Sea Level Rise: An Urgent Threat To Coastal Areas
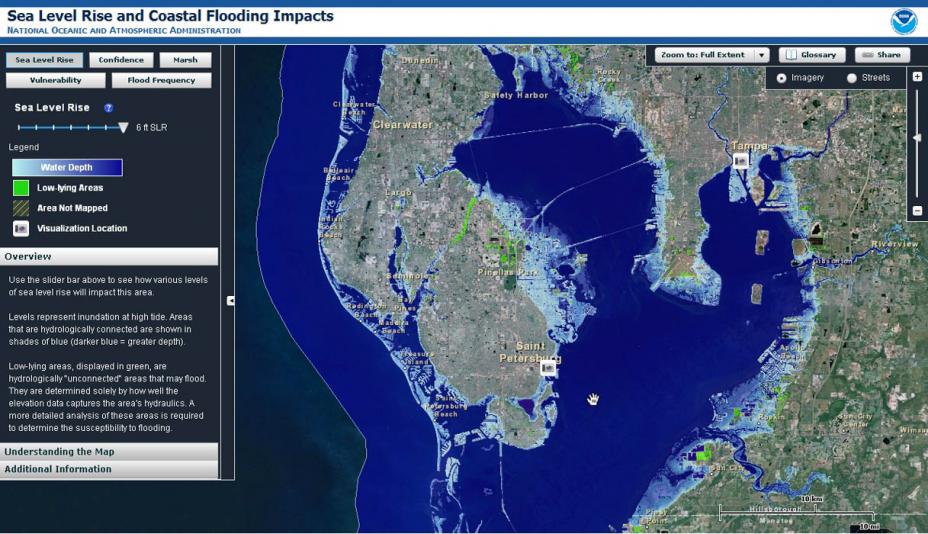
Table of Contents
Causes of Sea Level Rise
Several factors contribute to the alarming increase in global sea levels. These are primarily driven by climate change but also include human-induced factors.
Thermal Expansion
Warming ocean temperatures are a major driver of sea level rise through thermal expansion. As water heats up, it expands, occupying a larger volume and contributing to higher sea levels. This thermal expansion is directly linked to ocean warming, a consequence of increased greenhouse gas emissions.
- Studies show that thermal expansion accounts for a significant portion of observed sea level rise.
- The absorption of excess heat by the oceans is a critical factor in climate change, directly influencing thermal expansion.
- The relationship between greenhouse gas emissions, primarily CO2, and ocean temperature is well-established through scientific research.
Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets
The melting of glaciers and ice sheets, particularly in Greenland and Antarctica, significantly contributes to rising sea levels. Glacial melt and ice sheet melt release vast quantities of water into the oceans, leading to a substantial increase in global sea levels. The polar ice caps are particularly vulnerable to rising temperatures.
- The Greenland ice sheet is losing mass at an alarming rate, contributing significantly to sea level rise.
- The Antarctic ice sheet, while currently melting at a slower rate, holds the potential for catastrophic sea level rise if its melting accelerates.
- Accelerated ice melt due to rising global temperatures poses a major threat to coastal regions worldwide.
Groundwater Extraction
Human activities, such as excessive groundwater extraction, also contribute to apparent sea level rise. The removal of groundwater causes land subsidence, where the land sinks, leading to a relative increase in sea level. This groundwater depletion is particularly problematic in coastal areas.
- Over-extraction of groundwater for agriculture and urban use is a significant contributor to land subsidence in many coastal regions.
- The process of land subsidence, coupled with actual sea level rise, exacerbates the threat to coastal communities.
- Regions heavily reliant on groundwater, particularly those with high population densities, are particularly vulnerable to this phenomenon.
Impacts of Sea Level Rise on Coastal Areas
The consequences of rising sea levels are far-reaching and devastating, affecting coastal areas in numerous ways.
Coastal Erosion and Flooding
Rising sea levels are causing increased coastal erosion and more frequent and severe flooding. High tide flooding is becoming increasingly common, while storm surges are amplified by higher baseline sea levels.
- Many coastal communities are already experiencing significant erosion, leading to the loss of land and infrastructure.
- Increased flooding leads to property damage, displacement of residents, and disruption of economic activities.
- The economic and social costs of coastal erosion and flooding are substantial and are projected to increase dramatically in the coming decades.
Loss of Habitat and Biodiversity
Sea level rise significantly impacts coastal ecosystems and biodiversity. Habitat loss due to inundation and saltwater intrusion threatens numerous species and disrupts delicate ecological balances.
- Mangrove forests, salt marshes, and coral reefs are particularly vulnerable to sea level rise and saltwater intrusion.
- The loss of these vital habitats leads to a decline in biodiversity and impacts the overall health of coastal environments.
- Many coastal species are at risk of extinction due to habitat loss and changes in salinity.
Displacement and Migration
The human cost of sea level rise is substantial, leading to climate migration and the creation of climate refugees. Coastal communities are facing displacement as their homes and livelihoods are threatened.
- Low-lying island nations and coastal communities are particularly vulnerable to displacement due to sea level rise.
- The social and economic challenges associated with climate migration are significant, placing a strain on resources and infrastructure in receiving areas.
- The issue of climate displacement requires international cooperation and effective strategies for resettlement and support.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Addressing sea level rise requires a two-pronged approach: mitigating the causes and adapting to the inevitable impacts.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The most crucial step in addressing sea level rise is to drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This requires a global commitment to climate change mitigation and a transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is essential.
- Improving energy efficiency and adopting sustainable transportation systems are vital strategies.
- International cooperation and agreements are crucial for achieving global emission reduction targets.
Coastal Protection Measures
Protecting coastal areas from the impacts of sea level rise requires implementing various coastal protection measures. This includes building sea walls, developing other coastal defenses, and considering managed retreat in highly vulnerable areas.
- Sea walls offer a physical barrier against rising sea levels but can be expensive and have environmental drawbacks.
- Other coastal defense strategies include beach nourishment, dune restoration, and wetland creation.
- Managed retreat involves strategically relocating communities and infrastructure away from vulnerable areas.
Community Resilience and Adaptation
Building community resilience is crucial for adapting to the unavoidable impacts of sea level rise. This requires developing adaptation strategies, establishing early warning systems, and improving disaster preparedness.
- Investing in infrastructure that is resilient to sea level rise is crucial.
- Educating communities about the risks of sea level rise and empowering them to take action is vital.
- Developing effective early warning systems for floods and storm surges can save lives and minimize damage.
Conclusion
Sea level rise is a multifaceted problem with devastating consequences for coastal communities and ecosystems worldwide. Understanding the causes—thermal expansion, melting ice, and groundwater extraction—is key to addressing the impacts—coastal erosion, habitat loss, and displacement. The urgency demands immediate and concerted action. We must drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions through a global commitment to climate change mitigation and simultaneously implement adaptation strategies to protect vulnerable communities and ecosystems. Learn more about the threats of sea level rise and get involved in efforts to protect our coasts. Support initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and advocate for policies that protect coastal communities from the devastating effects of rising sea levels.

Featured Posts
-
 The Ethical Night Hunter Responsible Practices For Observing Nocturnal Animals
May 11, 2025
The Ethical Night Hunter Responsible Practices For Observing Nocturnal Animals
May 11, 2025 -
 A Verdadeira Historia Por Tras Da Adaptacao Em Quadrinhos De Sylvester Stallone
May 11, 2025
A Verdadeira Historia Por Tras Da Adaptacao Em Quadrinhos De Sylvester Stallone
May 11, 2025 -
 Tensions Flare Belal Muhammad And Jack Della Maddalena At Ufc 315
May 11, 2025
Tensions Flare Belal Muhammad And Jack Della Maddalena At Ufc 315
May 11, 2025 -
 The Untold Story Tom Cruises Response To Suri Cruises Arrival
May 11, 2025
The Untold Story Tom Cruises Response To Suri Cruises Arrival
May 11, 2025 -
 Ines Reg Eliminee De Dals La Polemique Autour De La Trop Grande Ouverture
May 11, 2025
Ines Reg Eliminee De Dals La Polemique Autour De La Trop Grande Ouverture
May 11, 2025
