Google Vs. OpenAI: A Deep Dive Into I/O And Io Differences

Table of Contents
Understanding I/O in the Context of Google and OpenAI
Input/Output (I/O) in the context of AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) refers to how a model interacts with its environment. It encompasses the process of receiving input data (text, images, audio, etc.), processing that data, and generating output (text, code, images, predictions, etc.). Google and OpenAI, while both working in the same broad field, have distinct approaches to I/O.
-
Google's I/O: Google's strength lies in its vast and diverse data sources. This breadth of data allows for robust and versatile models, capable of handling a wide range of I/O tasks. The sheer scale of Google's data often translates to higher I/O performance in terms of speed and accuracy, especially for general-purpose tasks. Their approach often prioritizes efficiency and scalability, leading to optimized I/O pipelines within their infrastructure.
-
OpenAI's I/O: OpenAI, on the other hand, often focuses on data curation and meticulous refinement. While their data sets might be smaller than Google's, they prioritize quality and relevance, resulting in models that can excel in specific tasks or domains. This curated approach can lead to more specialized but potentially less adaptable I/O capabilities compared to Google's more general-purpose models. OpenAI’s focus on specific model architectures also influences their I/O characteristics.
-
Model Architecture's Role: The underlying architecture of the AI model significantly impacts I/O. Google utilizes a variety of architectures, including transformer models, while OpenAI has gained prominence with its transformer-based models like GPT-3 and DALL-E. These architectural differences affect factors such as the type and format of acceptable input, the speed of processing, and the nature of the output generated.
The Nuances of "I/O" vs. "io": A Terminology Deep Dive
While seemingly interchangeable, the use of uppercase "I/O" and lowercase "io" carries subtle yet important distinctions in the context of Google and OpenAI's work.
-
I/O (Uppercase): Generally refers to the broad concept of Input/Output in the context of computer systems and, in this case, AI models. It encompasses the overall process of data flow and interaction. Google frequently uses "I/O" in this broader sense in its documentation and presentations. For instance, Google I/O, their annual developer conference, highlights this broader scope.
-
io (Lowercase): Often signifies more specific technical contexts, such as file I/O (dealing with files on a system), network I/O (data transfer over networks), or even within specific API calls. OpenAI's documentation might use "io" in this more granular fashion, especially when referring to API interactions or low-level operations.
-
Potential for Misunderstanding: This inconsistency can lead to misunderstandings. Understanding the context—whether the discussion is about the high-level interaction of an AI model or a specific technical aspect—is critical for accurate interpretation of documentation and research papers from both organizations.
Google I/O and OpenAI API: A Comparative Analysis
Comparing the APIs of Google and OpenAI reveals significant differences in functionality, ease of use, and cost.
-
Google's APIs (TensorFlow, Cloud APIs, etc.): Offer a broad range of tools and services for AI development, often requiring more technical expertise. They are highly versatile and scalable, fitting larger projects and infrastructure. The pricing model is usually usage-based, making it cost-effective for large-scale deployments but potentially expensive for smaller projects.
-
OpenAI's APIs (GPT-3, DALL-E, etc.): Provide more user-friendly interfaces, often requiring less coding expertise to get started. While offering powerful capabilities, their functionalities are often more focused on specific tasks like text generation or image creation. Their pricing models are generally token-based, potentially making them less cost-effective for large-scale applications.
-
Developer Experience: Google's APIs, while powerful, often necessitate a deeper understanding of underlying technologies. OpenAI's APIs aim for simpler integration, making them more accessible to a wider range of developers.
-
Limitations: Both platforms have limitations. Google's scale can sometimes lead to complexities in management, while OpenAI's APIs might lack the breadth of capabilities found in Google's broader ecosystem.
Future Implications: The Evolving I/O Landscape
The future of I/O for both Google and OpenAI is brimming with exciting possibilities.
-
Multimodal I/O: We can expect significant advancements in multimodal I/O, where models seamlessly handle various data types (text, images, audio, video) simultaneously. This will create more natural and intuitive interactions with AI systems.
-
Efficiency and Latency: Reducing latency and improving efficiency will be crucial. Faster processing and reduced response times will be essential for real-time applications and seamless user experiences.
-
Ethical Considerations: As I/O capabilities advance, ethical concerns regarding bias, fairness, and responsible use of AI will need to be addressed proactively by both Google and OpenAI.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right I/O Approach: Google or OpenAI?
Google and OpenAI represent distinct approaches to I/O in AI. Google emphasizes scale and diversity in data, leading to highly versatile but potentially complex systems. OpenAI focuses on data curation and specialized model architectures, resulting in powerful but potentially less adaptable solutions. The choice between them depends heavily on the specific needs and constraints of your project. Understanding the differences between "I/O" and "io" and their implications within each platform is crucial. Deepen your understanding of Google and OpenAI's I/O capabilities by exploring their respective documentation and APIs today!

Featured Posts
-
 Najib Razak French Investigation Links Former Malaysian Pm To 2002 Submarine Bribes
May 25, 2025
Najib Razak French Investigation Links Former Malaysian Pm To 2002 Submarine Bribes
May 25, 2025 -
 Amundi Msci World Catholic Principles Ucits Etf Acc A Guide To Net Asset Value Nav
May 25, 2025
Amundi Msci World Catholic Principles Ucits Etf Acc A Guide To Net Asset Value Nav
May 25, 2025 -
 Fujifilm X H2 A Hands On Look At Its Whimsical Design And Fun Features
May 25, 2025
Fujifilm X H2 A Hands On Look At Its Whimsical Design And Fun Features
May 25, 2025 -
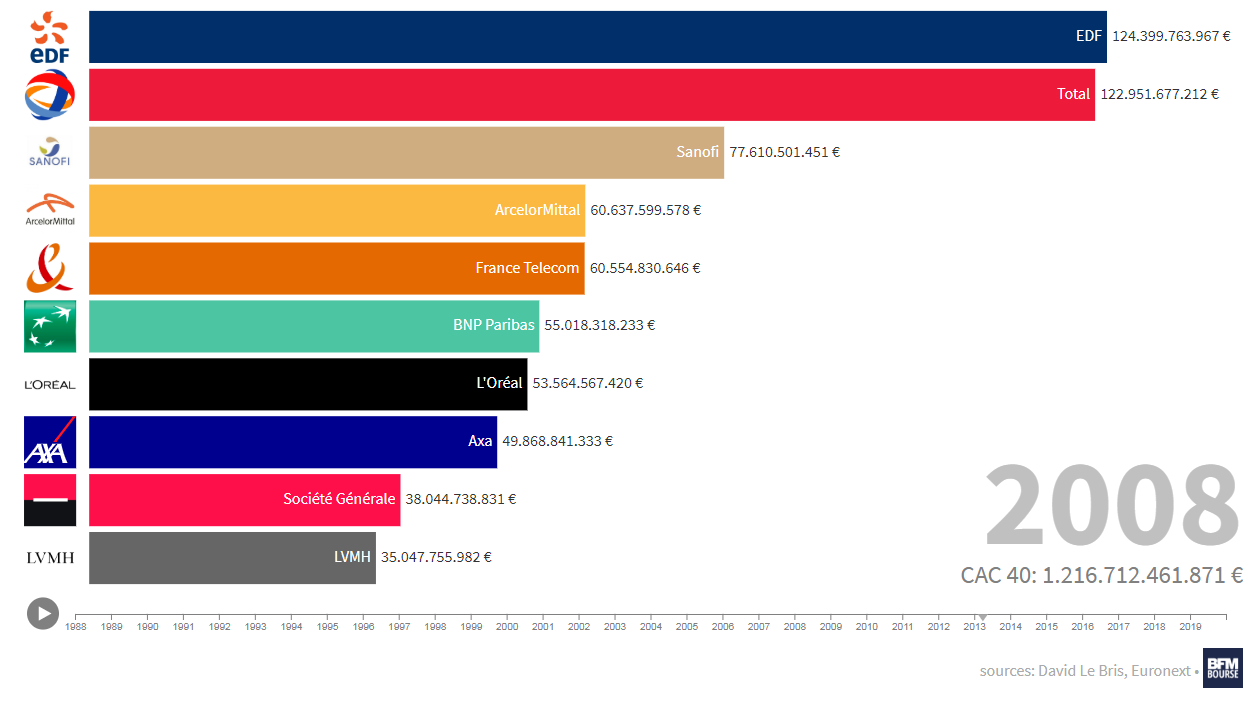 Cac 40 Index Week Ends Down But Shows Resilience March 7 2025
May 25, 2025
Cac 40 Index Week Ends Down But Shows Resilience March 7 2025
May 25, 2025 -
 President Snows Casting A 3 Time Oscar Nominee Joins The Hunger Games Prequel
May 25, 2025
President Snows Casting A 3 Time Oscar Nominee Joins The Hunger Games Prequel
May 25, 2025
