Interdisciplinary And Transdisciplinary Approaches: A Critical Analysis
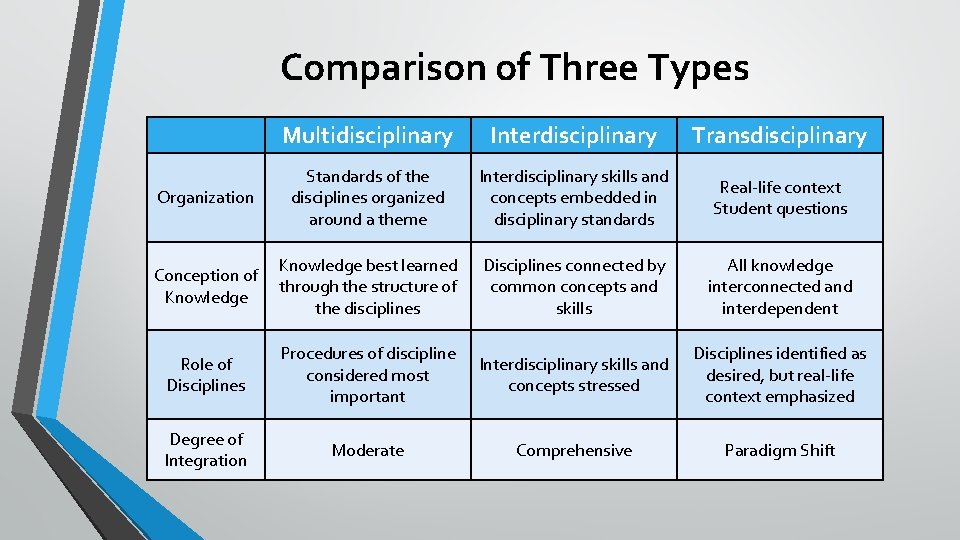
Table of Contents
Understanding Interdisciplinary Approaches: Collaboration Across Disciplines
Defining Interdisciplinary Research
Interdisciplinary research involves the collaboration of researchers from different established disciplines working together to address a shared problem. It leverages the diverse expertise of each discipline, integrating their methods and theories to achieve a more comprehensive understanding than any single discipline could offer. For example, a project studying the impact of climate change on coastal communities might combine the expertise of climatologists, economists, sociologists, and marine biologists. This integrated approach allows for a holistic analysis of the interconnected social, economic, and environmental factors at play. Successful interdisciplinary research relies on effective communication and a shared understanding of the overall research goals. Keywords like integrated research and knowledge integration are central to this approach.
Advantages of Interdisciplinary Approaches
- Broader Perspectives: By bringing together diverse perspectives, interdisciplinary research fosters a richer and more nuanced understanding of complex issues.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving: The combination of diverse skill sets and methodologies leads to more creative and effective problem-solving strategies.
- Innovative Solutions: The cross-pollination of ideas often sparks innovative solutions that might not have emerged within a single discipline.
- Improved Knowledge Sharing: Interdisciplinary collaborations facilitate the exchange of knowledge and best practices across different fields.
Challenges of Interdisciplinary Approaches
- Methodological Integration: Integrating diverse methodologies and theoretical frameworks can be challenging, requiring careful planning and coordination.
- Communication Barriers: Differing disciplinary jargon and communication styles can hinder effective collaboration.
- Power Imbalances: Power dynamics between disciplines can create conflict and impede the equitable contribution of all participants.
- Funding and Publication: Securing funding and publishing interdisciplinary research can be more difficult than publishing within established disciplinary boundaries.
Exploring Transdisciplinary Approaches: Integrating Knowledge Beyond Disciplines
Defining Transdisciplinary Research
Transdisciplinary research goes beyond interdisciplinary collaboration by actively involving stakeholders beyond academia. This includes policymakers, practitioners, community members, and other relevant actors in the research process. The goal is not just to integrate knowledge from different disciplines but also to co-create solutions with those who will ultimately implement them. For example, a transdisciplinary project focused on improving urban sustainability might involve researchers, city planners, community leaders, and residents working together to develop and implement sustainable urban development strategies. This ensures practical relevance and increases the likelihood of successful implementation.
Advantages of Transdisciplinary Approaches
- Participatory and Inclusive: Transdisciplinary approaches are highly participatory and inclusive, ensuring that the research is relevant and responsive to the needs of those affected.
- Stakeholder Buy-in: The involvement of stakeholders fosters a sense of ownership and increases the likelihood of successful implementation of the research findings.
- New Knowledge Creation: The integration of diverse perspectives and experiences generates new knowledge and understanding that surpasses what could be achieved through disciplinary research alone.
- Improved Translation of Findings: Transdisciplinary research facilitates the translation of research findings into practical applications and policy recommendations.
Challenges of Transdisciplinary Approaches
- Managing Diverse Stakeholders: Managing diverse stakeholder groups with varying interests and priorities can be complex and challenging.
- Establishing Shared Goals: Reaching consensus on shared goals and a common language can be time-consuming.
- Longer Timelines: Transdisciplinary projects typically require longer timelines and more complex processes than purely interdisciplinary projects.
- Impact Evaluation: Evaluating the impact of transdisciplinary projects using traditional research metrics can be difficult.
Comparing and Contrasting Interdisciplinary and Transdisciplinary Approaches
| Feature | Interdisciplinary Approach | Transdisciplinary Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Collaboration | Primarily between researchers from different disciplines | Between researchers and various stakeholders (e.g., community members, policymakers) |
| Stakeholders | Primarily researchers | Researchers and diverse stakeholders |
| Knowledge Integration | Integration of disciplinary knowledge and methods | Integration of disciplinary knowledge and stakeholder perspectives |
| Goal | Advance knowledge and understanding within a specific problem area | Solve real-world problems with direct application and stakeholder involvement |
| Challenges | Methodological integration, communication barriers | Stakeholder management, consensus building, impact evaluation |
The choice between an interdisciplinary or transdisciplinary approach depends on the specific research question, context, and stakeholders involved. Sometimes, a hybrid approach, combining elements of both, is the most effective strategy.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Research and Problem Solving
Both interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches offer significant advantages for tackling complex problems. However, they also present unique challenges. Interdisciplinary research excels at integrating knowledge from different disciplines to gain a deeper understanding, while transdisciplinary research prioritizes co-creation and implementation with diverse stakeholders to solve real-world problems. The choice depends on the specific context.
We encourage you to consider the potential of interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches in your own work. Explore the rich literature on collaborative research methodologies and specific techniques within both approaches. By embracing these powerful tools, we can unlock innovative solutions to the pressing challenges of our time and build a more sustainable and equitable future. The effective use of interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary research is paramount for achieving meaningful progress.

Featured Posts
-
 Esc Today Hosts 9th Annual Eurovision 2024 Infe Poll
May 19, 2025
Esc Today Hosts 9th Annual Eurovision 2024 Infe Poll
May 19, 2025 -
 Travel Vlogger Jyoti Malhotras Arrest Spying Allegations And Current Status
May 19, 2025
Travel Vlogger Jyoti Malhotras Arrest Spying Allegations And Current Status
May 19, 2025 -
 Reduced Library Funding And Services Under Trumps Executive Order
May 19, 2025
Reduced Library Funding And Services Under Trumps Executive Order
May 19, 2025 -
 Taksidi Stin Kyriaki Toy Antipasxa Sta Ierosolyma Organosi Kai Proetoimasia
May 19, 2025
Taksidi Stin Kyriaki Toy Antipasxa Sta Ierosolyma Organosi Kai Proetoimasia
May 19, 2025 -
 Libraries Face Staff And Service Cuts Following Trump Administrations Agency Dismantlement
May 19, 2025
Libraries Face Staff And Service Cuts Following Trump Administrations Agency Dismantlement
May 19, 2025
