Global Bond Market Instability: A Posthaste Analysis Of Emerging Risks

Table of Contents
Rising Interest Rates and Their Impact on Bond Yields
The direct correlation between interest rate increases and bond yields is a fundamental principle of fixed-income investing. When central banks like the Federal Reserve raise interest rates, newly issued bonds offer higher yields to attract investors. This, in turn, puts downward pressure on the prices of existing bonds with lower coupon rates. This impact is felt across various bond types, including government bonds and corporate bonds. The longer the maturity of a bond (its duration), the greater its sensitivity to interest rate changes.
- Impact of central bank policies on bond yields: Central bank actions are a primary driver of interest rate movements and consequently, bond yields. Aggressive rate hikes, as seen recently in many countries, can significantly impact bond prices.
- The mechanics of duration risk and how it affects bond prices: Duration risk refers to the sensitivity of a bond's price to changes in interest rates. Longer-duration bonds are more susceptible to interest rate risk.
- Strategies for managing interest rate risk in a portfolio: Strategies for mitigating interest rate risk include diversifying across bonds with varying maturities, using hedging techniques, and considering shorter-term bonds.
- Analysis of the current yield curve and its implications: The yield curve, which plots the yields of bonds with different maturities, provides insights into future interest rate expectations. An inverted yield curve (where short-term yields are higher than long-term yields) is often considered a recessionary signal.
Geopolitical Uncertainty and its Influence on Bond Markets
Geopolitical events, from wars and political instability to trade disputes and sanctions, significantly influence investor sentiment and bond market performance. Emerging markets are particularly vulnerable to these shifts, often experiencing capital flight and increased borrowing costs during periods of heightened uncertainty. The impact can be dramatic, leading to sharp price swings and increased volatility in sovereign debt.
- Case studies of geopolitical events and their impact on bond markets: The Russian invasion of Ukraine serves as a recent example, causing significant disruptions in global bond markets and increasing risk aversion among investors.
- Diversification strategies to mitigate geopolitical risk: Diversifying investments across different regions and asset classes is a key strategy to reduce geopolitical risk exposure.
- Assessment of the risks associated with investing in specific regions: Investors need to carefully assess the political and economic stability of each region before investing in their bonds.
- The role of sovereign credit ratings in assessing geopolitical risk: Credit rating agencies provide assessments of the creditworthiness of sovereign nations, reflecting the level of geopolitical risk associated with their debt.
Inflationary Pressures and Their Effect on Bond Values
Inflation, the persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, has a detrimental impact on bond values. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of fixed-income investments, as the future payments from a bond are worth less in real terms. This inverse relationship between inflation and bond prices is a critical factor to consider.
- The impact of unexpected inflation on bond returns: Unexpected inflation can significantly reduce the real return on bond investments, leading to losses for investors.
- Strategies for hedging against inflation risk (e.g., inflation-linked bonds): Inflation-linked bonds, or index-linked bonds, are designed to protect investors from inflation by adjusting their principal and coupon payments based on inflation rates.
- Analyzing inflation expectations and their effect on bond yields: Market expectations of future inflation influence current bond yields, with higher inflation expectations leading to higher yields.
- The role of central bank actions in managing inflation: Central banks utilize monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments, to manage inflation and maintain price stability.
The Growing Threat of Recession and its Impact on Bond Markets
The heightened risk of a global recession presents significant challenges for bond markets. During economic downturns, corporate defaults increase, impacting the value of corporate bonds, particularly high-yield bonds. This credit risk is a key concern for investors.
- Economic indicators that signal a potential recession: Economic indicators like GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer confidence provide insights into the likelihood of a recession.
- The correlation between recessions and corporate bond defaults: Recessions often lead to increased corporate bankruptcies and defaults, impacting the value of corporate bonds.
- Strategies for navigating a recessionary environment: Diversifying into less cyclical sectors and investing in higher-quality bonds can help mitigate recessionary risks.
- The importance of credit analysis in mitigating recessionary risks: Thorough credit analysis is essential to identify companies with a higher probability of default during economic downturns.
Conclusion
The global bond market faces a confluence of significant risks: rising interest rates impacting bond yields, geopolitical uncertainty creating volatility, inflationary pressures eroding purchasing power, and the looming threat of recession increasing default risk. These factors collectively present a challenging environment for fixed-income investors. To effectively navigate this volatile landscape, investors must proactively assess their exposure to these risks, diversify their portfolios strategically, and potentially seek professional guidance on risk management techniques tailored to their specific circumstances. Continued monitoring of macroeconomic indicators and geopolitical developments is vital for making informed investment decisions in this dynamic and increasingly complex global bond market. Don't underestimate the importance of understanding and addressing global bond market instability to secure your financial future.

Featured Posts
-
 Cambridge And Somerville Events Viva Central Hot Sauce Festival And Open Studios
May 23, 2025
Cambridge And Somerville Events Viva Central Hot Sauce Festival And Open Studios
May 23, 2025 -
 The Truth About Suraj Venjaramoodu And The Kieran Culkin Oscar Speech Mimicry
May 23, 2025
The Truth About Suraj Venjaramoodu And The Kieran Culkin Oscar Speech Mimicry
May 23, 2025 -
 Dublin 2026 Metallicas Two Night Aviva Stadium Concert Announced
May 23, 2025
Dublin 2026 Metallicas Two Night Aviva Stadium Concert Announced
May 23, 2025 -
 University Of Maryland Commencement Famous Amphibian To Deliver Speech
May 23, 2025
University Of Maryland Commencement Famous Amphibian To Deliver Speech
May 23, 2025 -
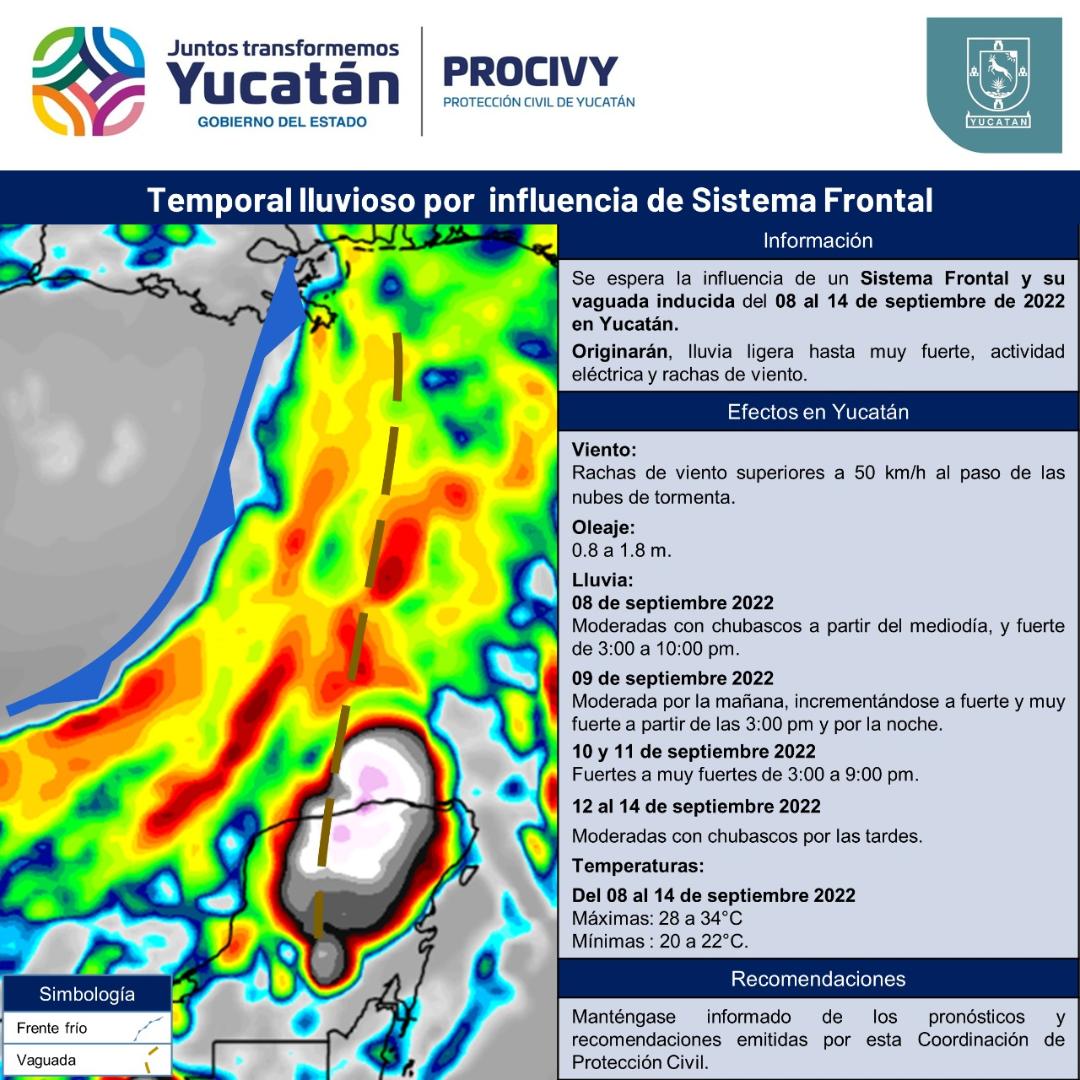 Sistema Frontal Y Vaguada Causaran Lluvias Este Sabado
May 23, 2025
Sistema Frontal Y Vaguada Causaran Lluvias Este Sabado
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Hilarious Reaction
May 23, 2025
Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Hilarious Reaction
May 23, 2025 -
 Joe Jonass Hilarious Response To Couples Fight Over Him
May 23, 2025
Joe Jonass Hilarious Response To Couples Fight Over Him
May 23, 2025 -
 The Jonas Brothers Joes Response To A Fans Relationship Drama
May 23, 2025
The Jonas Brothers Joes Response To A Fans Relationship Drama
May 23, 2025 -
 The Jonas Brothers Joe And The Unexpected Couples Argument
May 23, 2025
The Jonas Brothers Joe And The Unexpected Couples Argument
May 23, 2025 -
 How Joe Jonas Defused A Couples Argument About Him
May 23, 2025
How Joe Jonas Defused A Couples Argument About Him
May 23, 2025
