PFAS Contamination In Blue Mountains Reservoir: Health Concerns Raised
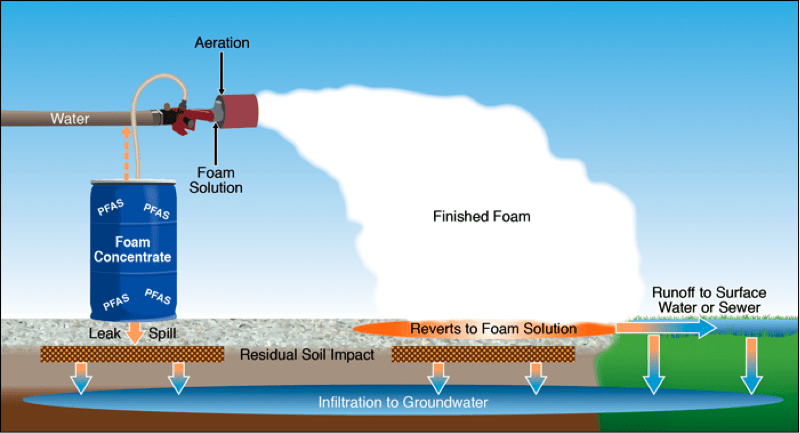
Table of Contents
Understanding PFAS Contamination
What are PFAS?
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a large group of synthetic chemicals characterized by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, making them incredibly stable and resistant to degradation. This "forever chemical" characteristic leads to their persistence in the environment, accumulating in soil, water, and even our bodies over time. Their widespread use in numerous industrial and consumer products, including non-stick cookware, firefighting foam, and food packaging, has contributed to their global presence and environmental contamination.
Sources of PFAS Contamination in the Blue Mountains Reservoir
Identifying the precise sources of PFAS contamination in the Blue Mountains Reservoir is crucial for effective remediation. Several potential pathways are currently under investigation:
- Industrial Discharge: Nearby industrial facilities using PFAS-containing processes or disposing of PFAS-laden waste could be significant contributors. Further investigation is needed to pinpoint specific facilities and assess their contribution to the contamination.
- Firefighting Foam Runoff: Airports and military bases frequently utilize aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF), which contains high concentrations of PFAS. Runoff from these sites can easily contaminate nearby water bodies, as seen in numerous cases worldwide.
- Agricultural Runoff: The use of PFAS-containing products in agriculture, such as some pesticides and soil treatments, can lead to soil contamination and subsequent runoff into water systems like the Blue Mountains Reservoir.
- Wastewater Treatment Plant Discharge: While many plants are upgrading to remove PFAS, some older facilities may still discharge PFAS into receiving waterways. This requires investigation to determine if this is a significant source of contamination for the reservoir.
Health Risks Associated with PFAS Exposure
Exposure to PFAS is linked to a wide range of adverse health effects, posing a significant threat to public health. The severity of these effects depends on factors such as the level and duration of exposure. Research suggests a strong association between PFAS exposure and:
- Increased risk of several cancers: Including kidney, testicular, and liver cancers.
- Immune system dysfunction: Leading to increased susceptibility to infections.
- Thyroid disorders: Affecting hormone production and regulation.
- Developmental effects in children: Including lower birth weights and developmental delays.
- Liver damage: PFAS accumulation can impair liver function and lead to chronic diseases.
The Impact on the Blue Mountains Community
Water Supply Concerns
The PFAS contamination of the Blue Mountains Reservoir directly impacts the drinking water supply for a significant portion of the community. The long-term health consequences of ingesting PFAS-contaminated water are a major concern, prompting fears and anxieties among residents. The need for transparency and timely communication from authorities is paramount to address these concerns effectively.
Economic Impact
Beyond the health concerns, the PFAS contamination poses a severe economic threat to the Blue Mountains region. The potential impacts include:
- Decreased property values: The stigma associated with PFAS contamination can significantly reduce property values, impacting residents' financial well-being.
- Reduced tourism: Negative publicity surrounding the contamination can deter tourists, negatively affecting local businesses and the overall economy.
- Increased healthcare costs: The potential rise in health problems linked to PFAS exposure will likely result in increased healthcare costs for individuals and the public health system.
Community Response and Advocacy
The community's response has been swift and decisive, demonstrating a strong commitment to protecting their water source and their health. Residents are actively engaged in advocacy efforts, demanding:
- Transparent and accurate information from authorities regarding the extent of the contamination and remediation plans.
- Increased funding for testing and remediation efforts.
- Stricter regulations on the use and disposal of PFAS-containing products.
- Increased public awareness campaigns about PFAS and the associated health risks.
Ongoing Investigations and Remediation Efforts
Government Response and Testing
Government agencies are actively involved in investigating the extent of the PFAS contamination, identifying sources, and developing remediation strategies. Comprehensive water testing is crucial to accurately assess the levels of PFAS throughout the reservoir and identify the most affected areas.
Remediation Technologies
Various remediation technologies exist for removing or reducing PFAS levels in water, including:
- Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) filtration: A common and effective method for removing PFAS from water.
- Ion exchange: A process that uses resins to selectively remove PFAS from the water.
- Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs): Methods that utilize strong oxidants to break down PFAS molecules.
The selection of appropriate technology will depend on several factors, including the level of contamination, cost-effectiveness, and the specific characteristics of the water source.
Long-term Monitoring Plans
Continuous monitoring of PFAS levels is critical to assess the long-term effectiveness of remediation efforts and ensure the ongoing safety of the drinking water supply. Regular testing and data analysis will provide valuable information to guide future actions and protect public health.
Conclusion
The PFAS contamination in the Blue Mountains Reservoir poses a significant and ongoing threat to public health and the local economy. Addressing this issue demands a multi-faceted approach, encompassing thorough investigation, rapid implementation of effective remediation strategies, transparent communication with the community, and long-term monitoring. Securing a safe and reliable supply of PFAS-free water is paramount. We must demand accountability from authorities and actively participate in community efforts to protect our water resources and safeguard public health. Let's work together to ensure the Blue Mountains community has access to clean, safe drinking water for generations to come. Demand action for PFAS-free water in the Blue Mountains!

Featured Posts
-
 Andor Season 2 Trailer The Long Wait And Growing Fan Theories
May 16, 2025
Andor Season 2 Trailer The Long Wait And Growing Fan Theories
May 16, 2025 -
 Election 2024 A Deep Dive Into Albanese And Duttons Campaign Platforms
May 16, 2025
Election 2024 A Deep Dive Into Albanese And Duttons Campaign Platforms
May 16, 2025 -
 Foot Locker Headquarters Move Confirmed St Petersburg Lease Details
May 16, 2025
Foot Locker Headquarters Move Confirmed St Petersburg Lease Details
May 16, 2025 -
 Watch 3 Free Star Wars Andor Episodes On You Tube Now
May 16, 2025
Watch 3 Free Star Wars Andor Episodes On You Tube Now
May 16, 2025 -
 Tom Cruise Still Owes Tom Hanks 1 The Story Behind The Unpaid Acting Fee
May 16, 2025
Tom Cruise Still Owes Tom Hanks 1 The Story Behind The Unpaid Acting Fee
May 16, 2025
