Iron Ore Price Drop: China's Steel Output Restrictions Explained
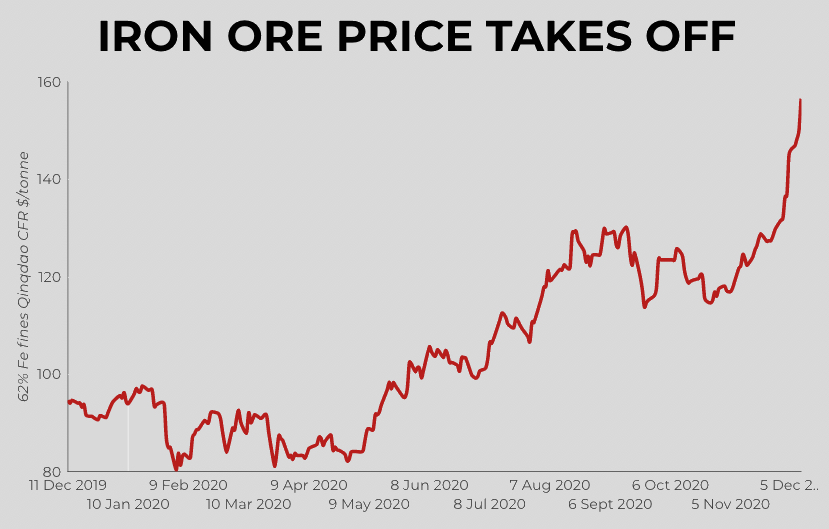
Table of Contents
China's Environmental Concerns and Steel Production Curbs
China's ambitious environmental goals are significantly impacting its steel industry, leading to a substantial iron ore price drop.
The Drive for Carbon Neutrality
China's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060 necessitates a dramatic reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Steel production, a notoriously carbon-intensive process, is a major target.
- China aims to peak carbon emissions before 2030, requiring substantial cuts in energy consumption and industrial emissions.
- Penalties for exceeding emission limits are increasingly severe, forcing steel mills to curtail production or invest heavily in cleaner technologies.
- The government is aggressively promoting the use of renewable energy sources, such as hydropower and solar power, to decarbonize the steel industry.
- China's steel production accounts for approximately half of global output, making its emission reduction efforts crucial for global climate goals. In 2022, China produced an estimated 1.01 billion tonnes of crude steel. The carbon footprint associated with this level of production is immense.
Air Quality Regulations and Their Impact
Provincial governments across China have implemented increasingly strict air quality regulations, directly impacting steel mill operations.
- Many provinces have imposed production quotas and operational restrictions on steel mills, particularly during peak pollution seasons.
- These regulations often involve temporary shutdowns or reductions in production capacity, leading to a decrease in steel production and, consequently, iron ore demand.
- The impact varies across different steel types. Construction steel, for instance, has been more heavily affected than specialty steels due to the nature of demand fluctuations.
Impact of Reduced Steel Demand on Iron Ore Prices
The decrease in China's steel production directly translates into lower iron ore demand, driving down iron ore prices globally.
The Correlation Between Steel and Iron Ore
Iron ore is the primary raw material for steelmaking. Therefore, a decrease in steel production inevitably leads to a reduction in iron ore consumption.
- The demand for iron ore is directly proportional to the level of steel production.
- Data shows a strong negative correlation between China steel output and iron ore prices. When steel production falls, iron ore prices follow suit.
- China consumes a vast majority of the world's iron ore, making its production decisions a critical factor in global market dynamics.
Global Market Dynamics and Price Volatility
Reduced demand from China creates ripples throughout the global iron ore market, resulting in price volatility.
- Major iron ore producers like Australia and Brazil are directly impacted by the reduced demand from China.
- Producers have responded by adjusting production levels and implementing hedging strategies to mitigate the impact of price fluctuations.
- This price volatility impacts the profitability of mining companies and the overall stability of the global commodity market.
Government Policies and Their Role in Shaping the Iron Ore Market
Chinese government policies, beyond environmental concerns, are also contributing to the reduced demand for steel and the subsequent iron ore price drop.
Real Estate Regulations and Their Consequences
The Chinese government's crackdown on the real estate sector significantly impacts steel demand, as construction is a major consumer of steel.
- Tighter regulations on property development and financing have reduced the number of new construction projects.
- This decreased construction activity directly translates into lower steel demand and, consequently, lower iron ore demand.
- The effect cascades to related industries, like cement and other construction materials, exacerbating the overall decline in demand.
Long-Term Strategies for Sustainable Steel Production
China is investing in long-term strategies to transition to greener steel production methods, although this may involve further short-term reductions in output.
- Government initiatives are promoting the adoption of more efficient and environmentally friendly steelmaking technologies.
- Investments in renewable energy sources are aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of the steel industry.
- The long-term impact on the iron ore market depends on the success of these initiatives and the pace of technological advancements.
Conclusion
The decline in iron ore prices is largely attributed to China's stringent steel output restrictions, driven by environmental concerns and broader economic policies. While the short-term implications for the iron ore market are marked by price volatility and uncertainty, China's commitment to sustainable development and its long-term strategies for greener steel production will ultimately reshape the industry landscape. Understanding the complexities of China's policies is crucial for anyone involved in the iron ore market, from investors and traders to producers and consumers. Stay informed about the latest developments in iron ore price fluctuations and China's steel output restrictions to make informed decisions in this dynamic market.

Featured Posts
-
 Elizabeth Hurleys Maldives Bikini Vacation Photos And Highlights
May 09, 2025
Elizabeth Hurleys Maldives Bikini Vacation Photos And Highlights
May 09, 2025 -
 Young Thug Will Not Join The Next Blue Origin Space Flight
May 09, 2025
Young Thug Will Not Join The Next Blue Origin Space Flight
May 09, 2025 -
 Xu Ly Nghiem Hanh Vi Bao Hanh Tre Em Nang Cao Chat Luong Giam Sat Co So Giu Tre Tu Nhan
May 09, 2025
Xu Ly Nghiem Hanh Vi Bao Hanh Tre Em Nang Cao Chat Luong Giam Sat Co So Giu Tre Tu Nhan
May 09, 2025 -
 Tf Ls Elizabeth Line Navigating Accessibility Challenges For Wheelchair Users
May 09, 2025
Tf Ls Elizabeth Line Navigating Accessibility Challenges For Wheelchair Users
May 09, 2025 -
 Greenlands Geopolitical Shift The Impact Of Trumps Presidency
May 09, 2025
Greenlands Geopolitical Shift The Impact Of Trumps Presidency
May 09, 2025
