New Study: PFAS Contamination Impacts Almost 100 Million Americans' Drinking Water
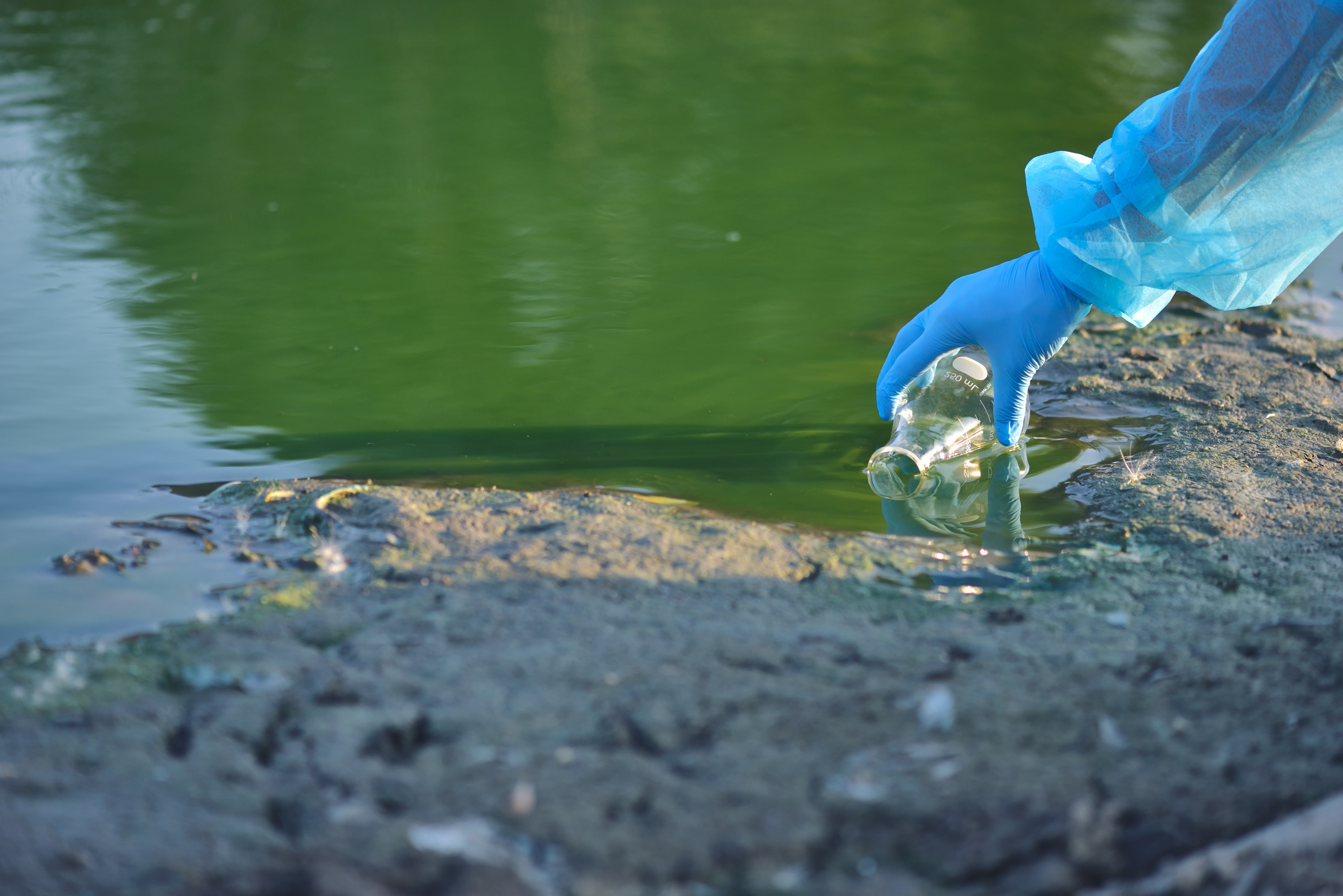

Table of Contents
The Extent of PFAS Contamination Across the US
The geographical distribution of PFAS contamination in the US is alarming. Interactive maps, compiled from various government and independent studies, paint a concerning picture. Areas with historically high levels of industrial activity, particularly those involving manufacturing of non-stick cookware, firefighting foam, and other PFAS-containing products, show significantly higher concentrations of these dangerous chemicals in their water supplies. States like Michigan, New Hampshire, and California have emerged as hotspots, though contamination is far more widespread.
- Specific examples of affected regions and populations: Communities near military bases (where firefighting foam is frequently used) and industrial sites are disproportionately impacted. Low-income communities and communities of color often bear the brunt of this environmental injustice.
- Statistics on the number of water systems affected: The study suggests that thousands of public water systems across the country are affected by PFAS contamination, leaving millions without access to clean drinking water.
- Mention of vulnerable populations disproportionately affected: Children, pregnant women, and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to the adverse health effects of PFAS exposure.
The sources of PFAS contamination are varied and complex. Industrial discharge from manufacturing plants represents a significant contributor. The widespread use of firefighting foam containing PFAS at airports and military bases has also led to substantial groundwater contamination. Improper disposal of PFAS-containing products adds to the overall pollution problem.
The Health Risks Associated with PFAS Exposure
PFAS chemicals are known as "forever chemicals" due to their persistence in the environment and the human body. Exposure to these substances is linked to a range of serious health problems. Studies have established correlations between PFAS exposure and:
- List key health problems linked to PFAS exposure: Liver cancer, kidney cancer, thyroid disease, immune deficiency, high cholesterol, and developmental delays in children.
- Mention studies supporting the health risks: Numerous epidemiological studies have demonstrated a strong link between PFAS exposure and the development of these health issues.
- Explain the challenges in diagnosing PFAS-related illnesses: The long latency period between exposure and the onset of symptoms makes diagnosis and treatment particularly challenging. The variety of PFAS chemicals and their differing toxicities add further complexity.
Different types of PFAS chemicals exhibit varying levels of toxicity. While research continues to uncover the precise mechanisms and long-term health effects, the overall consensus is that PFAS exposure carries substantial health risks. This makes addressing water contamination a pressing public health concern.
Current Regulations and Government Response to PFAS Contamination
Current federal and state regulations concerning PFAS in drinking water vary widely. The EPA has established health advisories, but enforceable standards are still lagging behind scientific evidence, leaving many communities vulnerable. Some states have implemented stricter regulations and initiated remediation projects, while others have yet to take significant action.
- EPA guidelines and regulations: The EPA's health advisories are non-enforceable, meaning water systems are not legally obligated to take action unless their levels exceed these guidelines.
- State-level regulations and actions: Several states have established their own, more stringent, drinking water standards for PFAS, and actively funding research and cleanup efforts.
- Funding for PFAS remediation projects: Federal funding for PFAS remediation has been inadequate to meet the scope of the problem.
- Legislative efforts to address the issue: Numerous legislative proposals have been introduced at the state and federal levels, advocating for stronger regulations and increased funding for remediation efforts.
The lack of comprehensive and uniform federal regulations hinders effective nationwide action. Gaps in enforcement and inconsistencies between state-level regulations make a coordinated response challenging. Further legislative action and increased funding are critical to address this issue effectively.
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies for PFAS Contamination
Several methods exist for removing or reducing PFAS from drinking water. Granular activated carbon (GAC) filtration and ion exchange are among the most widely used technologies.
- Explain different PFAS treatment technologies: Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), membrane filtration (reverse osmosis), and bioremediation are also being explored.
- Discuss the cost-effectiveness of each method: The cost-effectiveness of each method varies depending on the level of contamination and the scale of the project.
- Mention the role of water treatment plants: Upgrading water treatment plants to incorporate PFAS removal technologies is crucial to ensuring safe drinking water.
- Suggest ways individuals can protect themselves: Home water filtration systems can provide an additional layer of protection, although it is crucial to carefully select systems certified to remove PFAS.
Preventative measures are equally important. Stricter regulations on industrial discharge, safer alternatives to PFAS-containing products, and improved waste management practices can significantly reduce future contamination. Community-based monitoring and advocacy efforts also play a crucial role in raising awareness and holding responsible parties accountable.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against PFAS Contamination in Your Drinking Water
This new study underscores the urgent need to address PFAS contamination in our drinking water. The widespread impact on nearly 100 million Americans highlights the severity of this public health crisis and demands immediate, decisive action. We must strengthen regulations, increase funding for remediation projects, and implement preventative measures to protect our communities from the devastating effects of PFAS. Learn more about PFAS contamination in your community and demand action to protect your drinking water from these forever chemicals. Contact your elected officials, support environmental advocacy groups, and stay informed about the latest research and developments. Your health, and the health of future generations, depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 The Padres Resistance Challenging The Dodgers Blueprint For Success
May 16, 2025
The Padres Resistance Challenging The Dodgers Blueprint For Success
May 16, 2025 -
 Rossiya Atakovala Ukrainu Svyshe 200 Raket I Bespilotnikov
May 16, 2025
Rossiya Atakovala Ukrainu Svyshe 200 Raket I Bespilotnikov
May 16, 2025 -
 Nhl 25 The Arcade Mode Comeback
May 16, 2025
Nhl 25 The Arcade Mode Comeback
May 16, 2025 -
 Dwyane Wade Comments On Jimmy Butler Leaving The Miami Heat
May 16, 2025
Dwyane Wade Comments On Jimmy Butler Leaving The Miami Heat
May 16, 2025 -
 Daniels Injury A Turning Point In San Jose Earthquakes Vs Lafc Match
May 16, 2025
Daniels Injury A Turning Point In San Jose Earthquakes Vs Lafc Match
May 16, 2025
