Invasive Seaweed: Exterminating Australian Marine Life

Table of Contents
Identifying Invasive Seaweed Species in Australia
Several invasive seaweed species pose a significant threat to Australia's marine environment. Recognizing these species is the first step in effective management. Among the most problematic are:
- Caulerpa taxifolia: This fast-growing seaweed, often called "killer algae," forms dense mats, smothering native seagrass beds and other marine plants. It's characterized by its bright green color, feathery branching pattern, and rapid growth rate. It is particularly prevalent in areas of southwestern Australia and parts of New South Wales.
- Undaria pinnatifida: Also known as wakame, this brown seaweed is native to Japan but has spread globally through ballast water and aquaculture activities. It can quickly outcompete native species for resources. It's identifiable by its large, leathery brown blades and ribbon-like structure. It's found along many parts of the Australian coast, particularly in cooler waters.
Key Characteristics for Identification:
- Color: Variations in color (green, brown, red) are key indicators.
- Texture: Seaweed texture ranges from delicate and feathery to leathery and tough.
- Growth Pattern: Observe whether it forms mats, isolated clumps, or individual fronds.
- Geographic Location: Knowing the typical distribution of invasive species within Australia helps in identification.
The introduction pathways of these invasive seaweeds often involve ballast water from ships and unintentional introduction through aquaculture practices.
The Ecological Impact of Invasive Seaweed
Invasive seaweeds wreak havoc on Australia's marine ecosystems through several mechanisms:
- Outcompeting Native Species: Invasive seaweeds aggressively compete with native plants and algae for resources such as sunlight and nutrients. Their rapid growth often leads to the shading and smothering of native flora, reducing biodiversity.
- Habitat Destruction: Dense mats of invasive seaweed disrupt habitats, reducing the availability of suitable areas for fish and invertebrates. This leads to a decline in population numbers and species diversity within affected areas.
- Impact on Commercially Important Species and Fisheries: The displacement of native seagrasses and kelp forests—critical habitats for commercially important fish and shellfish—can severely damage fisheries, resulting in significant economic losses.
Specific Impacts:
- Caulerpa taxifolia has been linked to declines in populations of native fish and invertebrate species in several areas.
- Undaria pinnatifida can outcompete native kelp forests, reducing habitats for valuable abalone and other commercially important species.
- Estimates of economic losses due to invasive seaweed control and fishery impacts are substantial but often difficult to quantify fully.
Current Control and Management Strategies for Invasive Seaweed
Controlling invasive seaweed is a complex and challenging undertaking, requiring a multi-pronged approach:
- Manual Removal: This involves physically removing the seaweed by hand (diving) or using mechanical methods like dredging. While effective in small, localized infestations, it can be labor-intensive, expensive, and may not be suitable for large-scale invasions.
- Chemical Control: Chemical herbicides can be used to kill invasive seaweed, but they carry significant environmental risks, potentially harming non-target species. Their effectiveness is also variable and depends on the species and environmental conditions.
- Biological Control: This involves using natural predators or pathogens to control the seaweed population. Research is ongoing to explore potential biological control agents, but caution is essential to avoid unintended consequences.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM strategies combine multiple control methods to achieve the most effective and environmentally sound approach, often tailored to specific locations and the species involved.
The Role of Citizen Science in Combating Invasive Seaweed
Citizen science plays a vital role in the detection and management of invasive seaweed. Early detection is crucial for effective control, and public participation is essential.
- How to Identify Invasive Seaweed: Utilize online resources, field guides, and participate in workshops to learn how to identify invasive seaweed species.
- Where to Report Sightings: Report suspected sightings to relevant authorities, such as your state's Department of Primary Industries or local environmental organizations. Many online reporting systems are available.
- How to Participate in Monitoring Programs: Volunteer for monitoring programs organized by research institutions or conservation groups.
Conclusion
Invasive seaweed poses a significant and growing threat to Australia's unique marine ecosystems and the livelihoods that depend on them. The economic consequences, stemming from damaged fisheries and costly control measures, are substantial. Successful management requires a multi-faceted approach employing various control strategies, including manual removal, chemical control (used cautiously and strategically), biological control (where feasible and safe), and integrated pest management. Critically, the success of any invasive seaweed management strategy relies heavily on early detection. Citizen science initiatives are vital for early detection and reporting, allowing for swift intervention. Help protect Australia's precious marine life by learning to identify and report invasive seaweed. Your vigilance is crucial in the fight against this ecological threat. Visit [link to relevant organization 1] and [link to relevant organization 2] to learn more about invasive seaweed identification and control in your area.

Featured Posts
-
 San Diego Weather 4 Days Of Sunshine Predicted
May 30, 2025
San Diego Weather 4 Days Of Sunshine Predicted
May 30, 2025 -
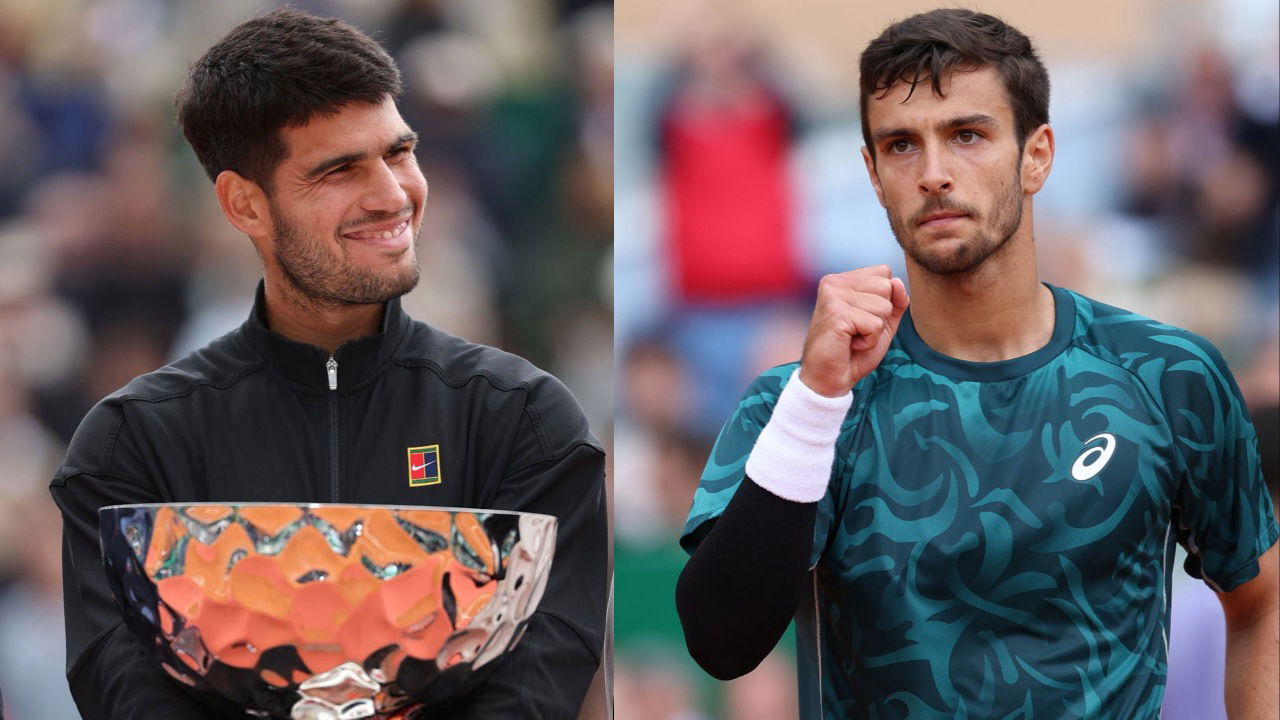 Monte Carlo Masters Final Alcaraz Begins Musetti Withdraws Injured
May 30, 2025
Monte Carlo Masters Final Alcaraz Begins Musetti Withdraws Injured
May 30, 2025 -
 The Enduring Legacy Of The Baim Collection A Lifetime Ago
May 30, 2025
The Enduring Legacy Of The Baim Collection A Lifetime Ago
May 30, 2025 -
 Strategic Energy Corridor Manitoba And Nunavut Partner On Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Project
May 30, 2025
Strategic Energy Corridor Manitoba And Nunavut Partner On Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Project
May 30, 2025 -
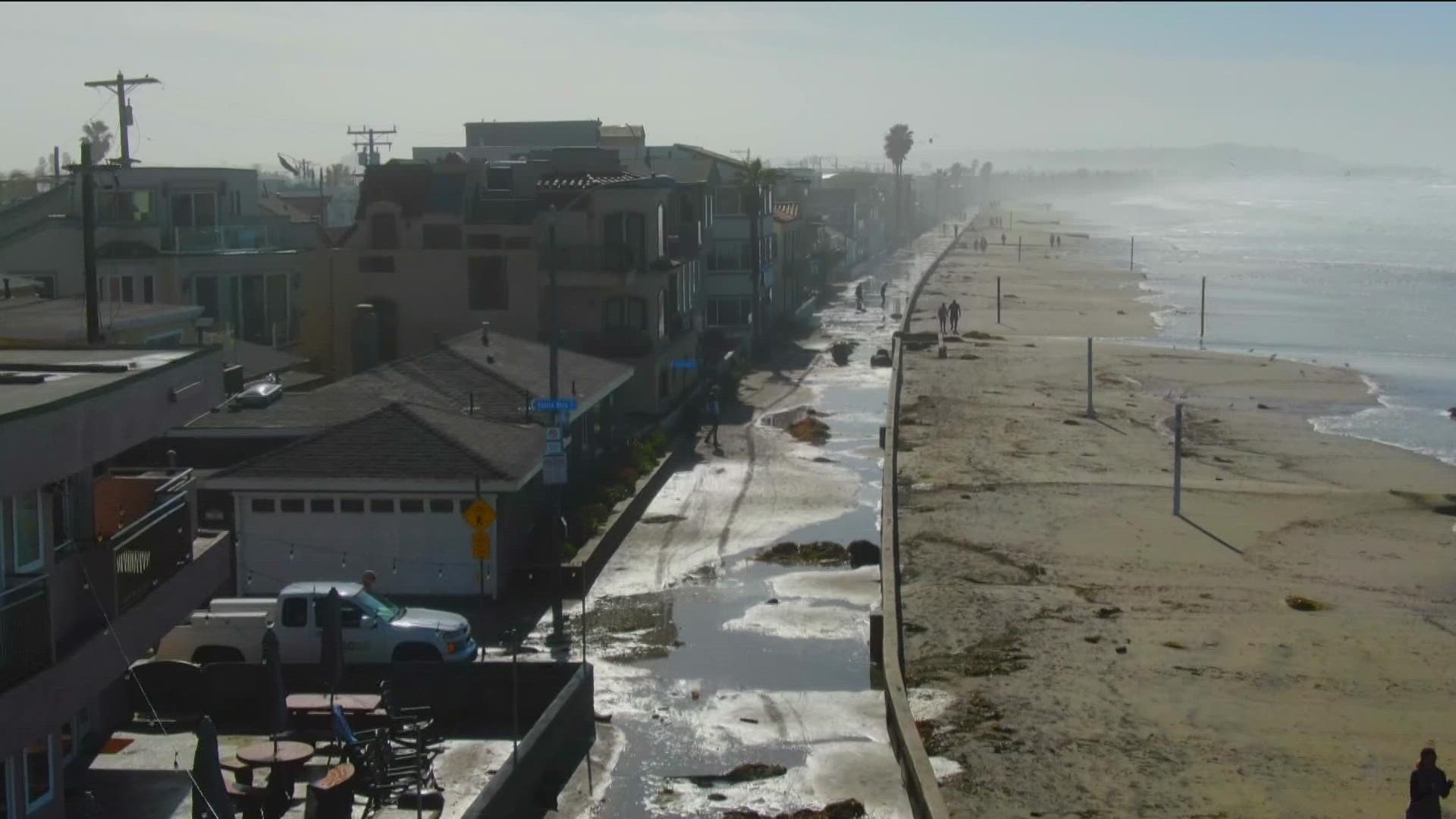 San Diego County Faces Record Heat Impacts And Expected Relief
May 30, 2025
San Diego County Faces Record Heat Impacts And Expected Relief
May 30, 2025
