth: Aggressive interest rate hikes risk dampening economic activity and leading to a slowdown in job creation, potentially increasing unemployment.
Balancing Act: Risks and Uncertainties in the Economic Outlook
The Fed's decision to hold interest rates reflects a careful assessment of the inherent risks involved. Raising interest rates too aggressively risks pushing the economy into a recession, while keeping rates too low risks allowing inflation to become entrenched. Several scenarios are possible: a soft landing (slowing growth without a recession), persistent inflation, or a full-blown recession. Global economic factors, such as geopolitical instability and energy price volatility, further complicate the outlook.
- Risk of Recession: Aggressive interest rate hikes significantly increase the risk of a recession, impacting businesses and consumers alike.
- Risk of Persistent Inflation: Maintaining low interest rates for too long risks allowing inflation to become entrenched, requiring even more drastic measures later.
- Potential for a Soft Landing: A soft landing, a scenario where economic growth slows without triggering a recession, is the Fed's preferred outcome but remains uncertain.
- Global Economic Factors: Global events and economic conditions play a significant role in influencing the Fed's monetary policy decisions.
Market Reactions and Investor Sentiment
The financial markets reacted to the Fed's decision with a degree of cautious optimism. While stock prices showed some initial gains, bond yields remained relatively stable. Investor sentiment is currently mixed, with some anticipating further interest rate hikes in the future, while others believe the current pause reflects a shift towards a more accommodative monetary policy stance.
- Stock Market Performance: Stock markets generally reacted positively to the news, reflecting investor confidence in the Fed's ability to navigate the economic challenges.
- Changes in Bond Yields: Bond yields, which reflect borrowing costs, remained relatively stable, indicating a degree of confidence in the Fed's approach.
- Analysis of Investor Confidence: Investor confidence remains somewhat fragile, with ongoing uncertainty about the future path of inflation and economic growth.
Conclusion: Understanding the Fed's Interest Rate Decision and its Long-Term Impact
The Fed's decision to hold interest rates reflects a careful balancing act between controlling inflation and maintaining a healthy job market. The decision acknowledges persistent inflationary pressures, yet prioritizes the strength of the current job market and the risks of triggering a recession through aggressive rate hikes. The economic outlook remains uncertain, with various potential scenarios playing out. It's crucial to monitor future economic data releases, Fed announcements regarding Federal Reserve interest rate policy, and any potential future interest rate hikes to gain a comprehensive understanding of the evolving economic landscape. To stay informed about future Fed interest rate decisions and their impact, subscribe to reputable financial newsletters, follow financial news outlets, and regularly review economic reports. Understanding the Federal Reserve's interest rate policy is key to navigating the complexities of the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Strengthening Europes Energy Security Through Nuclear Collaboration A French Strategy
May 10, 2025
Strengthening Europes Energy Security Through Nuclear Collaboration A French Strategy
May 10, 2025 -
 Dc Prosecutor Appointment Trump Selects Fox News Personality Jeanine Pirro
May 10, 2025
Dc Prosecutor Appointment Trump Selects Fox News Personality Jeanine Pirro
May 10, 2025 -
 From Wolves Reject To European Champion His Rise To The Top
May 10, 2025
From Wolves Reject To European Champion His Rise To The Top
May 10, 2025 -
 How Harry Styles Reacted To A Bad Snl Impression Of Himself
May 10, 2025
How Harry Styles Reacted To A Bad Snl Impression Of Himself
May 10, 2025 -
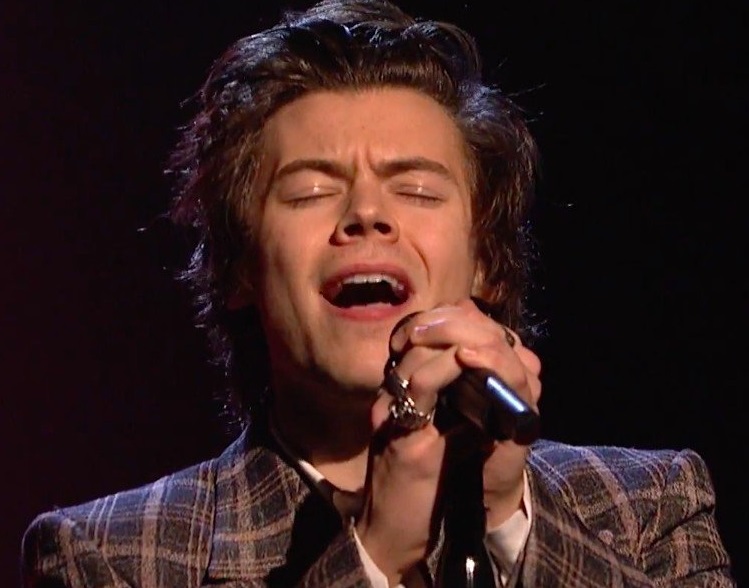
 Palantir Stock Pltr Buy Before May 5th A Risk Assessment
May 10, 2025
Palantir Stock Pltr Buy Before May 5th A Risk Assessment
May 10, 2025
