Increased Measles Transmission In Israel Tied To Texas

Table of Contents
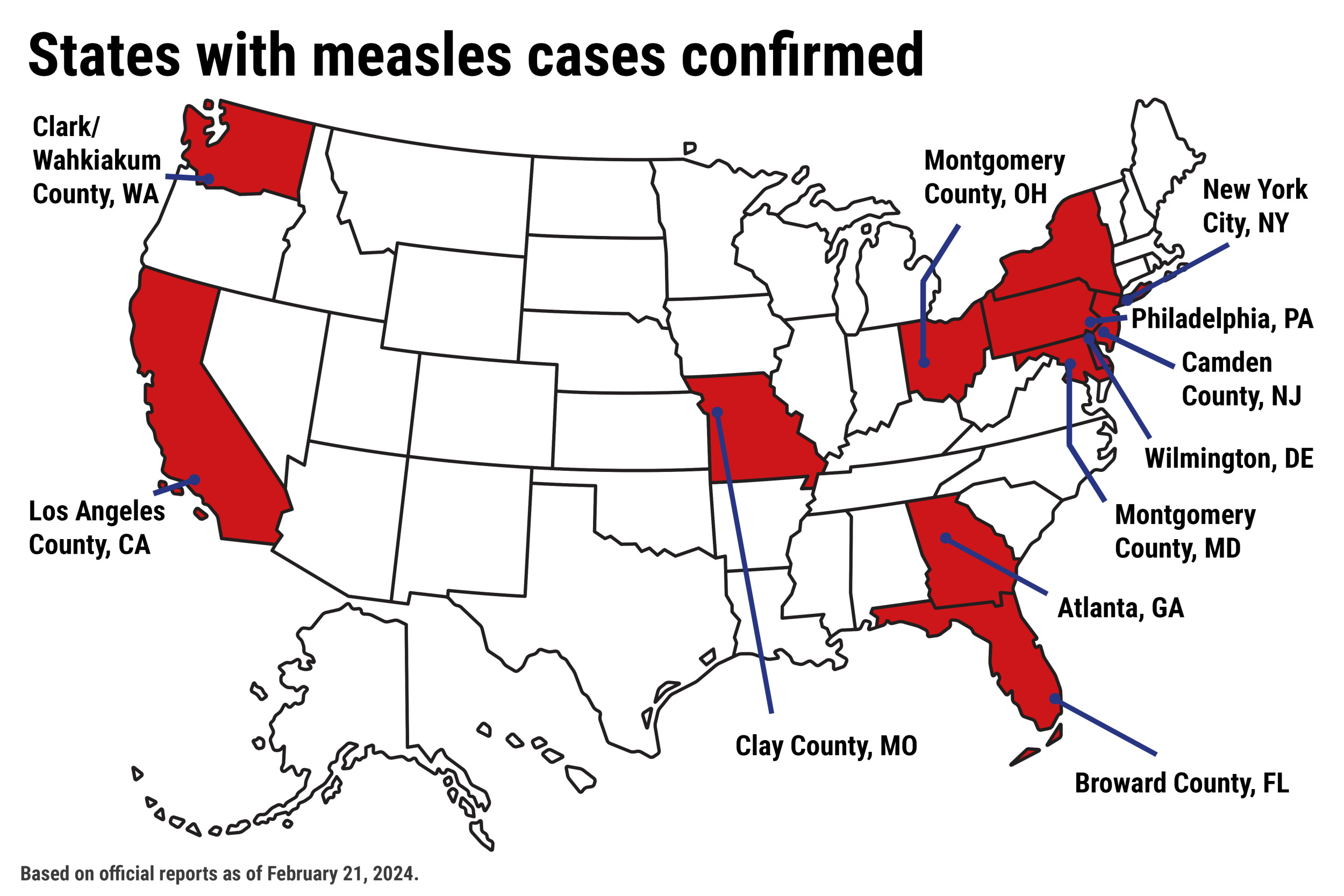
The Role of Unvaccinated Travelers in Measles Transmission from Texas to Israel
The most likely explanation for the increased measles transmission from Texas to Israel points to unvaccinated individuals traveling between the two regions. Unvaccinated persons act as vectors, capable of carrying and spreading the highly contagious measles virus, especially in densely populated areas like airports and tourist destinations. The relatively low vaccination rates in certain communities within Texas, coupled with increased air travel between the two countries, created a perfect storm for transmission.
Analyzing vaccination rates is crucial. While Israel boasts high overall vaccination coverage, pockets of unvaccinated individuals exist, making them vulnerable. Similarly, data reveals lower-than-ideal vaccination rates in some Texan communities, creating a reservoir for the virus. Specific travel routes or events may further facilitate spread, though pinpointing them precisely requires ongoing epidemiological investigation.
- Low vaccination rates in specific Texas communities: Studies have shown that lower vaccination rates in specific demographics within Texas significantly increase the risk of measles outbreaks and subsequent transmission.
- Increased air travel between Texas and Israel: The frequency of direct flights between major Texas cities and Israeli airports increases the likelihood of an infected individual spreading the virus during transit.
- Potential for transmission in crowded airports or tourist sites: Airports and popular tourist attractions are high-risk environments for measles transmission due to close proximity and prolonged exposure to potentially infected individuals.
- Lack of awareness regarding measles symptoms and contagiousness: A lack of public awareness about the symptoms and highly contagious nature of measles can delay diagnosis and appropriate isolation measures, furthering transmission.
Public Health Response and Control Measures in Israel
Following the detection of the outbreak, Israeli health authorities swiftly implemented a comprehensive public health response. This included large-scale vaccination drives targeting susceptible populations in affected areas, isolating and quarantining infected individuals to prevent further spread, and launching public health messaging campaigns to raise awareness about the symptoms, prevention, and importance of vaccination. Collaboration with Texas health authorities has also been crucial in tracing potential sources of infection.
Despite these efforts, challenges remain. Contact tracing, while effective, can be complex and time-consuming, especially when dealing with international travel and large numbers of potential contacts. Furthermore, vaccine hesitancy continues to pose a significant hurdle in achieving herd immunity and controlling the spread of measles.
- Large-scale vaccination drives in affected areas: Israel's swift response included widespread vaccination campaigns targeting high-risk populations and areas with confirmed cases.
- Isolation and quarantine of infected individuals: Rigorous isolation and quarantine protocols helped prevent further spread within communities.
- Public health messaging campaigns to raise awareness: Targeted campaigns informed the public about measles symptoms, prevention strategies, and the importance of vaccination.
- Collaboration with Texas health authorities: International collaboration was key to identifying potential sources of infection and coordinating prevention efforts.
The Implications of International Measles Transmission
The Texas-Israel measles connection underscores the interconnectedness of global health and the potential for rapid international spread of infectious diseases. This outbreak highlights the urgent need for enhanced international collaboration in disease surveillance, data sharing, and coordinated public health responses. Maintaining high vaccination rates globally is paramount in preventing future outbreaks and limiting the international transmission of measles and other vaccine-preventable diseases. This requires not only robust national vaccination programs but also strong international partnerships and the implementation of stricter travel health regulations.
- Increased risk of measles outbreaks in other countries: The ease of international travel increases the risk of measles spreading to other countries with lower vaccination rates.
- Need for improved global surveillance systems: Effective global surveillance is crucial for early detection and rapid response to outbreaks.
- Importance of maintaining high vaccination rates worldwide: High vaccination rates globally are essential for achieving herd immunity and preventing outbreaks.
- Call for stricter travel health regulations: Strengthening travel health regulations could help limit the spread of infectious diseases across international borders.
Preventing Future Measles Transmission: A Call to Action
The link between the Texas measles cases and the subsequent outbreak in Israel serves as a stark reminder of the importance of high vaccination rates in preventing future outbreaks. The international spread of measles is a clear indication of the interconnected nature of global health, emphasizing the need for collective action. Getting vaccinated against measles is the most effective way to protect yourself and your community. Promote vaccination amongst your family, friends and community. Together, we can prevent future outbreaks of measles transmission. Contact your local health authority for information on measles vaccination and learn more about measles prevention and vaccination to protect yourself and your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Virtual Venue De Ticketmaster Compra De Entradas Simplificada Y Redefinida
May 30, 2025
Virtual Venue De Ticketmaster Compra De Entradas Simplificada Y Redefinida
May 30, 2025 -
 Mozarts Clavierkonzert In Augsburg Ein Erlebnis Fuer Musikliebhaber
May 30, 2025
Mozarts Clavierkonzert In Augsburg Ein Erlebnis Fuer Musikliebhaber
May 30, 2025 -
 Susquehanna River Assault Case Advancement To Court
May 30, 2025
Susquehanna River Assault Case Advancement To Court
May 30, 2025 -
 Rising Measles Cases In Kansas Public Health Response
May 30, 2025
Rising Measles Cases In Kansas Public Health Response
May 30, 2025 -
 A69 Contournement Judiciaire Et Reprise Des Travaux
May 30, 2025
A69 Contournement Judiciaire Et Reprise Des Travaux
May 30, 2025
