Japan's Steep Bond Curve: A Challenge For Monetary Policy
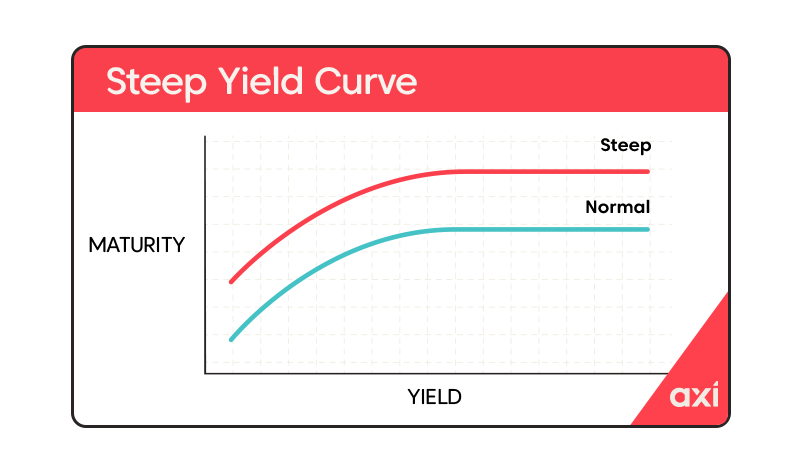
Table of Contents
Understanding Japan's Steep Bond Curve
A yield curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between interest rates and the time to maturity of debt instruments of the same credit quality. It typically plots the yields of government bonds with varying maturities. A normal yield curve slopes upward, indicating that longer-term bonds offer higher yields to compensate investors for the increased risk associated with longer-term investments. However, Japan's yield curve presents a different picture. Currently, Japan exhibits a steep yield curve, meaning a substantial difference exists between short-term and long-term interest rates. This steepness signifies a significant divergence in market expectations about future interest rates.
(Insert a graph or chart visualizing Japan's current yield curve here. Source should be cited.)
- Short-term interest rates: These are the rates on bonds with maturities of less than one year. The BOJ's policies significantly influence these rates.
- Long-term interest rates: These are the rates on bonds with maturities of 10 years or more. These rates are more sensitive to inflation expectations and broader market sentiment.
- The unusually large gap: The striking feature of Japan's current situation is the unusually large gap between short-term and long-term interest rates, significantly deviating from the historical norm and posing a challenge to the BOJ’s monetary policy.
- Historical context: Japan's yield curve has not always been this steep. Its evolution is intrinsically linked to the BOJ's monetary policy adjustments over the past decades, including periods of quantitative easing and yield curve control.
Causes of the Steep Bond Curve
Several factors contribute to the steepness of Japan's yield curve.
The BOJ's Yield Curve Control (YCC) Policy
The BOJ's Yield Curve Control (YCC) policy aims to maintain a specific target for 10-year Japanese government bond (JGB) yields. While intending to stimulate the economy by keeping long-term interest rates low, YCC has inadvertently contributed to the steepening of the curve.
- Target for 10-year JGB yields: The BOJ's target range for 10-year JGB yields has been a key element of its monetary policy, impacting the overall shape of the curve.
- Limitations of YCC: YCC primarily focuses on the 10-year yield, leaving other segments of the curve more susceptible to market forces. This can lead to inconsistencies and distortions across the yield curve.
- Market expectations: Market participants' expectations about future interest rate changes, influenced by inflation forecasts and global economic conditions, also significantly impact the shape of the yield curve, especially concerning longer-term yields.
Inflationary Pressures and Market Expectations
Recent inflationary pressures in Japan, albeit relatively modest compared to other developed economies, have influenced long-term interest rates.
- Impact of global inflation: Global inflationary pressures have spilled over into Japan, affecting domestic inflation expectations and consequently influencing the longer end of the yield curve.
- Speculation and market sentiment: Market speculation and shifting sentiment regarding future inflation and BOJ policy contribute to the volatility and steepness of the curve.
- Future inflation scenarios: Different scenarios regarding future inflation rates are reflected in the long-term bond yields, adding to the complexity of Japan's yield curve.
Global Economic Uncertainty
Global economic factors significantly influence Japan's bond market and the shape of its yield curve.
- US Federal Reserve's monetary policy: The US Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes have ripple effects on global financial markets, including Japan's, impacting bond yields.
- Other global economic events: Geopolitical events, global economic slowdowns, and other significant economic developments worldwide influence investor sentiment and capital flows, impacting Japan's bond yields.
- Flight to safety: During periods of global uncertainty, investors may seek the safety of Japanese government bonds, increasing demand and potentially impacting the yield curve's shape.
Implications of the Steep Bond Curve for Monetary Policy
The steep yield curve poses significant challenges and implications for the BOJ and the Japanese economy.
Challenges for the BOJ
The steep yield curve complicates the BOJ's efforts to manage monetary policy effectively.
- Unintended consequences of YCC adjustments: Adjustments to the BOJ's YCC policy can have unintended consequences, potentially leading to further distortions in the yield curve.
- Limitations of quantitative easing: Quantitative easing (QE) may be less effective in influencing the entire yield curve when a steep slope already exists.
- Risks of further steepening or sudden shifts: A further steepening or sudden shifts in the yield curve could trigger market instability and disrupt economic activity.
Impact on the Japanese Economy
The steep yield curve affects borrowing costs, investment decisions, and economic growth.
- Impact on corporate investment: Higher long-term interest rates can increase the cost of borrowing for corporations, potentially discouraging investment and hindering economic growth.
- Effects on consumer spending and borrowing: Increased borrowing costs for consumers can dampen consumer spending and reduce overall economic activity.
- Potential for economic slowdown: The combined impact of higher borrowing costs and decreased investment can potentially lead to a slowdown in Japan's economic growth.
Conclusion
Japan's steep bond curve presents a significant challenge for the BOJ's monetary policy. The interplay of YCC, inflation expectations, and global economic uncertainties contributes to this complex situation. The steep curve poses risks to economic growth and necessitates careful consideration of policy adjustments by the BOJ. Understanding the dynamics of Japan's steep bond curve is crucial for navigating the future economic landscape of Japan. Further research and analysis are needed to fully grasp the long-term implications and develop effective strategies for managing this unique challenge. Stay informed on developments concerning Japan's steep bond curve and its variations to better understand the complexities of Japan's monetary policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Thu Thiem Thien Duong Dien Anh Voi Phoi Canh Ven Song Hut Hon
May 17, 2025
Thu Thiem Thien Duong Dien Anh Voi Phoi Canh Ven Song Hut Hon
May 17, 2025 -
 Nba Live Score Knicks Vs Trail Blazers 77 77 March 13 2025
May 17, 2025
Nba Live Score Knicks Vs Trail Blazers 77 77 March 13 2025
May 17, 2025 -
 Ta Zeygaria Ton Playoffs Toy Nba And Oi Imerominies Ton Agonon
May 17, 2025
Ta Zeygaria Ton Playoffs Toy Nba And Oi Imerominies Ton Agonon
May 17, 2025 -
 De Xerem Aos Emirados Ex Vasco Conquista Camisa 10 E Almeja Copa 2026
May 17, 2025
De Xerem Aos Emirados Ex Vasco Conquista Camisa 10 E Almeja Copa 2026
May 17, 2025 -
 Tesla I Prosvjednici Detaljan Pregled Incidenta U Berlinu I Globalnih Implikacija
May 17, 2025
Tesla I Prosvjednici Detaljan Pregled Incidenta U Berlinu I Globalnih Implikacija
May 17, 2025
