From Fiction To Fact: The Rise Of Egg Prices Under Scrutiny
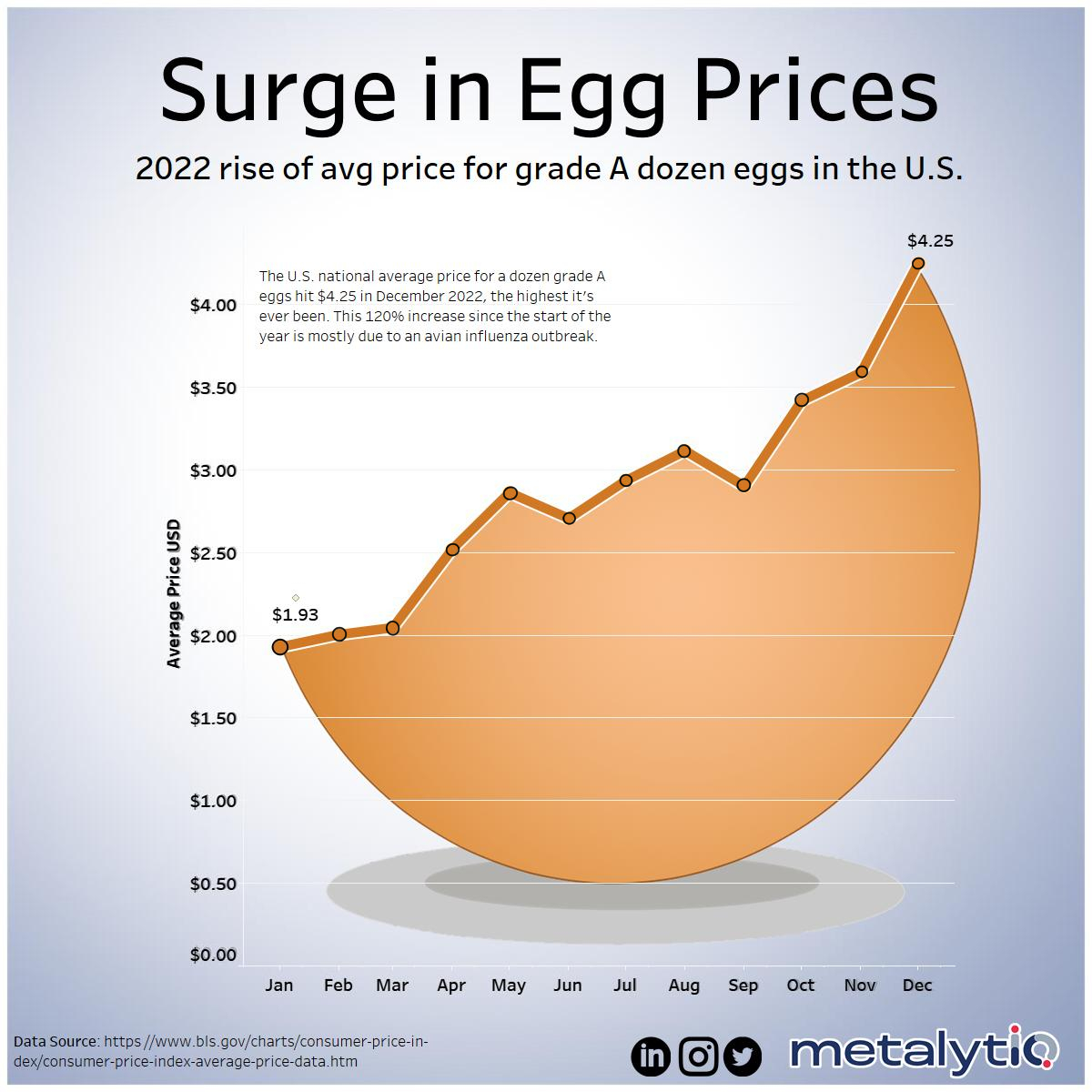
Table of Contents
The Avian Flu's Devastating Impact on Egg Production
The highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) outbreak has been a major catalyst in the dramatic increase in egg prices. This devastating virus has decimated poultry flocks across the globe, leading to a significant reduction in egg supply and a subsequent surge in the cost of eggs.
Reduced Hen Population
The avian flu's impact on the hen population has been catastrophic. Millions of laying hens have perished, drastically reducing the number of birds available to produce eggs.
- Regions heavily affected: Outbreaks have significantly impacted the United States, Europe, and parts of Asia, disrupting egg production in key agricultural regions.
- Hen mortality rates: In severely affected flocks, mortality rates have reached upwards of 90%, leading to a massive depletion of laying hens.
- Rebuild time: Rebuilding flocks takes considerable time – several months – due to biosecurity measures and the need to acquire healthy chicks, further exacerbating the egg shortage and driving up egg price inflation.
Increased Mortality Costs
The economic burden on egg farmers due to the avian flu is immense. Culling infected flocks and implementing rigorous biosecurity measures are expensive necessities.
- Disposal costs: Safe and responsible disposal of infected birds is costly, adding to the financial strain on farms.
- Cleaning and disinfection: Thorough cleaning and disinfection of poultry houses are crucial to prevent further outbreaks, adding significant expenses to farmers' operational costs.
- Impact on farm profitability: The combination of reduced egg production, increased mortality costs, and higher input prices (feed, fuel) has significantly squeezed farmers' profit margins, directly influencing the cost of eggs.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The reduced supply of eggs has created significant disruptions throughout the egg supply chain.
- Increased transportation costs: The need to transport eggs from fewer remaining sources has led to increased transportation costs, pushing up egg prices.
- Labor shortages: The industry is facing labor shortages, adding another layer of complexity to the already strained supply chain and influencing the cost of eggs.
- Delays in getting eggs to market: These disruptions have led to delays in getting eggs to market, exacerbating the shortage and driving up prices.
Beyond the Avian Flu: Other Factors Contributing to High Egg Prices
While the avian flu is a primary driver, other factors contribute to the current surge in egg prices. The cost of eggs is influenced by a confluence of economic and environmental factors.
Rising Feed Costs
The cost of producing eggs is heavily reliant on feed prices. The soaring costs of grains like corn and soy, which form the bulk of chicken feed, are directly impacting the cost of egg production.
- Feed price increases: Grain prices have increased significantly due to various factors, including global supply chain disruptions, unfavorable weather patterns, and geopolitical instability.
- Global factors affecting grain prices: Events like droughts, conflicts, and changes in global trade policies all influence grain prices and, consequently, the cost of eggs.
- Impact on farmers' profit margins: The increased cost of feed significantly reduces farmers' profit margins, forcing them to pass on these costs to consumers, further impacting the cost of eggs.
Inflation and Fuel Costs
Broader economic inflation and rising fuel prices are also contributing to the increase in egg prices.
- Inflation rates: High inflation rates across many countries increase the cost of almost every aspect of egg production, from packaging to labor.
- Fuel price increases: Fuel price increases directly impact transportation costs, adding to the final price of eggs that reach the consumer.
- Correlation to egg prices: These economic factors are directly correlated to the final price of eggs, creating a perfect storm of increasing costs.
Increased Consumer Demand
While not the sole driver, increased consumer demand has potentially exacerbated the price increases.
- Eggs as a health food: The growing popularity of eggs as a healthy and versatile protein source contributes to consistent demand.
- Increased demand during holidays: Demand for eggs typically surges during holidays, such as Easter, further straining supply and potentially pushing up egg prices.
The Future of Egg Prices: Predictions and Consumer Implications
Predicting the future trajectory of egg prices is challenging, but several factors suggest potential shifts.
Potential for Price Stabilization
Several factors may contribute to price stabilization in the future.
- Disease control advancements: Improved disease surveillance and control measures can help prevent future outbreaks of avian flu and other poultry diseases.
- Recovery in hen populations: As farmers rebuild their flocks, egg supply is expected to gradually increase, potentially easing price pressures.
- Expert opinions and predictions: Agricultural organizations and experts are closely monitoring the situation and providing forecasts about the potential timeline for price normalization.
Consumer Strategies for Managing Egg Costs
Consumers can adopt several strategies to mitigate the impact of high egg prices.
- Substituting eggs in recipes: Many recipes can be adapted to use egg alternatives or reduce the amount of eggs needed.
- Buying in bulk (when cost-effective): Purchasing eggs in bulk can sometimes offer cost savings, but only if storage is properly managed.
- Exploring alternative protein sources: Diversifying protein sources with beans, lentils, tofu, or other meat alternatives can help reduce reliance on eggs.
Conclusion
The current surge in egg prices is a complex issue driven by multiple interacting factors. The avian flu outbreak has played a significant role, causing a dramatic reduction in egg supply and increased production costs. However, rising feed costs, inflation, fuel price increases, and increased consumer demand have further exacerbated the situation, resulting in the high cost of eggs we see today. Understanding the factors driving the current rise in egg prices is crucial for both consumers and producers. Stay informed about future developments and consider the long-term implications of these price fluctuations. Monitoring egg price trends and adapting consumption habits accordingly are key steps for navigating the current market.

Featured Posts
-
 Padres Vs Cubs Prediction Will The Cubs Inflict A Second Defeat
May 16, 2025
Padres Vs Cubs Prediction Will The Cubs Inflict A Second Defeat
May 16, 2025 -
 Tactical Analysis Preparing To Face The San Jose Earthquakes
May 16, 2025
Tactical Analysis Preparing To Face The San Jose Earthquakes
May 16, 2025 -
 Ere Zilveren Nipkowschijf Voor Jiskefet Een Terugblik Op Een Legendarische Serie
May 16, 2025
Ere Zilveren Nipkowschijf Voor Jiskefet Een Terugblik Op Een Legendarische Serie
May 16, 2025 -
 Black Decker Steam Irons Comparison And Recommendations
May 16, 2025
Black Decker Steam Irons Comparison And Recommendations
May 16, 2025 -
 Elon Musk Fathered Amber Heards Twins Years After Embryo Controversy
May 16, 2025
Elon Musk Fathered Amber Heards Twins Years After Embryo Controversy
May 16, 2025
