Gray Wolf From Colorado Dies In Wyoming After Relocation Program
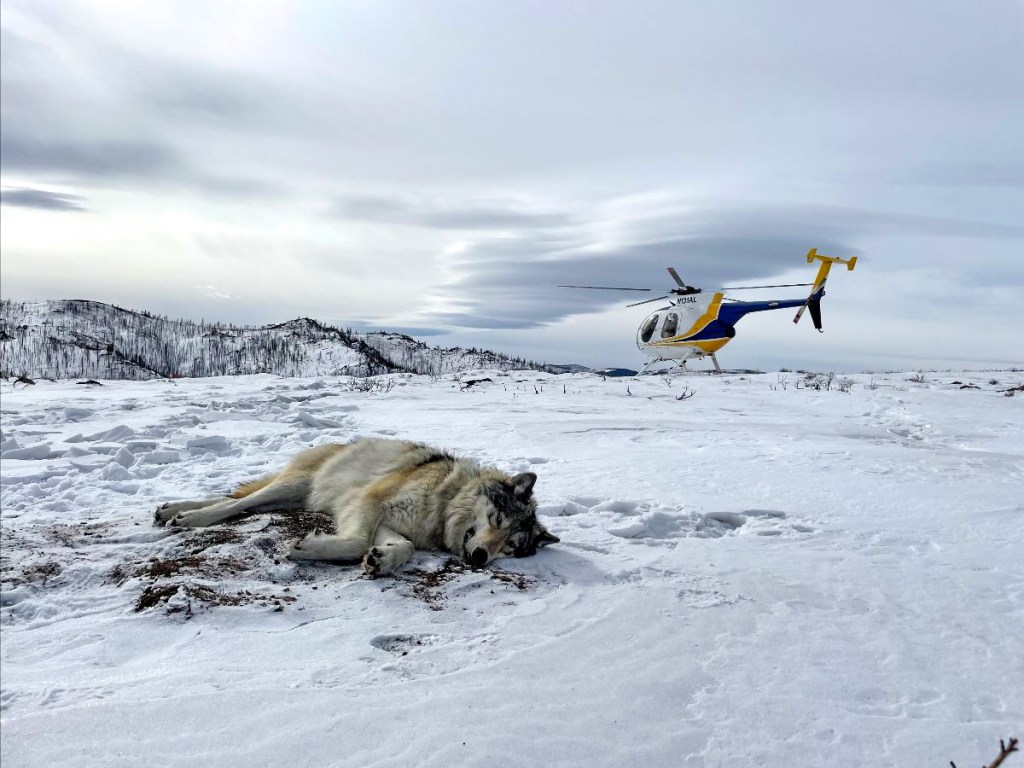

Table of Contents
Details of the Wolf's Relocation and Death
Origin and Relocation
The gray wolf, designated CW-123 by wildlife officials, originated from a pack in northwest Colorado. Its relocation to Wyoming was part of a larger effort to bolster dwindling gray wolf populations in the state. This specific program, overseen by the Wyoming Game and Fish Department in collaboration with Colorado Parks and Wildlife, aimed to increase genetic diversity and expand the range of the endangered species.
- Pack Origin: CW-123 belonged to a relatively stable pack in the Flat Tops Wilderness Area of Colorado.
- Age and Sex: The wolf was a young adult male, approximately 2 years old at the time of relocation.
- Health Prior to Relocation: Pre-relocation health assessments indicated CW-123 was in good physical condition.
- Relocation Timing: The wolf was relocated in late Spring of 2024, a time considered optimal for establishing a new territory.
- Post-Relocation Monitoring: The wolf was fitted with a GPS collar to monitor its movements and overall health. Initial tracking data indicated the wolf was attempting to establish a territory.
Cause of Death
The cause of CW-123's death is currently under investigation. Preliminary findings suggest the wolf died from injuries consistent with a large animal attack, though the exact circumstances remain unclear. The Wyoming Game and Fish Department is conducting a thorough necropsy to determine the precise cause of death.
- Preliminary Findings: Initial examination revealed injuries consistent with a possible conflict with another large predator.
- Ongoing Investigations: Wildlife officials are currently analyzing GPS tracking data to reconstruct the wolf's movements in the days leading up to its death.
- Potential Causes: Possible causes under consideration include intraspecific conflict (fighting with other wolves), predation by other large carnivores, or even accidental injury.
Public Reaction and Controversy
The death of CW-123 has sparked considerable debate and controversy. Conservation groups expressed disappointment and concern, highlighting the potential setbacks for wolf recovery efforts. Conversely, some hunting advocacy groups have questioned the necessity and effectiveness of relocation programs, citing potential negative impacts on existing wildlife populations. Local communities near the relocation site have also expressed mixed reactions, with some expressing concerns about potential human-wildlife conflicts.
- Conservation Group Statements: Several organizations voiced concerns about the implications of this death for the long-term success of wolf recovery efforts in Wyoming.
- Hunting Advocacy Group Response: Groups advocating for hunting rights highlighted this event as evidence against the effectiveness and necessity of relocation programs.
- Local Community Concerns: Some residents expressed concerns about the safety and potential economic implications associated with expanding wolf populations.
Impact on Wolf Conservation Efforts
The Role of Relocation Programs
Gray wolf relocation programs have a mixed track record. While some have demonstrably contributed to population growth and range expansion, others have faced significant challenges, leading to high mortality rates among relocated wolves. Success often depends heavily on careful site selection, pre-relocation health assessments, and robust post-relocation monitoring.
- Survival Rates: Data from various relocation programs shows survival rates ranging from 30% to 70%, depending on factors such as habitat suitability and existing predator populations.
- Importance of Monitoring: Effective pre- and post-relocation monitoring is crucial for assessing the success of such programs and adapting strategies as needed.
Challenges in Wildlife Management
Managing gray wolf populations presents complex challenges. Habitat loss due to human development continues to fragment wolf territories. Human-wildlife conflict, particularly concerning livestock depredation, remains a significant concern. Climate change is also predicted to further complicate matters, potentially altering habitat suitability and exacerbating existing issues.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Development and habitat destruction continue to impact wolf populations, reducing available territory and increasing competition.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Livestock depredation often leads to conflict between ranchers and conservationists, necessitating effective management strategies.
- Climate Change Impacts: Shifts in climate patterns can significantly affect prey availability and wolf habitat suitability.
Long-Term Implications for the Gray Wolf Population
The death of CW-123, while a single event, underscores the inherent risks and challenges associated with wolf relocation programs. It raises questions about the long-term viability of these programs as a conservation strategy, emphasizing the need for ongoing evaluation and adaptive management. The incident highlights the importance of considering potential risks and mitigating factors before undertaking such initiatives.
- Future Conservation Strategies: This incident necessitates a thorough review of current relocation protocols and consideration of alternative conservation strategies.
- Management Plan Adjustments: Wildlife management agencies may need to revise their plans to account for the challenges and risks involved in gray wolf relocation.
Conclusion
The death of the Colorado gray wolf in Wyoming after its relocation highlights the complexities and challenges of wildlife management and conservation efforts. The incident underscores the need for careful planning, thorough risk assessment, robust monitoring, and adaptive management strategies in all gray wolf relocation programs. While such programs can play a vital role in species recovery, their effectiveness hinges on a nuanced understanding of ecological factors, potential risks, and the capacity for successful integration into existing populations.
Call to Action: Support responsible gray wolf conservation by learning more about gray wolf relocation programs and their impacts. Get involved in protecting Colorado and Wyoming's gray wolf populations by supporting organizations dedicated to their conservation. Advocate for effective wildlife management practices that balance conservation goals with the needs of local communities. Learn more and get involved: [Link to relevant organization 1], [Link to relevant organization 2], [Link to relevant research].

Featured Posts
-
 Abn Amro Kamerbrief Certificaten Verkoopstrategie En Programma Overzicht
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Kamerbrief Certificaten Verkoopstrategie En Programma Overzicht
May 22, 2025 -
 Fastest Across Australia Man Completes Unprecedented Foot Race
May 22, 2025
Fastest Across Australia Man Completes Unprecedented Foot Race
May 22, 2025 -
 Barry Ward Interview The Irish Actor On Type Casting
May 22, 2025
Barry Ward Interview The Irish Actor On Type Casting
May 22, 2025 -
 Blake Lively Lawyers Alleged Threat To Leak Taylor Swift Texts A Deeper Dive
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively Lawyers Alleged Threat To Leak Taylor Swift Texts A Deeper Dive
May 22, 2025 -
 Is A Little Britain Revival Happening Matt Lucas Weighs In
May 22, 2025
Is A Little Britain Revival Happening Matt Lucas Weighs In
May 22, 2025
