Impact Of Tariffs: China Lowers Interest Rates To Stimulate Lending

Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on the Chinese Economy
The ongoing trade war has undeniably inflicted significant damage on the Chinese economy. Tariffs imposed on Chinese exports have led to a noticeable decline in global demand for Chinese goods. This tariff impact on China manifests in several ways, triggering a ripple effect throughout various sectors. Keywords: tariff impact China, trade war consequences, export decline, economic contraction.
-
Reduced export volumes to key markets: The imposition of tariffs has made Chinese goods less competitive in international markets, resulting in reduced export volumes to crucial trading partners like the United States and the European Union.
-
Increased production costs for businesses: Businesses face higher costs due to tariffs on imported raw materials and components, impacting their profitability and competitiveness.
-
Weakening of the Chinese Yuan: The ongoing trade uncertainty has contributed to a weakening of the Chinese Yuan, further complicating the situation for Chinese exporters.
-
Impact on specific sectors: The manufacturing and technology sectors, heavily reliant on exports, have been particularly hard hit, leading to potential job losses and decreased economic growth. The agricultural sector also faces challenges due to decreased demand and trade restrictions.
China's Response: Lowering Interest Rates to Boost Lending
In response to the economic slowdown spurred by tariffs, the PBOC has implemented a series of interest rate cuts. This monetary policy adjustment aims to reduce borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, thereby stimulating investment and consumer spending. Keywords: PBOC interest rate, monetary policy, stimulus package, lending growth, consumer spending.
-
Reduced borrowing costs for businesses to encourage investment: Lower interest rates make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, encouraging investment in new projects and expansion. This should, in theory, lead to job creation and economic growth.
-
Lower mortgage rates to stimulate housing market activity: Reduced mortgage rates are expected to boost the housing market, a significant driver of economic activity in China.
-
Increased availability of credit for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): SMEs, the backbone of the Chinese economy, often struggle to access credit. Lower interest rates should improve their access to funding, fostering growth and job creation.
-
Potential impact on inflation: While stimulating the economy, lower interest rates also carry the risk of increased inflation. The PBOC must carefully monitor this aspect to avoid unintended consequences.
Effectiveness and Potential Risks of the Stimulus
The effectiveness of the interest rate cut in fully counteracting the negative impacts of tariffs remains to be seen. While lower borrowing costs can stimulate lending and investment, the severity of the trade war's impact might require a more comprehensive approach. Keywords: economic stimulus effectiveness, inflation risk, debt sustainability, monetary policy risks.
-
Effectiveness of previous stimulus measures: Past stimulus measures have shown varying degrees of effectiveness. The current situation presents unique challenges due to the global nature of the trade conflict.
-
Potential for increased non-performing loans: Lower interest rates could lead to an increase in non-performing loans if businesses struggle to repay their debts due to prolonged economic weakness.
-
Impact on government debt: Increased government spending to supplement the monetary policy stimulus could exacerbate existing government debt concerns.
-
The role of fiscal policy alongside monetary policy: A coordinated approach combining monetary policy (interest rate cuts) with fiscal policy (government spending) may be more effective in stimulating the economy.
Conclusion: Navigating the Impact of Tariffs – The Role of Interest Rates in China's Economic Strategy
The ongoing trade war has undeniably impacted the Chinese economy, leading to decreased export volumes, increased production costs, and a slowdown in economic growth. China's response, including the lowering of interest rates, aims to stimulate lending and mitigate these negative effects. However, the effectiveness and potential risks of this approach need careful monitoring. The impact of tariffs on China's economy underscores the complex interplay between global trade and domestic economic policies. The success of this strategy will depend on various factors, including the duration of the trade war and the effectiveness of complementary fiscal policies. Stay informed about the impact of tariffs on China and future developments in its economic policy by following reputable financial news sources and engaging with further reading on China's economic outlook and global trade tensions.

Featured Posts
-
 Cryptocurrency Investment Alert Van Ecks 185 Prediction For Cryptocurrency Name
May 08, 2025
Cryptocurrency Investment Alert Van Ecks 185 Prediction For Cryptocurrency Name
May 08, 2025 -
 Bitcoin Piyasasi Guencel Durum Ve Gelecek Tahminleri
May 08, 2025
Bitcoin Piyasasi Guencel Durum Ve Gelecek Tahminleri
May 08, 2025 -
 Filipe Luis Celebra Un Nuevo Titulo En Su Carrera
May 08, 2025
Filipe Luis Celebra Un Nuevo Titulo En Su Carrera
May 08, 2025 -
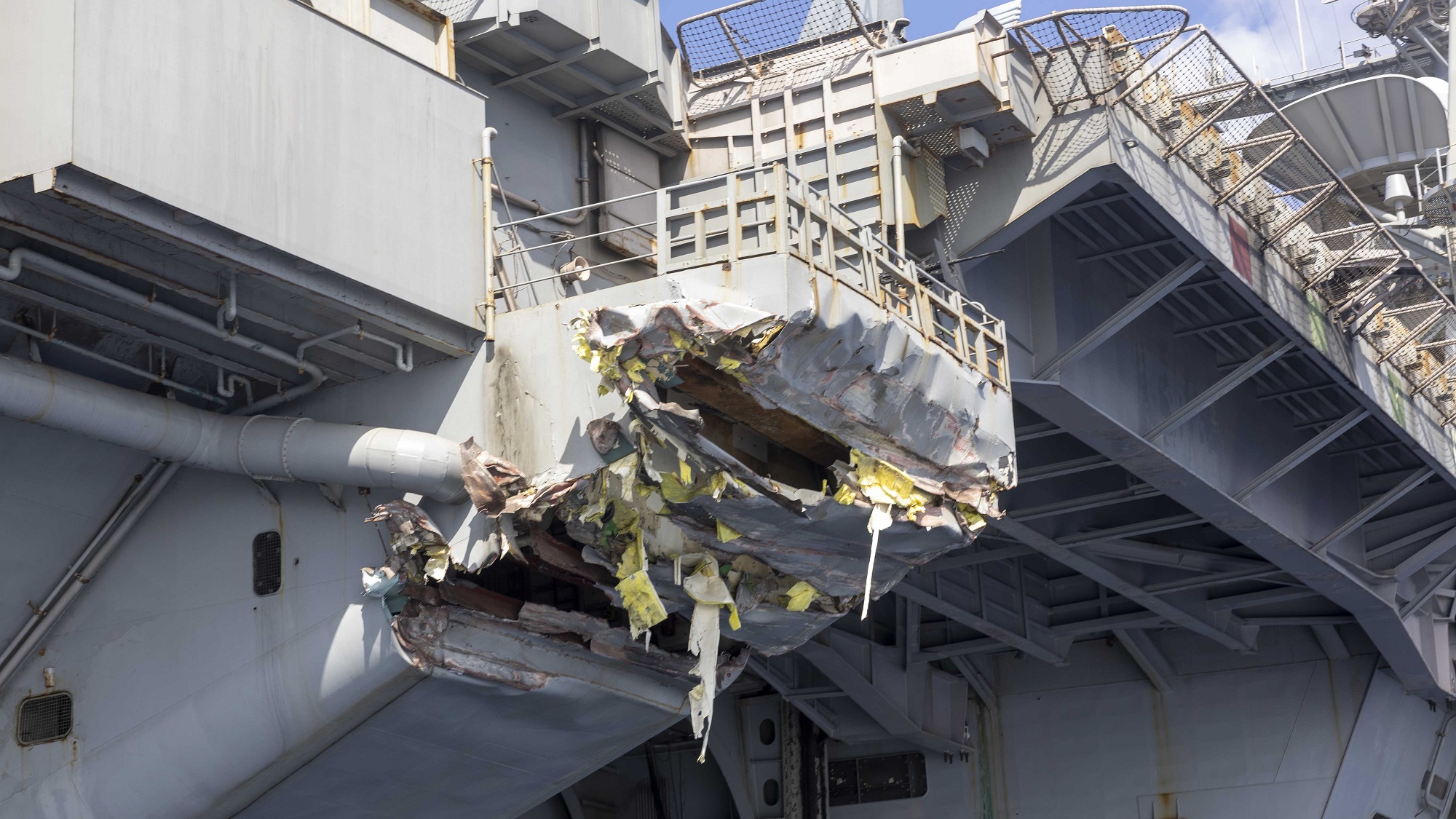 Second Aircraft Carrier Jet Lost From Uss Truman Details Of The Incident
May 08, 2025
Second Aircraft Carrier Jet Lost From Uss Truman Details Of The Incident
May 08, 2025 -
 Analysis Canadas Trade Deficit Falls To 506 Million
May 08, 2025
Analysis Canadas Trade Deficit Falls To 506 Million
May 08, 2025
