Impact Of Reduced Spending And Tariffs: U.S. Economy Contracts By 0.2%
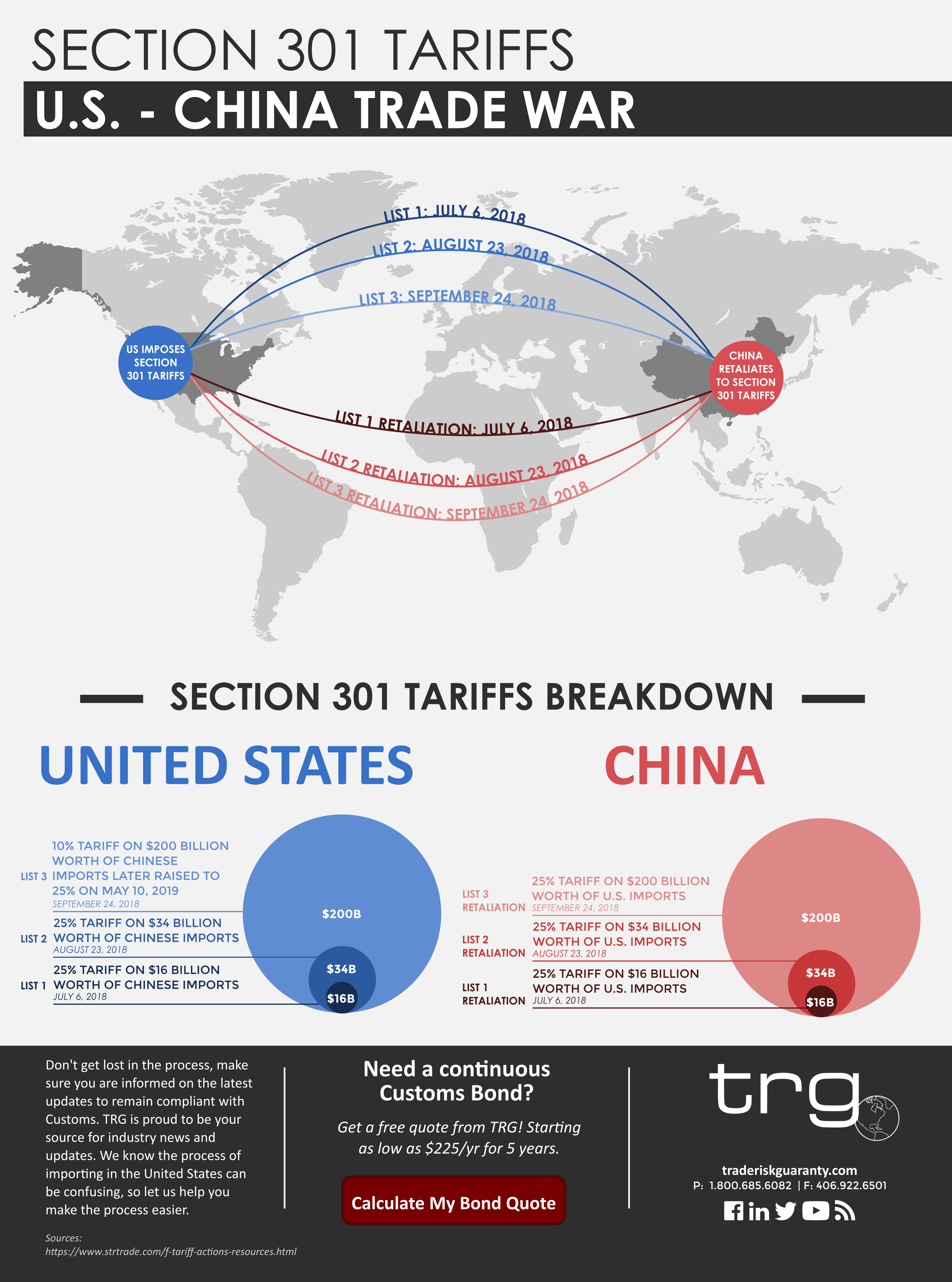
Table of Contents
Reduced Consumer Spending: A Major Contributing Factor
Decreased consumer spending is a primary driver of the recent economic contraction. This downturn reflects a confluence of factors impacting consumers' ability and willingness to spend.
Decreased Disposable Income: The Squeeze on Household Budgets
Several factors have contributed to lower disposable income, leaving less money for consumers to spend.
- Soaring Inflation: Inflation continues to erode purchasing power, with significant price increases across essential goods and services.
- Rising Housing Costs: Rent and mortgage payments have skyrocketed, consuming a larger portion of household budgets.
- Increased Food and Fuel Prices: The cost of groceries and gasoline has dramatically increased, forcing consumers to make difficult choices about their spending.
- Higher Interest Rates: Rising interest rates increase borrowing costs, making it more expensive to finance purchases, further reducing disposable income.
Data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis shows a significant decline in consumer spending confidence indices, reflecting the anxieties of households facing these financial pressures. The impact is evident across all sectors; for example, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) indicates a substantial increase in the cost of living, outpacing wage growth in many sectors.
Shifting Consumer Priorities: Saving Over Spending
Economic uncertainty is causing consumers to adjust their spending habits. Many are prioritizing essential goods and services while significantly reducing discretionary spending.
- Increased Savings Rates: Consumers are increasingly setting aside a larger portion of their income for future uncertainties.
- Prioritizing Essential Goods: Spending is focused on necessities like food, shelter, and healthcare, leaving less room for non-essential items and experiences.
- Delayed Purchases: Big-ticket items like cars and appliances are being postponed until economic conditions improve.
Data shows a notable shift in consumer spending patterns, with significant decreases in sectors like retail and hospitality, reflecting a pullback in discretionary spending.
The Impact of Tariffs on Businesses and Consumers
Tariffs imposed on imported goods have significantly impacted both businesses and consumers, exacerbating the economic downturn.
Increased Import Costs: A Direct Impact on Prices
Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for businesses and consumers.
- Higher Prices for Consumers: Tariffs translate to increased prices for a wide range of products, from electronics and clothing to furniture and building materials.
- Reduced Competitiveness for Businesses: Businesses reliant on imported goods face increased input costs, reducing their competitiveness and profitability.
Statistics show a direct correlation between tariff rates and the prices of imported goods. Specific sectors, such as manufacturing and agriculture, have been particularly affected by these price increases.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Ripple Effects Across the Economy
Tariffs have contributed to supply chain disruptions, causing shortages and delays that further impact production and costs.
- Reduced Availability of Goods: Tariffs can lead to shortages of certain goods, impacting both businesses and consumers.
- Increased Production Costs: Disruptions necessitate adjustments and alternative sourcing, increasing production costs.
Data from various industry reports highlight significant disruptions in global supply chains, leading to delays and increased costs for many businesses.
Other Contributing Factors to the Economic Contraction
Beyond reduced spending and tariffs, other factors contribute to the current economic contraction.
Geopolitical Uncertainty: Global Instability's Impact
Global events and geopolitical instability significantly influence the U.S. economy.
- International Conflicts: Geopolitical tensions and conflicts disrupt global trade and investment flows.
- Political Instability: Uncertainty in global politics can negatively impact economic confidence and investment decisions.
Economic data reflects the impact of global events, demonstrating how international instability translates into economic consequences for the U.S.
Interest Rate Hikes: Curbing Investment and Growth
The Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes, aimed at controlling inflation, have also impacted economic growth and investment.
- Reduced Borrowing and Investment: Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, leading to decreased investment and business expansion.
- Slower Economic Growth: Reduced investment translates to slower economic growth and job creation.
Statistics on interest rate changes clearly show their correlation with reduced investment and slower economic growth.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing the U.S. Economic Contraction
The 0.2% contraction in the U.S. economy is a consequence of a combination of factors, with reduced consumer spending and the impact of tariffs playing significant roles. The decreased disposable income of consumers, coupled with shifting spending priorities, significantly impacts overall demand. Simultaneously, tariffs increase import costs and disrupt supply chains, further hindering economic growth. Geopolitical uncertainty and interest rate hikes compound these challenges.
Key Takeaways: The economic slowdown is multi-faceted, stemming from decreased consumer spending, the impact of tariffs, geopolitical factors, and monetary policy decisions.
Future Outlook: The short-term economic outlook remains cautious, with continued uncertainty surrounding inflation, consumer spending, and global events.
Call to Action: Stay informed on the impact of reduced spending and tariffs on the U.S. economy. Learn more about how to navigate the current economic climate affected by reduced consumer spending and the effects of tariffs. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for both individual financial planning and informed policy decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Impact Of Souring Loans Rbcs Earnings Fall Short Of Forecasts
May 31, 2025
Impact Of Souring Loans Rbcs Earnings Fall Short Of Forecasts
May 31, 2025 -
 Womans Basement Holds A Mystery A Plumbers Unusual Find
May 31, 2025
Womans Basement Holds A Mystery A Plumbers Unusual Find
May 31, 2025 -
 Showers And Thunderstorms In Ne Ohio Your Complete Weather Guide
May 31, 2025
Showers And Thunderstorms In Ne Ohio Your Complete Weather Guide
May 31, 2025 -
 Constanza Incendio Forestal Causa Densa Humo Y Afecta A La Poblacion Bomberos Intervienen
May 31, 2025
Constanza Incendio Forestal Causa Densa Humo Y Afecta A La Poblacion Bomberos Intervienen
May 31, 2025 -
 Climate Whiplash How Cities Are Facing Increasingly Erratic Weather
May 31, 2025
Climate Whiplash How Cities Are Facing Increasingly Erratic Weather
May 31, 2025
