Measles Cases Rising: Where The Outbreak Is Affecting The U.S.
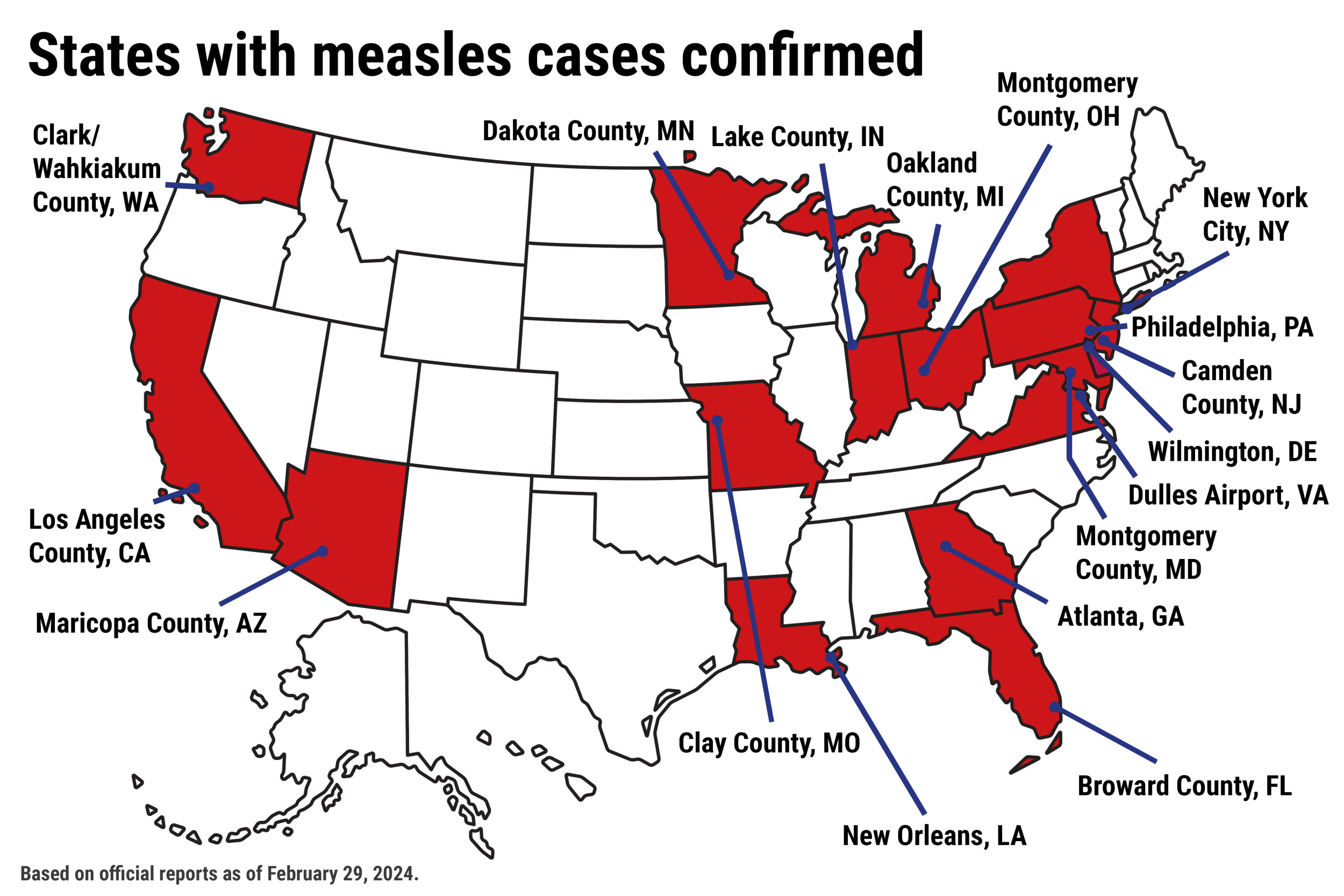
Table of Contents
Geographic Distribution of the Measles Outbreak in the U.S.
Pinpointing the precise locations of measles hotspots within the U.S. is essential for targeted public health interventions. A clear understanding of the measles map USA is key to effective resource allocation and containment strategies. While the outbreak is not confined to a single region, certain areas are experiencing a disproportionately high number of cases. Analyzing state-by-state measles cases reveals clear patterns.
- Top 5 States with Highest Reported Cases: (Note: Specific state data would need to be inserted here based on the most up-to-date information from the CDC or other reliable sources. This section should be updated regularly to reflect current conditions. Examples would include: "Ohio," "Texas," "California," etc.)
- Specific Counties/Cities: (Insert specific locations experiencing significant outbreaks, referencing reliable sources)
- Geographic Patterns: Many outbreaks are clustered in communities with lower vaccination rates. This highlights the correlation between vaccination rates and measles transmission.
- Contributing Factors: Population density, international travel, and the movement of unvaccinated individuals between communities are all factors impacting the geographic distribution of the measles outbreak.
Understanding the Factors Contributing to the Measles Outbreak
The sharp increase in measles cases is multifaceted, but a critical factor is the decline in measles vaccination rates. This correlates strongly with rising vaccine hesitancy and the spread of misinformation within the anti-vaccine movement. These factors significantly undermine herd immunity, making the population more vulnerable to large-scale outbreaks.
- Importance of High Vaccination Rates: High vaccination rates are paramount to achieving herd immunity, a critical aspect of measles prevention. Herd immunity protects even those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
- Measles Transmission: Measles is highly contagious, spreading through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Its ease of transmission contributes to rapid outbreaks in unvaccinated populations.
- Role of Misinformation: The anti-vaccine movement and the spread of inaccurate information regarding vaccine safety significantly contribute to vaccine hesitancy and lower vaccination rates. Combating misinformation is crucial for public health.
- Other Contributing Factors: International travel introduces the potential for importing measles cases from other countries experiencing outbreaks. This underscores the importance of global collaboration in managing measles epidemics.
Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Measles
Recognizing measles symptoms promptly is crucial for early intervention and preventing further transmission. The characteristic measles rash, accompanied by other symptoms, serves as a key identifier.
- Common Symptoms: Fever, cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis (red eyes), and the Koplik's spots (small white spots inside the mouth) precede the characteristic measles rash. The rash typically starts on the face and spreads downwards.
- Seeking Medical Attention: If you suspect measles, it is vital to seek immediate medical attention for diagnosis and appropriate management.
- Diagnostic Tests: Blood tests can confirm a measles diagnosis by detecting measles-specific antibodies.
- Treatment: Treatment is primarily supportive, focusing on managing symptoms like fever and cough. Hospitalization may be necessary for severe cases.
- Potential Complications: Severe complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis (brain inflammation), can occur, particularly in young children or immunocompromised individuals.
Prevention and Control Measures for the Measles Outbreak
The most effective way to prevent measles is through vaccination with the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine. Public health initiatives play a crucial role in promoting vaccination and controlling outbreaks.
- MMR Vaccine Efficacy: The MMR vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles, significantly reducing the risk of infection and severe complications.
- Recommended Vaccination Schedule: The recommended schedule involves two doses of the MMR vaccine, typically administered in childhood. Adults who are unsure of their vaccination status should consult their healthcare provider.
- Public Health Campaigns: Effective public health campaigns are vital to increase awareness, address vaccine hesitancy, and encourage vaccination.
- Preventive Measures: While vaccination is the primary prevention strategy, avoiding close contact with infected individuals and practicing good hand hygiene can also help to reduce the risk of infection.
Conclusion
The rising number of measles cases in the U.S. underscores the urgent need for increased vaccination rates and robust public health interventions. The geographic spread of the measles outbreak highlights the vulnerability of communities with low vaccination coverage. Vaccine hesitancy fueled by misinformation poses a significant challenge, requiring proactive efforts to disseminate accurate information and address concerns. To curb this resurgence and protect public health, we must prioritize measles vaccination and strengthen public health initiatives. Consult your healthcare provider to ensure you and your family are properly vaccinated against measles. Combat misinformation and advocate for evidence-based decisions concerning this preventable disease. Collective action is crucial to controlling this measles outbreak and protecting the health of our communities.

Featured Posts
-
 National Weather Service Simplifies Heat Alerts Easier Warnings For Safer Summers
May 30, 2025
National Weather Service Simplifies Heat Alerts Easier Warnings For Safer Summers
May 30, 2025 -
 Cyberpunk 2077s Future Cd Projekt Reds Next Steps
May 30, 2025
Cyberpunk 2077s Future Cd Projekt Reds Next Steps
May 30, 2025 -
 The Hottest Air Jordans Dropping In May 2025
May 30, 2025
The Hottest Air Jordans Dropping In May 2025
May 30, 2025 -
 Hondas Winning Motorcycles A Magnet For Top Talent
May 30, 2025
Hondas Winning Motorcycles A Magnet For Top Talent
May 30, 2025 -
 Bells Ai Data Centre Expansion Six New Facilities In British Columbia
May 30, 2025
Bells Ai Data Centre Expansion Six New Facilities In British Columbia
May 30, 2025
