OECD Economic Outlook: Canada To See Stagnant Growth In 2025
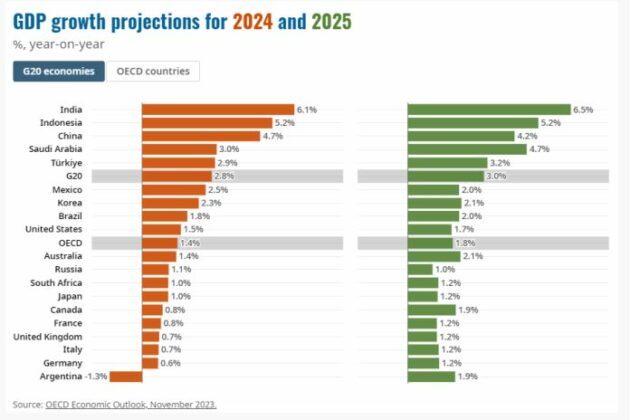
Table of Contents
Key Findings from the OECD Economic Outlook Report
The OECD's forecast paints a picture of significantly reduced economic expansion for Canada in 2025. The report highlights a period of stagnant growth, characterized by a substantial deceleration compared to previous years. While the exact figures vary depending on the specific metrics used, the overall message is clear: Canada is facing a period of significantly slower economic growth.
- GDP Growth Projection: The OECD projects a GDP growth rate of [Insert specific percentage from the report, e.g., 1%] for 2025, a sharp decline from [Insert previous year's growth rate, e.g., 3%]. This represents a considerable slowdown compared to recent years' performance.
- Regional Variations: The report may also indicate regional disparities in growth, with some provinces experiencing more pronounced slowdowns than others. [Insert details on regional variations if available in the report, specifying affected provinces and their projected growth rates].
- Data Points: The OECD’s prediction is supported by various indicators, including weakening consumer confidence, reduced business investment, and a softening housing market. These factors collectively point towards a period of sluggish economic activity.
Factors Contributing to Canada's Stagnant Growth in 2025
Several interconnected macroeconomic factors contribute to the OECD's prediction of stagnant growth in 2025 for the Canadian economy. These challenges represent a complex interplay of global and domestic forces.
- Global Economic Slowdown: The global economy faces headwinds, including geopolitical uncertainty and persistent inflation. This negatively impacts Canadian exports and reduces overall demand for Canadian goods and services.
- Example: Reduced demand for Canadian commodities from key trading partners could significantly impact resource-dependent provinces.
- Inflation and Interest Rate Hikes: Persistent inflation has forced central banks, including the Bank of Canada, to implement aggressive interest rate hikes. This increases borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, dampening investment and spending.
- Example: Higher mortgage rates are contributing to a correction in the housing market, a significant driver of economic activity.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Lingering supply chain bottlenecks continue to constrain production and increase input costs for businesses, impacting their profitability and investment decisions.
- Example: Delays in receiving essential components can lead to production slowdowns in various manufacturing sectors.
- Housing Market Correction: The rapid appreciation in housing prices in recent years is correcting, leading to reduced construction activity and impacting consumer wealth.
- Example: A decline in housing investment can have a knock-on effect on related industries, such as furniture and appliance manufacturing.
Potential Implications of Stagnant Growth for the Canadian Economy
The projected stagnant growth carries significant implications for various aspects of the Canadian economy. Addressing these potential consequences proactively is crucial for mitigating negative impacts.
- Employment: Slower economic growth could translate into reduced job creation and potentially even job losses in certain sectors. This could lead to increased unemployment and a decline in overall labor market participation.
- Example: Industries sensitive to economic downturns, such as construction and retail, might experience layoffs.
- Government Revenue: Stagnant growth will likely reduce government tax revenues, potentially impacting the government’s ability to fund crucial social programs and public services.
- Example: Reduced corporate tax revenue might necessitate cuts in government spending or increased borrowing.
- Social Inequality: The impact of stagnant growth might disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, potentially exacerbating existing social and economic inequalities.
- Example: Low-income families might face greater difficulties in affording essential goods and services.
- Investment and Business Confidence: Uncertainty surrounding economic prospects can lead to decreased business investment and a decline in overall business confidence, hindering long-term economic growth.
- Example: Businesses might postpone expansion plans or delay hiring decisions in the face of uncertainty.
Government Policy Responses and Mitigation Strategies
The Canadian government will need to implement effective policy measures to address the potential for stagnant growth and mitigate its negative consequences. A multi-pronged approach is likely necessary.
- Fiscal Stimulus: Targeted fiscal stimulus measures, such as infrastructure investments or tax credits for businesses, could help boost economic activity and create jobs.
- Example: Investing in green technology could stimulate innovation and create employment opportunities.
- Monetary Policy Adjustments: The Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions will play a crucial role in managing inflation and supporting economic growth. Carefully calibrated interest rate adjustments are essential.
- Investment in Growth Sectors: Government investment in key growth sectors, such as clean technology, digital infrastructure, and advanced manufacturing, could create jobs and enhance long-term economic competitiveness.
- Business Support Programs: Targeted support programs for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), can help them navigate economic headwinds and maintain employment.
Understanding Canada's Economic Slowdown and Looking Ahead
The OECD's prediction of stagnant growth in 2025 for Canada highlights the challenges facing the Canadian economy. This slowdown is driven by a complex interplay of global and domestic factors, including global economic weakness, inflation, supply chain disruptions, and a housing market correction. The potential implications are significant, ranging from reduced job creation and decreased government revenue to increased social inequality and diminished business confidence. Addressing these challenges will require a well-coordinated response from the government, involving fiscal and monetary policy adjustments, investments in growth-stimulating sectors, and targeted support for businesses. Stay informed about future updates on Canada's economic outlook and potential shifts in stagnant growth predictions by following [link to OECD or relevant source].

Featured Posts
-
 Italian Open Surprise Jannik Sinners Day Off Meeting With Pope Leo Xiv
May 28, 2025
Italian Open Surprise Jannik Sinners Day Off Meeting With Pope Leo Xiv
May 28, 2025 -
 Recent Photos Of Bianca Censori Public Reaction And Discussion
May 28, 2025
Recent Photos Of Bianca Censori Public Reaction And Discussion
May 28, 2025 -
 American Music Awards K Pops Strong Showing With Rose Rm Jimin Ateez And Stray Kids
May 28, 2025
American Music Awards K Pops Strong Showing With Rose Rm Jimin Ateez And Stray Kids
May 28, 2025 -
 Ajaxs 99th Minute Collapse A Tale Of Nine Points Lost
May 28, 2025
Ajaxs 99th Minute Collapse A Tale Of Nine Points Lost
May 28, 2025 -
 Diamondbacks Vs Dodgers A Comprehensive Game Prediction And Betting Odds
May 28, 2025
Diamondbacks Vs Dodgers A Comprehensive Game Prediction And Betting Odds
May 28, 2025
