Record Forest Loss: Wildfires Drive Unprecedented Global Destruction
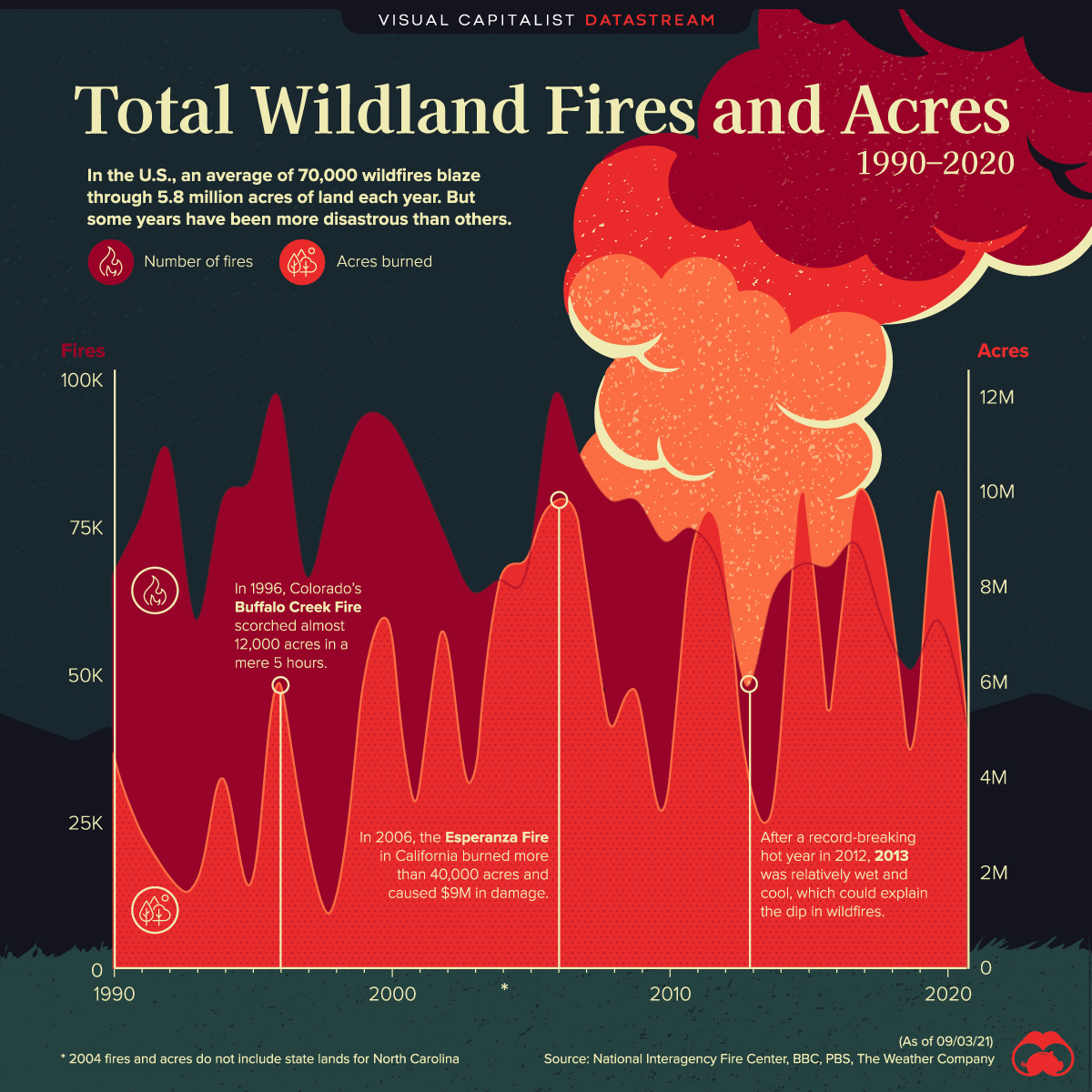
Table of Contents
The Unprecedented Scale of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
Statistics and Data
The sheer scale of forest loss due to wildfires is alarming. Recent years have witnessed a dramatic surge in the frequency and intensity of these catastrophic events, resulting in the destruction of millions of hectares of vital forest ecosystems. Data from the Global Forest Watch, among other organizations, reveals a stark reality:
- Amazon Rainforest: The Amazon, the world's largest rainforest, has experienced record-breaking wildfire seasons in recent years, losing millions of hectares of irreplaceable habitat. For example, in 2019, a surge in deforestation and forest fires resulted in a substantial loss of forest cover. (Source: [Insert credible source, e.g., Global Forest Watch])
- Australia: The devastating 2019-2020 Australian bushfires scorched an area larger than the size of some European countries, destroying vast tracts of eucalyptus forests and causing significant biodiversity loss. (Source: [Insert credible source])
- California, USA: California has experienced increasingly severe wildfire seasons, with megafires becoming more common, resulting in extensive forest loss and significant property damage. (Source: [Insert credible source, e.g., Cal Fire])
- Siberia: Vast areas of boreal forests in Siberia have been affected by increasingly frequent and intense wildfires, contributing significantly to global carbon emissions. (Source: [Insert credible source])
The increase in the frequency and intensity of these wildfires compared to previous decades is undeniable, highlighting a rapidly worsening situation. Analysis shows a clear upward trend, indicating a need for immediate and decisive action to address the root causes.
Geographic Distribution of Forest Loss
The geographic distribution of wildfire-driven forest loss is uneven, with certain regions disproportionately affected. Areas with a combination of factors, such as drought, high temperatures, and poor forest management practices, are particularly vulnerable.
- Mediterranean regions: Countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, including parts of Spain, Greece, Italy, and Turkey, are highly susceptible to intense wildfires due to hot, dry summers and increased human activity in forested areas.
- Boreal forests: The vast boreal forests of Canada, Russia, and Alaska face significant risks due to climate change-induced warming and increasingly dry conditions.
- Tropical rainforests: Tropical rainforests, including the Amazon and parts of Southeast Asia, are vulnerable to wildfires exacerbated by deforestation and land-clearing activities.
Specific forest types, such as those characterized by dense undergrowth or susceptible species, are disproportionately affected, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
Underlying Causes of Increased Wildfire Activity
Climate Change and its Impact
Climate change is a primary driver of increased wildfire activity. Rising global temperatures lead to:
- Drier conditions: Longer and more intense droughts create ideal conditions for the spread of wildfires, leaving vegetation highly flammable.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer temperatures extend the fire season, providing more opportunities for fires to ignite and spread.
- Increased wildfire intensity: Higher temperatures and drier conditions lead to more intense and rapid fire spread, making them harder to contain.
- Extreme weather events: Climate change increases the frequency and severity of extreme weather events like heatwaves and lightning storms, which can trigger wildfires.
Human Activities and Deforestation
Human activities significantly contribute to increased wildfire risk:
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, and urbanization removes natural barriers to fire spread and creates more flammable landscapes.
- Poor forest management: Inadequate forest management practices, such as the accumulation of flammable debris, increase the risk and severity of wildfires.
- Human-caused ignitions: Accidental and intentional human-caused ignitions, such as discarded cigarettes, campfires, and arson, are a major source of wildfires.
Consequences of Record Forest Loss
Biodiversity Loss and Extinction
Wildfires cause devastating biodiversity loss. The destruction of habitats leads to:
- Species extinction: Many plant and animal species are unable to survive the destruction of their habitats, leading to population declines and potential extinction.
- Disruption of ecosystems: The loss of forests disrupts intricate ecological relationships, impacting the entire ecosystem's balance and functioning.
Climate Change Amplification
Widespread forest loss exacerbates climate change through:
- Reduced carbon sequestration: Forests act as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Their destruction reduces the planet's ability to absorb greenhouse gases.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions: Wildfires release vast amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere, further contributing to global warming.
Economic and Social Impacts
Record forest loss has significant economic and social consequences:
- Economic losses: Wildfires cause billions of dollars in damage to property, infrastructure, and the tourism industry.
- Loss of livelihoods: Communities that depend on forests for their livelihoods, such as indigenous populations and those employed in forestry, are severely impacted.
- Displacement: Wildfires can force people to evacuate their homes, leading to displacement and disruption of their lives.
Conclusion
The unprecedented levels of forest loss due to increasingly frequent and intense wildfires represent a clear and present danger to our planet. Driven by a combination of climate change and human activities, this crisis has far-reaching consequences for biodiversity, climate stability, and human societies. We are witnessing global destruction on a scale never before seen. We must act now to combat record forest loss. Learn more about how you can help protect our forests from wildfires and support initiatives aimed at combating climate change and promoting sustainable forest management. Support organizations dedicated to wildfire prevention and forest conservation. Every effort, from individual actions to large-scale policy changes, contributes to mitigating the devastating impacts of record forest loss and safeguarding the future of our planet.

Featured Posts
-
 Amsterdam Stock Exchange Suffers Third Consecutive Major Loss Down 11 Since Wednesday
May 25, 2025
Amsterdam Stock Exchange Suffers Third Consecutive Major Loss Down 11 Since Wednesday
May 25, 2025 -
 Alcaraz And Sabalenka Triumphant In Italian Open Debut
May 25, 2025
Alcaraz And Sabalenka Triumphant In Italian Open Debut
May 25, 2025 -
 How To Get Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 Tickets Full Line Up And Booking Guide
May 25, 2025
How To Get Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 Tickets Full Line Up And Booking Guide
May 25, 2025 -
 Musk Zuckerberg Bezos La Classifica Forbes Degli Uomini Piu Ricchi Del 2025
May 25, 2025
Musk Zuckerberg Bezos La Classifica Forbes Degli Uomini Piu Ricchi Del 2025
May 25, 2025 -
 U S Tariff Suspension Euronext Amsterdam Stocks Up 8
May 25, 2025
U S Tariff Suspension Euronext Amsterdam Stocks Up 8
May 25, 2025
