The Great Decoupling: Its Impact On Global Supply Chains
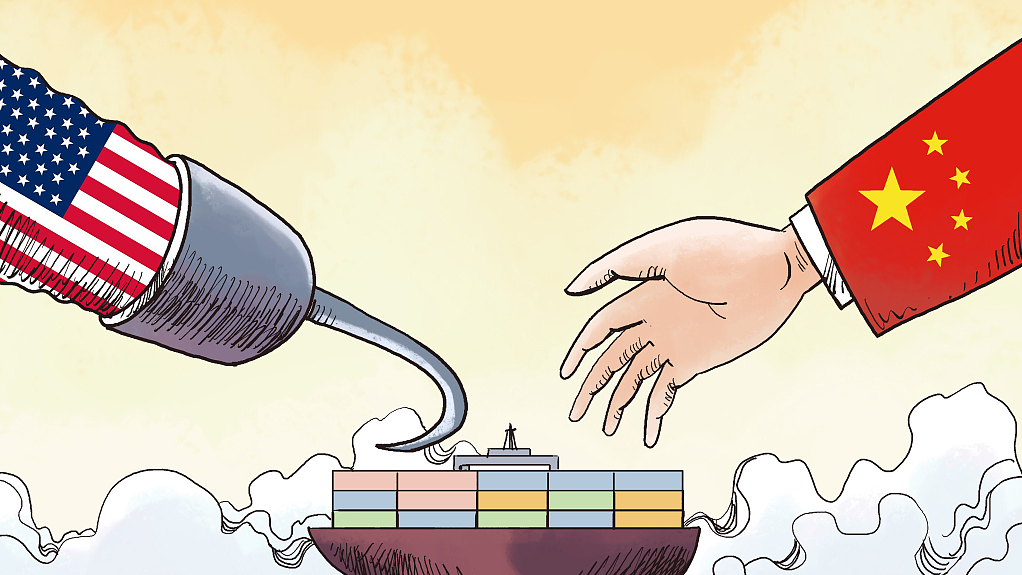
Table of Contents
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Wars Fueling the Decoupling
The escalating tensions between major global powers, most notably the US-China trade war, are primary catalysts for the Great Decoupling. Increased geopolitical uncertainty, fueled by trade protectionism and the imposition of sanctions, has forced nations to reassess their reliance on globally dispersed supply chains. The desire for greater economic self-sufficiency and reduced dependence on potentially adversarial nations is a powerful driving force behind this shift.
- Increased tariffs and trade barriers: The imposition of tariffs and other trade barriers significantly disrupts established supply chains, forcing companies to re-evaluate sourcing strategies and potentially incur higher costs.
- Sanctions against specific countries: Sanctions, often used as a geopolitical tool, immediately impact supply chains reliant on sanctioned nations, leading to urgent searches for alternative suppliers and increased complexity.
- Geopolitical instability creates unpredictable risks: The inherent unpredictability of geopolitical events makes relying on long, complex global supply chains increasingly risky. Businesses are seeking more stable and predictable supply partners.
- Diversification of supplier bases becomes crucial: To mitigate the risk associated with geopolitical instability and potential disruptions, diversification of supplier bases across multiple regions is becoming a critical strategy.
Pandemic's Impact on Global Supply Chain Vulnerability
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a stark reminder of the fragility inherent in highly interconnected global supply chains. Lockdowns, port congestion, and widespread transportation disruptions led to significant shortages of goods and exposed the vulnerabilities of "just-in-time" inventory management strategies. This experience has spurred a renewed focus on building more resilient and diversified supply chains.
- Pandemic-induced lockdowns revealed vulnerabilities: The pandemic demonstrated how easily disruptions in one part of the world could cascade through the entire global supply chain, causing widespread shortages and economic hardship.
- Supply chain bottlenecks caused significant delays and increased costs: Bottlenecks at ports, factories, and transportation hubs led to significant delays, increased transportation costs, and ultimately, higher prices for consumers.
- The pandemic spurred increased investment in supply chain diversification and resilience: Businesses are now actively investing in strategies to diversify their supplier base, increase inventory levels, and enhance the overall resilience of their supply chains.
- Enhanced visibility and traceability in supply chains became essential: The pandemic underscored the need for better visibility and traceability within supply chains to quickly identify and respond to disruptions.
Reshoring and Nearshoring: Rethinking Geographic Proximity
The Great Decoupling is accelerating the trends of reshoring (returning manufacturing to the home country) and nearshoring (moving production to nearby countries). Companies are actively seeking to reduce their reliance on distant suppliers to mitigate geopolitical and logistical risks. While reshoring and nearshoring present advantages, they also pose challenges.
- Reshoring reduces transportation costs and lead times: Bringing manufacturing closer to home reduces transportation costs, lead times, and the environmental impact of long-distance shipping.
- Nearshoring offers a balance between cost savings and reduced risk: Nearshoring allows companies to benefit from lower labor costs while simultaneously reducing the risks associated with long and complex supply chains.
- Regionalization of supply chains enhances supply chain agility and responsiveness: Regionalizing supply chains increases agility and responsiveness, allowing companies to adapt more quickly to changes in demand or disruptions.
- Increased labor costs in developed countries can offset the benefits of reshoring: Reshoring can be expensive due to higher labor costs in developed countries, potentially offsetting some of the advantages.
The Role of Technology in Adapting to the Great Decoupling
Technology is playing a pivotal role in adapting to the challenges of the Great Decoupling. Digitalization, automation, and advanced analytics are empowering businesses to enhance supply chain visibility, optimize logistics, and improve overall resilience.
- AI-powered demand forecasting enables better inventory management: Artificial intelligence can improve demand forecasting accuracy, helping businesses optimize inventory levels and reduce waste.
- Blockchain technology enhances supply chain transparency and traceability: Blockchain provides enhanced transparency and traceability, enabling better tracking of goods and materials throughout the supply chain.
- Automation reduces reliance on human labor in certain processes: Automation can improve efficiency and reduce reliance on human labor in repetitive or hazardous tasks.
- Advanced analytics helps in risk identification and mitigation: Advanced analytics can identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in supply chains, allowing businesses to take proactive measures to mitigate them.
Conclusion
The Great Decoupling is fundamentally altering the global economic landscape and reshaping global supply chains. Geopolitical instability, pandemic-related disruptions, and a growing preference for economic independence are driving a significant shift towards regionalization, reshoring, and nearshoring. Businesses must adapt by investing in supply chain resilience, embracing technological advancements, and diversifying their supplier networks. Ignoring the implications of the Great Decoupling is not an option. To thrive in this new era, companies must proactively strategize and implement robust solutions to effectively manage the complexities and risks associated with this transformative shift in global supply chains. Successfully navigating the challenges of the Great Decoupling requires a proactive and adaptable approach to global supply chain management.

Featured Posts
-
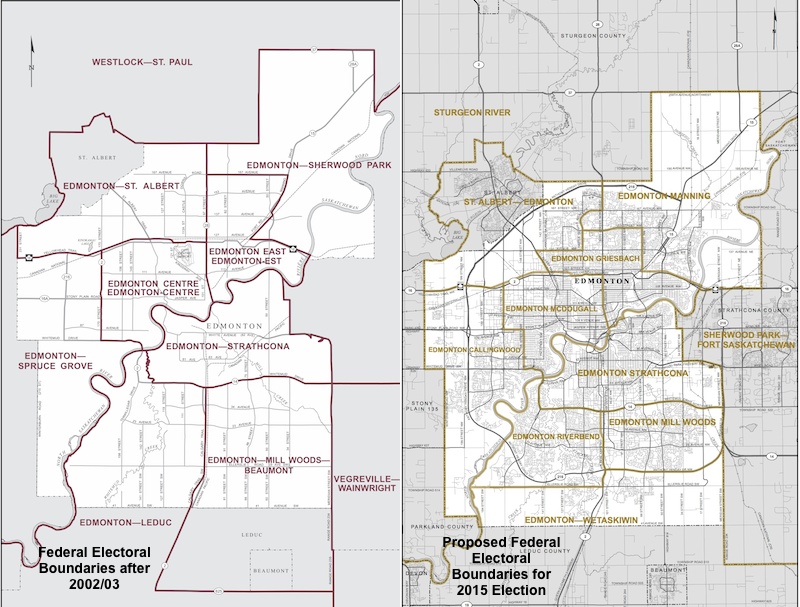 Greater Edmontons New Federal Ridings An Analysis Of Voter Impact
May 09, 2025
Greater Edmontons New Federal Ridings An Analysis Of Voter Impact
May 09, 2025 -
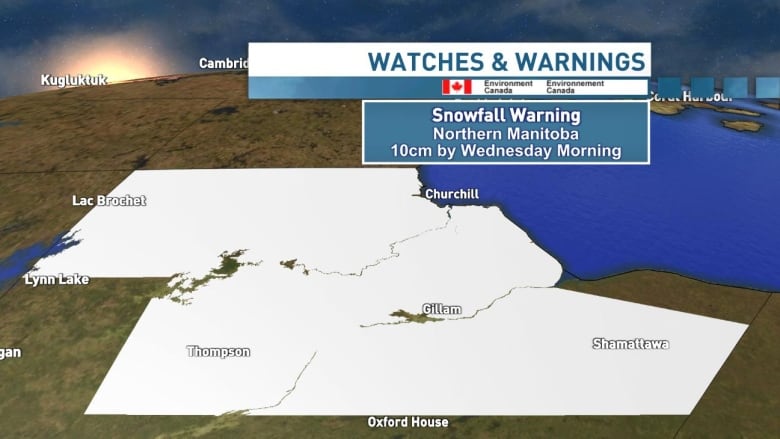 Manitoba Snowfall Warning 10 20 Cm Expected Tuesday
May 09, 2025
Manitoba Snowfall Warning 10 20 Cm Expected Tuesday
May 09, 2025 -
 The Trump Administration On May 8th 2025 A Retrospective On Day 109
May 09, 2025
The Trump Administration On May 8th 2025 A Retrospective On Day 109
May 09, 2025 -
 Police Operation Nets Suspected Madeleine Mc Cann Imposter In Uk
May 09, 2025
Police Operation Nets Suspected Madeleine Mc Cann Imposter In Uk
May 09, 2025 -
 Nova Kniga Stivena Kinga Ta Yogo Pozitsiya Schodo Trampa Ta Maska
May 09, 2025
Nova Kniga Stivena Kinga Ta Yogo Pozitsiya Schodo Trampa Ta Maska
May 09, 2025
