Investigation Into CWD Case At Jackson Hole Elk Feedground
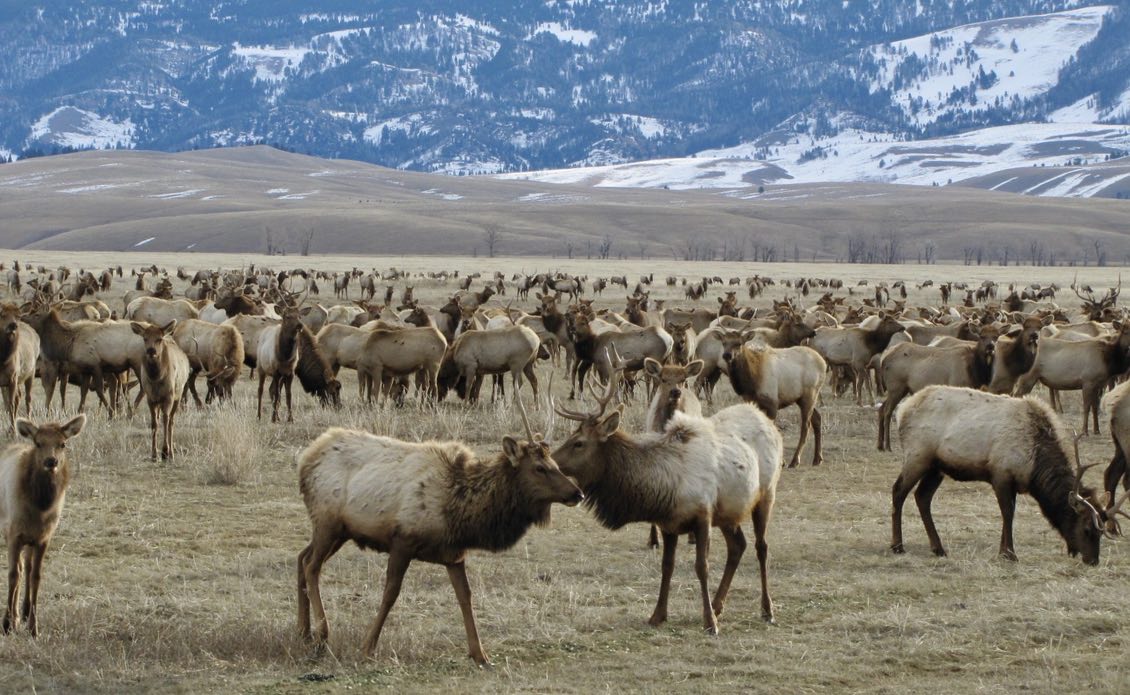

Table of Contents
The Discovery and Initial Response to the CWD Case
The detection of CWD-positive elk at the Jackson Hole elk feedground marked a critical turning point. The process began with routine surveillance testing conducted by the Wyoming Game and Fish Department (WGFD). Upon identifying a positive case, a swift and decisive response was initiated. This involved immediate quarantine measures to prevent further spread, a rapid expansion of testing to encompass a wider population of elk within the feedground, and close collaboration between multiple agencies.
- Date of discovery: [Insert Date - replace bracketed information with actual date]
- Number of affected elk initially identified: [Insert Number]
- Agencies involved: Wyoming Game and Fish Department (WGFD), US Forest Service, National Park Service (if applicable), and potentially others.
- Initial public reaction: Initial public reactions ranged from concern and alarm to calls for immediate action, highlighting the significance of this discovery in the local community.
Spread and Transmission of CWD at the Feedground
The concentrated nature of the elk feedground significantly increases the risk of CWD transmission. Elk congregate in large numbers, creating ideal conditions for the prion protein responsible for CWD to spread through direct contact, such as through saliva, urine, or feces. The feedground itself acts as a potential vector, possibly facilitating the contamination of the environment with prions.
- Mechanism of CWD transmission: CWD is caused by misfolded prion proteins that can infect and damage the brain of cervids. These prions are extremely resistant to degradation and can persist in the environment.
- Elk density: The high density of elk at the feedground exponentially increases the likelihood of CWD transmission.
- Research in similar environments: Studies on CWD transmission in other high-density wildlife feeding areas show a similar pattern of rapid spread.
- Mitigation strategies: Mitigation strategies under consideration include temporarily closing the feedground, implementing culling programs, and possibly exploring alternative feeding methods that reduce congregation.
The Ongoing Investigation and Testing Procedures
The investigation into the CWD outbreak at Jackson Hole involves rigorous testing procedures using a variety of methods. These tests aim to determine the prevalence of CWD within the elk population and to identify the extent of environmental contamination. The sensitivity and specificity of these tests are crucial for accurate assessment and effective management.
- Types of CWD tests: ELISA tests, Western Blot tests, and possibly other advanced diagnostic techniques are being employed.
- Number of elk tested: [Insert Number - replace bracketed information with the number of elk tested]
- Testing methodology and accuracy: The accuracy of the tests is vital for making informed decisions about management strategies.
- Timeline for completion: [Insert Timeline – replace bracketed information with a realistic timeframe]
Long-Term Implications and Management Strategies
The long-term effects of this CWD outbreak could be devastating for the Jackson Hole elk population. Reduced population numbers, decreased genetic diversity, and the potential for further spread to other cervid species are major concerns. The economic implications are also substantial, affecting the hunting and tourism industries that rely heavily on the region's wildlife.
- Impact on hunting seasons: Hunting seasons might be curtailed or modified to manage the CWD outbreak and protect the remaining elk population.
- Long-term effects on genetic diversity: A significant reduction in the elk population could lead to a loss of genetic diversity.
- Economic effects: The outbreak could significantly impact tourism and hunting, causing financial hardship for local communities.
- Proposed management strategies: Strategies include a combination of culling, habitat management, and potentially altering feeding practices to reduce congregation.
Conclusion: Understanding the Investigation into CWD Case at Jackson Hole Elk Feedground
The investigation into CWD case at Jackson Hole Elk Feedground is a critical undertaking with far-reaching consequences. The discovery of CWD highlights the vulnerability of wildlife populations to this devastating disease and underscores the importance of proactive monitoring and management strategies. The potential long-term effects on the elk population, the ecosystem, and the local economy cannot be overstated.
To stay updated on the ongoing investigation and learn more about the measures being taken to mitigate the spread of CWD, follow the Wyoming Game and Fish Department and other relevant agencies. For more information on CWD investigation updates Jackson Hole, search for "Chronic Wasting Disease in Jackson Hole" or "elk feedground CWD" online. Your engagement and support in preventing future outbreaks of CWD are crucial. What are your thoughts on the most effective strategies for managing this crisis? What further research do you believe is needed?

Featured Posts
-
 Nintendos Action Forces Ryujinx Switch Emulator To Cease Development
May 22, 2025
Nintendos Action Forces Ryujinx Switch Emulator To Cease Development
May 22, 2025 -
 Saskatchewans Political Landscape Analyzing The Federal Election Impact
May 22, 2025
Saskatchewans Political Landscape Analyzing The Federal Election Impact
May 22, 2025 -
 I 83 Closed After Tractor Trailer Produce Spill
May 22, 2025
I 83 Closed After Tractor Trailer Produce Spill
May 22, 2025 -
 Ntt Multi Interconnect At Be X Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025
Ntt Multi Interconnect At Be X Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025 -
 Updated The Trans Australia Run World Record Race
May 22, 2025
Updated The Trans Australia Run World Record Race
May 22, 2025
