Rising COVID-19 Infections: Investigating The Potential Of A New Variant

Table of Contents
The Current Epidemiological Situation
Global Infection Trends
Recent weeks have witnessed a noticeable uptick in COVID-19 cases across various regions. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports a significant increase in several countries, including a 30% rise in reported cases in the European region within the last month (Source: Insert citation from WHO website). Other regions are also experiencing increases, although the rate of increase varies.
- Europe: Several European nations are seeing a resurgence, particularly in [Specific Country Examples with citation].
- North America: [Specific Country Examples with citation showing infection rate increases].
- Asia: [Specific Country Examples with citation showing infection rate increases].
These increases aren't uniformly distributed, suggesting potential localized factors or the emergence of a variant better adapted to certain populations. The patterns observed warrant further investigation to identify contributing factors.
Severity of Current Infections
While infection rates are rising, the severity of the illness remains a crucial aspect to monitor. Initial data suggests a potential disconnect between case numbers and hospitalizations/deaths (Source: Insert citation from CDC or reputable medical journal). However, more data is needed to definitively assess whether the new infections are milder than previous waves.
- Hospitalization rates: [Insert data on hospitalization rates, comparing to previous waves].
- Mortality rates: [Insert data on mortality rates, comparing to previous waves].
- Healthcare system impact: The potential strain on healthcare systems remains a concern, even if the individual severity is lower. Increased cases can still lead to overwhelmed hospitals and a reduction in the quality of care.
Age Demographics and Risk Factors
The age groups most affected by this recent surge appear to be [Insert data on age demographics from reliable sources]. While older individuals remain vulnerable, it is essential to analyze whether younger age groups are experiencing a disproportionate increase in infections, hospitalizations, or severe illness.
- Age-related infection rates: [Insert data on infection rates across various age groups].
- Risk factors: Further research is needed to determine if new risk factors are emerging or if pre-existing conditions remain the primary determinants of severe illness. Underlying health conditions like diabetes, heart disease and obesity are still key concerns.
Investigating Potential New Variants
Genetic Sequencing and Surveillance
Robust genomic surveillance is crucial to identify potential new COVID-19 variants. This involves collecting samples from infected individuals, sequencing their viral genomes, and analyzing the data to detect changes that may affect the virus's transmissibility, severity, or immune escape potential.
- Sequencing methods: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a widely used method to rapidly and accurately sequence viral genomes.
- International collaboration: The global sharing of genomic data through initiatives like GISAID is critical for effective variant tracking and response.
Characteristics of Potential New Variants
A new variant driving this recent surge might possess characteristics such as increased transmissibility, enabling it to spread more rapidly than previous strains. Alternatively, it could exhibit increased immune evasion capabilities, allowing it to bypass immunity from prior infection or vaccination. Changes in pathogenicity, leading to more or less severe illness, are also possibilities.
- Immune escape: This refers to the ability of a virus to evade the immune system's response. Mutations can alter the virus's surface proteins, making it harder for antibodies to recognize and neutralize it.
- Altered pathogenicity: A new variant might cause milder or more severe illness than previous strains. Changes in symptom presentation are also a possibility.
Research and Scientific Studies
Scientists worldwide are actively investigating the potential role of new variants in this latest surge. This research involves analyzing genomic data, studying the virus's behavior in the lab, and conducting epidemiological studies to assess its impact on populations.
- Scientific publications: Stay updated on peer-reviewed publications in reputable medical journals for the latest research findings (e.g., The Lancet, The New England Journal of Medicine, etc.).
- Ongoing collaboration: International collaborations are vital for sharing data, resources, and expertise to effectively respond to emerging threats.
Public Health Implications and Mitigation Strategies
The Importance of Vaccination and Boosters
Vaccination remains a cornerstone of our defense against COVID-19, including new variants. While no vaccine offers 100% protection, they significantly reduce the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Booster shots are crucial for maintaining high levels of immunity over time, particularly against emerging variants.
- Vaccine efficacy: Studies continue to evaluate the effectiveness of current vaccines against new variants.
- Reducing transmission: Vaccination not only protects individuals but also contributes to reducing overall virus transmission.
Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs)
Non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) play a crucial role in mitigating transmission. While their implementation may vary depending on local circumstances, maintaining good hygiene practices, mask-wearing, social distancing, and improving ventilation in indoor spaces remain essential.
- Effectiveness of NPIs: The effectiveness of NPIs can vary depending on factors like population density, compliance, and the variant's characteristics.
- Adaptable strategies: Public health strategies must remain adaptable to changing circumstances, such as the emergence of new variants or shifts in infection rates.
Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and access to effective treatments are crucial for minimizing the impact of COVID-19. Rapid diagnostic testing allows for timely identification and isolation of cases, reducing the spread of infection. Antiviral medications can help to reduce the severity and duration of illness in high-risk individuals.
- Antiviral medications: Several antiviral drugs have shown effectiveness against COVID-19, helping to reduce hospitalization and death rates.
- Testing and contact tracing: Maintaining robust testing and contact tracing systems is critical for early identification and isolation of cases.
Conclusion
The recent rise in COVID-19 infections highlights the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive measures. While the severity of the current infections may vary, the potential emergence of a new variant necessitates continued genomic surveillance, research, and robust public health strategies. Maintaining high vaccination rates, utilizing effective NPIs, and ensuring access to rapid testing and treatments remain crucial for managing the pandemic. Stay informed about the latest developments regarding rising COVID-19 infections from trusted sources like the WHO and CDC and follow their recommended guidelines to help protect yourself and your community. Vigilance and proactive measures are essential in mitigating the impact of COVID-19 outbreaks and reducing the spread of potential new variants.

Featured Posts
-
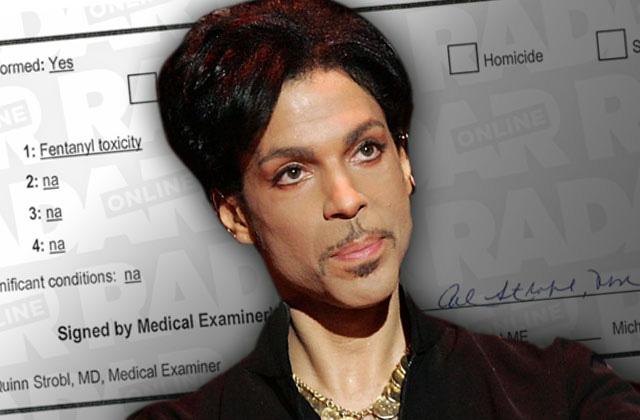 Princes Death Toxicology Report Reveals High Fentanyl Levels On March 26
May 31, 2025
Princes Death Toxicology Report Reveals High Fentanyl Levels On March 26
May 31, 2025 -
 2025 Cycle News Magazine Issue 12 Key Articles And Highlights
May 31, 2025
2025 Cycle News Magazine Issue 12 Key Articles And Highlights
May 31, 2025 -
 Essential Android Travel Apps My Top 10 Picks
May 31, 2025
Essential Android Travel Apps My Top 10 Picks
May 31, 2025 -
 Bmw Open 2025 Quarter Finals Zverev Vs Griekspoor Dominates Munich
May 31, 2025
Bmw Open 2025 Quarter Finals Zverev Vs Griekspoor Dominates Munich
May 31, 2025 -
 A Mysterious Banksy The Artworks Identity And Upcoming Auction
May 31, 2025
A Mysterious Banksy The Artworks Identity And Upcoming Auction
May 31, 2025
