Harmful Algal Blooms: A Growing Threat To California's Marine Life And Economy
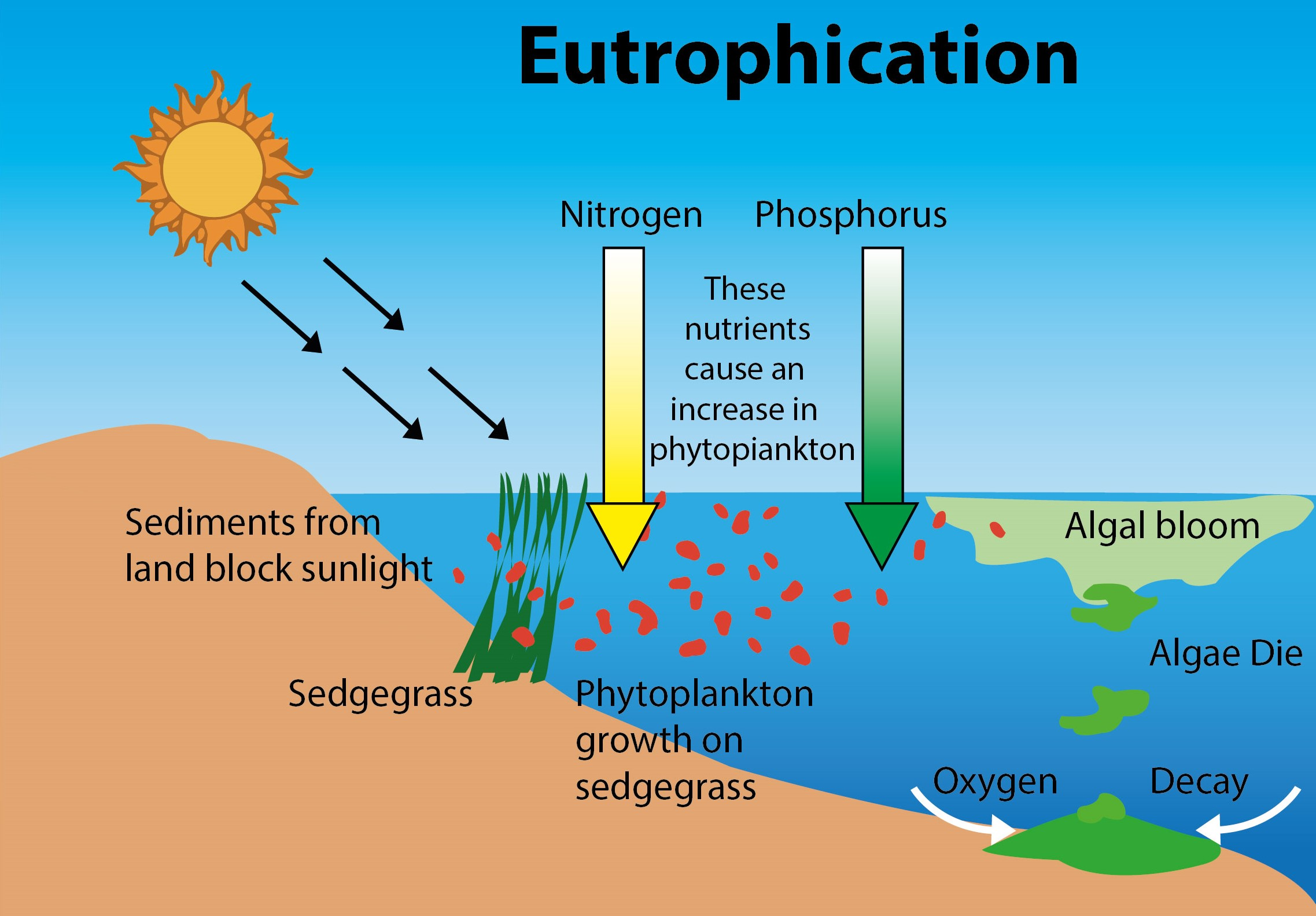
Table of Contents
Harmful algal blooms are proliferations of microscopic algae that produce toxins harmful to marine organisms and humans. These blooms, often visible as discolored patches of water, can release potent toxins like domoic acid (associated with amnesic shellfish poisoning) and brevetoxin (linked to neurotoxic shellfish poisoning). The consequences of these blooms are far-reaching, impacting everything from the delicate balance of the marine food web to the livelihoods of those who depend on the ocean. This article will delve into the ecological and economic impacts of HABs in California, explore their causes, and discuss strategies for monitoring, mitigation, and management.
The Ecological Impact of Harmful Algal Blooms in California
HABs disrupt the intricate balance of California's marine ecosystem in devastating ways. Their effects cascade through the food web, affecting countless species.
Disruption of the Marine Food Web
HABs wreak havoc on various trophic levels. The toxins produced by these blooms directly poison marine life, leading to widespread mortality.
- Shellfish Contamination: Filter-feeding shellfish, like mussels and clams, accumulate high concentrations of toxins, making them unsafe for human consumption and causing significant shellfish harvesting bans. This impacts both commercial and recreational shellfish industries.
- Fish Kills: Many fish species are directly affected by HAB toxins, leading to mass die-offs that disrupt the food chain and decimate fish populations.
- Seabird Mortality: Seabirds that feed on contaminated fish or shellfish can suffer neurological damage, reproductive failure, and death.
- Impacts on Marine Mammals: Marine mammals, such as sea otters and whales, are also susceptible to HAB toxins, suffering similar consequences as seabirds. These impacts ripple throughout the entire ecosystem.
Habitat Degradation
Beyond direct toxicity, HABs degrade vital marine habitats.
- Reduced Oxygen Levels (Hypoxia): As algae decompose, they consume large amounts of oxygen, creating hypoxic or anoxic (oxygen-depleted) zones that suffocate marine life. These "dead zones" can decimate benthic communities.
- Altered Water Chemistry: HABs can alter the chemical composition of the water, impacting the growth and survival of other marine organisms.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The cumulative effects of toxin exposure, habitat degradation, and reduced oxygen levels contribute to a significant loss of biodiversity in affected areas. The long-term consequences of these losses can be profound.
Long-term Consequences
Recurring HAB events can lead to significant and long-lasting changes in marine ecosystems. These shifts can include altered species composition, decreased resilience to environmental stressors, and a reduction in overall ecosystem health. The recovery from such events can be slow and unpredictable.
Economic Consequences of Harmful Algal Blooms
The economic impacts of HABs in California are substantial and far-reaching, affecting various sectors.
Impacts on the Fishing Industry
HABs cause significant economic losses to the fishing industry.
- Financial Losses: Fishing closures and shellfish harvesting bans directly impact fishermen's income, as well as the processing plants and businesses that rely on them. This translates to substantial financial losses and job losses.
- Reduced Seafood Sales: Consumer concerns over seafood safety following HAB events can lead to reduced seafood sales, even after the blooms have subsided. This further undermines the industry’s economic stability.
Tourism and Recreation
The negative impacts on tourism can be devastating.
- Loss of Revenue: Beach closures and warnings against water activities discourage tourism, leading to significant revenue losses for hotels, restaurants, and recreational businesses. The economic repercussions spread across multiple sectors.
- Damage to Tourism Reputation: Negative publicity associated with HAB events can damage California's reputation as a desirable tourist destination, leading to long-term economic consequences.
Public Health Concerns
HABs pose significant public health risks.
- Seafood Poisoning: Consumption of contaminated seafood can cause various illnesses, ranging from mild gastrointestinal distress to severe neurological damage.
- Respiratory Issues: Some HABs produce airborne toxins that can cause respiratory problems in humans.
- Costs Associated with Public Health: The costs associated with public health monitoring, testing, and responses to HAB outbreaks, including medical treatment, can be considerable.
Causes and Contributing Factors of Harmful Algal Blooms
Several factors contribute to the increasing frequency and intensity of HABs in California.
Nutrient Pollution
Excess nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus, from various sources fuel HAB growth.
- Agricultural Runoff: Fertilizers used in agriculture are a major source of nutrient pollution, especially following heavy rainfall events that wash nutrients into waterways.
- Wastewater Discharge: Untreated or inadequately treated wastewater can also contribute significant amounts of nutrients to coastal waters.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change exacerbates nutrient pollution through increased rainfall intensity and altered river flow patterns, leading to larger nutrient loads in coastal waters.
Climate Change
Climate change significantly impacts HAB development.
- Rising Ocean Temperatures: Warmer water temperatures can favor the growth of certain harmful algal species, extending their geographic range and prolonging bloom duration.
- Altered Ocean Currents: Changes in ocean currents can transport HABs to new areas and influence their distribution.
- Changes in Water Stratification: Altered water stratification can create conditions favorable for HAB growth.
Other Factors
Other factors that may contribute to HABs include ocean acidification and the introduction of invasive species. These factors interact in complex ways to influence HAB dynamics.
Monitoring, Mitigation, and Management Strategies
Effective monitoring, mitigation, and management strategies are essential to address the threat of HABs.
Early Warning Systems
Robust monitoring programs are critical for issuing timely warnings.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery can detect large-scale blooms and provide early warnings.
- Water Sampling: Regular water sampling allows for the detection of HABs and the measurement of toxin levels.
- Toxin Analysis: Accurate toxin analysis is essential for determining the risk to human health and marine life.
Mitigation and Control Measures
Various strategies can help reduce nutrient pollution and manage HABs.
- Improved Wastewater Treatment: Upgrading wastewater treatment facilities can significantly reduce nutrient inputs into coastal waters.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, such as reduced fertilizer use and improved irrigation techniques, can minimize nutrient runoff.
- Bioremediation Techniques: Research is exploring bioremediation techniques that use natural processes to remove or neutralize HAB toxins.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for developing effective management strategies.
Continued research into the causes, dynamics, and impacts of HABs is essential for developing effective prevention and mitigation measures. This research includes investigating new monitoring technologies, exploring novel mitigation approaches, and enhancing our understanding of the complex interactions between HABs and the environment.
Conclusion: Addressing the Threat of Harmful Algal Blooms in California
Harmful algal blooms pose a significant threat to California's marine ecosystems and economy. Their ecological impacts, including disruptions to the food web and habitat degradation, are substantial and long-lasting. The economic consequences, affecting fishing, tourism, and public health, are equally severe. Proactive measures are crucial to mitigate the risks associated with HABs. We must invest in robust monitoring programs, implement effective mitigation strategies, and support continued research into HABs. Learn more about HABs, support research initiatives, and advocate for policies that address nutrient pollution and climate change. Participate in citizen science initiatives to monitor for HABs and help protect California's precious marine resources. By working together, we can safeguard California's coast from the growing threat of harmful algal blooms.

Featured Posts
-
 El Servicio Militar Y El Futuro De Bts Un Analisis De Su Regreso
May 30, 2025
El Servicio Militar Y El Futuro De Bts Un Analisis De Su Regreso
May 30, 2025 -
 Air Jordan June 2025 Release Dates The Ultimate Sneakerheads Checklist
May 30, 2025
Air Jordan June 2025 Release Dates The Ultimate Sneakerheads Checklist
May 30, 2025 -
 Analyzing Deutsche Banks Fic Trading Teams Path To Global Success
May 30, 2025
Analyzing Deutsche Banks Fic Trading Teams Path To Global Success
May 30, 2025 -
 Ingolstadts Garteig Wechselt Nach Augsburg
May 30, 2025
Ingolstadts Garteig Wechselt Nach Augsburg
May 30, 2025 -
 Greve Sncf Du 8 Mai La Probabilite D Une Greve Augmente T Elle
May 30, 2025
Greve Sncf Du 8 Mai La Probabilite D Une Greve Augmente T Elle
May 30, 2025
