Seagrass Planting Projects: Restoring Scotland's Coastline
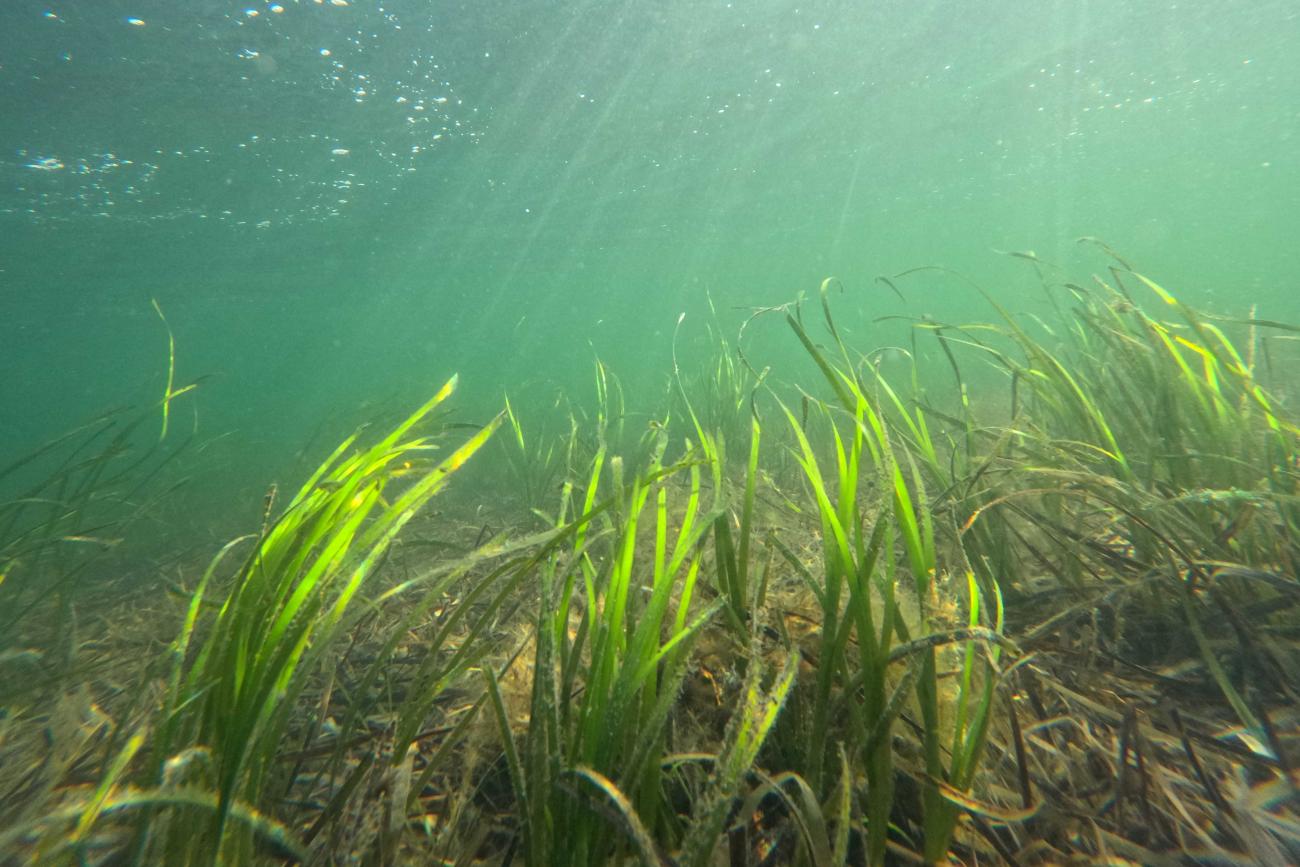

Table of Contents
The Ecological Importance of Seagrass Meadows in Scotland
Seagrass meadows are often referred to as the "lungs of the ocean," and for good reason. Their ecological importance is multifaceted and crucial for maintaining a healthy marine environment.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Scottish seagrass beds teem with life, acting as vital nurseries for commercially important fish species. Cod, haddock, and various flatfish species rely on these meadows for shelter and food during their juvenile stages. Invertebrates, such as shrimp, crabs, and worms, thrive in the seagrass, forming the base of the food web. Seabirds and marine mammals, including seals and dolphins, also depend on the rich biodiversity supported by these underwater forests.
- Specific examples: Common species found in Scottish seagrass meadows include the common shrimp (Crangon crangon), various crab species, and juvenile stages of commercially important fish like cod (Gadus morhua) and haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus).
- Food chain role: Seagrass itself provides food and habitat for many herbivores, which in turn become prey for larger predators, creating a complex and interconnected food web.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
Seagrass meadows are incredibly efficient at absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, making them powerful allies in the fight against climate change. This process, known as "blue carbon" sequestration, is significantly more efficient than that of terrestrial forests. Seagrass can capture and store carbon at a rate up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests.
- Quantifying carbon sequestration: Studies have shown that seagrass meadows in Scotland sequester considerable amounts of carbon per hectare annually, contributing to global carbon sinks.
- Blue carbon sequestration process: Seagrass absorbs CO2 through photosynthesis. Dead seagrass leaves and other organic matter settle on the seabed, where they are buried in the sediment, effectively locking away the carbon for centuries.
Coastal Protection
The dense root systems of seagrass meadows act as natural barriers, significantly reducing coastal erosion and mitigating the effects of storm damage. By stabilizing sediments and dissipating wave energy, seagrass protects shorelines, preventing land loss and protecting coastal communities.
- Examples of coastal erosion: Many areas of the Scottish coastline are vulnerable to erosion, and seagrass loss exacerbates this problem.
- Wave energy reduction: Seagrass meadows act as a natural breakwater, reducing the impact of waves on the coastline and protecting coastal infrastructure.
Current Seagrass Planting Projects in Scotland
Several dedicated organizations and initiatives are actively involved in seagrass restoration projects across Scotland’s coastline. These projects vary in scale and approach but share a common goal: to restore these vital ecosystems.
Project Locations and Scales
Seagrass planting efforts are underway in various locations across Scotland, including the Firth of Clyde, the Solway Firth, and other estuaries and bays. Organizations such as [mention specific organizations involved, e.g., Marine Conservation Society, local universities, etc.] are leading these initiatives.
- Specific projects: [List specific projects with locations, e.g., "The Loch Ryan Seagrass Restoration Project," "The Firth of Clyde Seagrass Initiative"].
- Project scale: These projects range in scale, from small-scale pilot projects to larger-scale restoration efforts covering several hectares.
Planting Techniques and Methods
A variety of techniques are employed for seagrass planting, including seed dispersal and transplanting of existing seagrass shoots. The choice of method depends on factors such as the site conditions, the availability of seeds or shoots, and the project's overall goals.
- Different planting techniques: Seed dispersal involves broadcasting seagrass seeds onto the seabed, while transplanting involves carefully relocating existing seagrass shoots to new areas.
- Monitoring and challenges: Successful seagrass restoration requires careful monitoring of planted areas to track growth, survival rates, and overall ecosystem development. Challenges include selecting suitable planting sites, managing environmental conditions, and preventing grazing by herbivores.
Funding and Partnerships
Seagrass restoration projects rely on a combination of funding sources, including government grants, private donations, and corporate sponsorships. These initiatives often involve collaborative partnerships between governmental agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and local communities.
- Key funding bodies: [Mention specific funding bodies, e.g., NatureScot, The Crown Estate].
- Community involvement: Community participation is crucial for the success of these projects, providing valuable volunteer support and increasing local awareness.
The Future of Seagrass Restoration in Scotland
The long-term success of seagrass restoration hinges on continued monitoring, research, community engagement, and supportive policies.
Long-Term Monitoring and Research
Ongoing monitoring is essential to evaluate the effectiveness of planting efforts, identify challenges, and adapt restoration strategies. Research into seagrass resilience and adaptation to climate change is vital for ensuring the long-term survival of these ecosystems.
- Long-term data collection: Consistent monitoring provides valuable data on seagrass growth, survival, and the overall health of the restored ecosystems.
- Scientific research: Research plays a crucial role in improving planting techniques, understanding the impacts of climate change on seagrass, and developing effective conservation strategies.
Community Engagement and Education
Raising public awareness about the importance of seagrass meadows and engaging local communities in restoration efforts is paramount. Educational outreach programs can play a significant role in promoting stewardship of these valuable ecosystems.
- Educational outreach: Workshops, educational materials, and citizen science initiatives can help engage communities in seagrass conservation.
- Volunteer opportunities: Volunteer participation in planting and monitoring activities is invaluable for the success of seagrass restoration projects.
Policy and Regulations
Strong governmental policies and regulations are vital for protecting existing seagrass meadows and fostering a supportive environment for restoration projects. This includes measures to reduce pollution, control destructive fishing practices, and promote sustainable coastal management.
- Environmental protection laws: Existing environmental regulations can be strengthened to better protect seagrass habitats.
- Policy frameworks: Developing robust policy frameworks can help ensure the long-term success of seagrass restoration and conservation efforts.
Conclusion
Seagrass planting projects are crucial for restoring Scotland's coastline and safeguarding its rich marine biodiversity. These initiatives not only protect valuable ecosystems but also contribute significantly to climate change mitigation and coastal resilience. By supporting and participating in seagrass planting projects, we can help ensure a healthy and thriving marine environment for future generations. Learn more about how you can get involved in seagrass restoration efforts in Scotland today! Find local organizations and volunteer opportunities near you to contribute to these crucial environmental initiatives. Let's work together to protect our precious seagrass meadows!

Featured Posts
-
 Kentucky Derby 2025 Your Guide To Online Streaming Pricing And Availability
May 04, 2025
Kentucky Derby 2025 Your Guide To Online Streaming Pricing And Availability
May 04, 2025 -
 Ufc Fight Night Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Betting Odds And Fight Predictions
May 04, 2025
Ufc Fight Night Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Betting Odds And Fight Predictions
May 04, 2025 -
 Lindsey Buckingham And Mick Fleetwoods Reunion What It Means For Fleetwood Mac
May 04, 2025
Lindsey Buckingham And Mick Fleetwoods Reunion What It Means For Fleetwood Mac
May 04, 2025 -
 Jet Zeros Triangular Jet On Track For 2027 Flight
May 04, 2025
Jet Zeros Triangular Jet On Track For 2027 Flight
May 04, 2025 -
 Canelo Vs Ggg How To Watch The Live Stream And Get Real Time Updates
May 04, 2025
Canelo Vs Ggg How To Watch The Live Stream And Get Real Time Updates
May 04, 2025
