The Power Of Music: Exploring The Sound Perimeter

Table of Contents
The Psychological Impact of Music: Exploring the Emotional Landscape
Music's ability to evoke intense emotions is undeniable. The power of music to shape our emotional landscape is a testament to its profound psychological impact.
Music and Emotion
Music has the unique ability to instantly transport us to different emotional states.
- Upbeat pop music often elicits feelings of joy and excitement.
- Melancholic blues music frequently evokes sadness and reflection.
- Classical music can inspire feelings of peace and tranquility.
These emotional responses are rooted in the neurological mechanisms of our brain. Listening to music triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, and activates the limbic system, the brain region responsible for processing emotions. The power of music over our emotional state is truly remarkable.
Music and Memory
Music possesses a remarkable ability to unlock vivid memories. A single note or melody can instantly transport us back to a specific time and place, resurrecting long-forgotten experiences.
- Hearing a song from your childhood might bring back memories of family gatherings.
- A particular piece of music might remind you of a significant life event or a cherished relationship.
This phenomenon is partly due to the close association between music and autobiographical memory. The intricate neural pathways linking auditory information with emotional and episodic memories explain this strong connection. Music therapy leverages this power, using familiar music to stimulate memory recall in patients with conditions like Alzheimer's disease.
Music and Mental Well-being
The therapeutic potential of music is increasingly recognized in addressing mental health challenges. Listening to calming music can reduce stress and anxiety, while engaging in musical activities can boost self-esteem and improve mood.
- Music therapy uses various techniques, such as active music making and receptive music listening, to improve mental well-being.
- Studies show that listening to soothing music can lower cortisol levels (the stress hormone).
The positive effects of music on mental health are well-documented, making music therapy a valuable tool in managing conditions such as depression and anxiety. The power of music to heal and soothe is undeniable.
The Physiological Effects of Music: A Sonic Body Scan
Beyond the psychological realm, music exerts a measurable influence on our physical bodies. The sonic impact extends beyond our ears, creating a measurable physiological response.
Music and Physical Responses
Music affects our autonomic nervous system, influencing our heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
- Fast-tempo music can increase heart rate and breathing, mirroring the physiological effects of exercise.
- Slow-tempo music can slow heart rate and induce relaxation.
This physiological response is harnessed in various contexts. Upbeat music is frequently used in sports and fitness to enhance performance and motivation, while calming music is used in relaxation and meditation practices. The power of music is felt in our very bodies.
Music and Pain Management
Research demonstrates music's analgesic properties – its ability to reduce pain perception. This effect stems from its ability to distract from pain and promote relaxation.
- Studies show that listening to music can reduce pain intensity in patients undergoing surgery or suffering from chronic pain.
- Music therapy is used in hospitals and pain management clinics as a non-pharmacological pain relief method.
The mechanisms behind music's pain-relieving effects involve the release of endorphins, natural pain-relieving chemicals in the brain, and the distraction it provides from painful stimuli. The power of music as a pain management tool is significant.
The Social Influence of Music: Connecting Through Sound
Music transcends individual experiences; it plays a crucial role in shaping social identities, fostering community, and driving social change. Its sound perimeter extends to encompass our collective experiences.
Music and Culture
Music is deeply embedded in cultural identities, reflecting the values, beliefs, and traditions of various societies.
- Different musical genres, like flamenco from Spain or reggae from Jamaica, represent distinct cultural expressions.
- Music serves as a powerful means of transmitting cultural heritage across generations.
The shared experience of music fosters a sense of belonging and unity within communities, reinforcing cultural ties and transmitting traditions. The power of music as a cultural force is immense.
Music and Social Movements
Throughout history, music has played a powerful role in social and political movements, acting as a catalyst for change and a unifying force for activists.
- The civil rights movement in the US utilized gospel and soul music to inspire hope and solidarity.
- Protest songs have been used throughout history to articulate grievances and challenge oppressive regimes.
Music's ability to communicate emotions and ideas effectively makes it an ideal vehicle for social commentary and mobilization. The sound perimeter of music encompasses powerful movements for social change.
Music and Communication
Music's ability to communicate emotions and ideas universally is remarkable, transcending language barriers and connecting people from diverse backgrounds.
- Musical phrases can express a wide range of feelings without words.
- The universal language of music allows for shared emotional experiences regardless of linguistic differences.
The power of music to unite individuals across cultures and languages underlines its profound social impact. The sound perimeter of music includes a powerful capacity to build bridges between communities.
Conclusion
The power of music is multifaceted, encompassing psychological, physiological, and social dimensions. We've explored the sound perimeter of music, revealing its extensive reach in shaping our emotional lives, influencing our physical responses, and fostering connections between people. From evoking profound emotions to managing pain and driving social change, music's influence is profound and far-reaching. Explore the power of music further by engaging with diverse musical genres, attending live performances, or even learning to play an instrument. Expand your understanding of the sound perimeter and discover the profound impact musical experiences can have on your life. Embrace the transformative power of music and allow its audio experiences to enrich your life.

Featured Posts
-
 Dywan Almhasbt Ykshf En Mkhalfat Jsymt Rdwd Afeal Alnwab W Alkhtwat Alqadmt
May 21, 2025
Dywan Almhasbt Ykshf En Mkhalfat Jsymt Rdwd Afeal Alnwab W Alkhtwat Alqadmt
May 21, 2025 -
 Novelistes A L Espace Julien Avant Le Hellfest Une Immersion
May 21, 2025
Novelistes A L Espace Julien Avant Le Hellfest Une Immersion
May 21, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers March 20 2025
May 21, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers March 20 2025
May 21, 2025 -
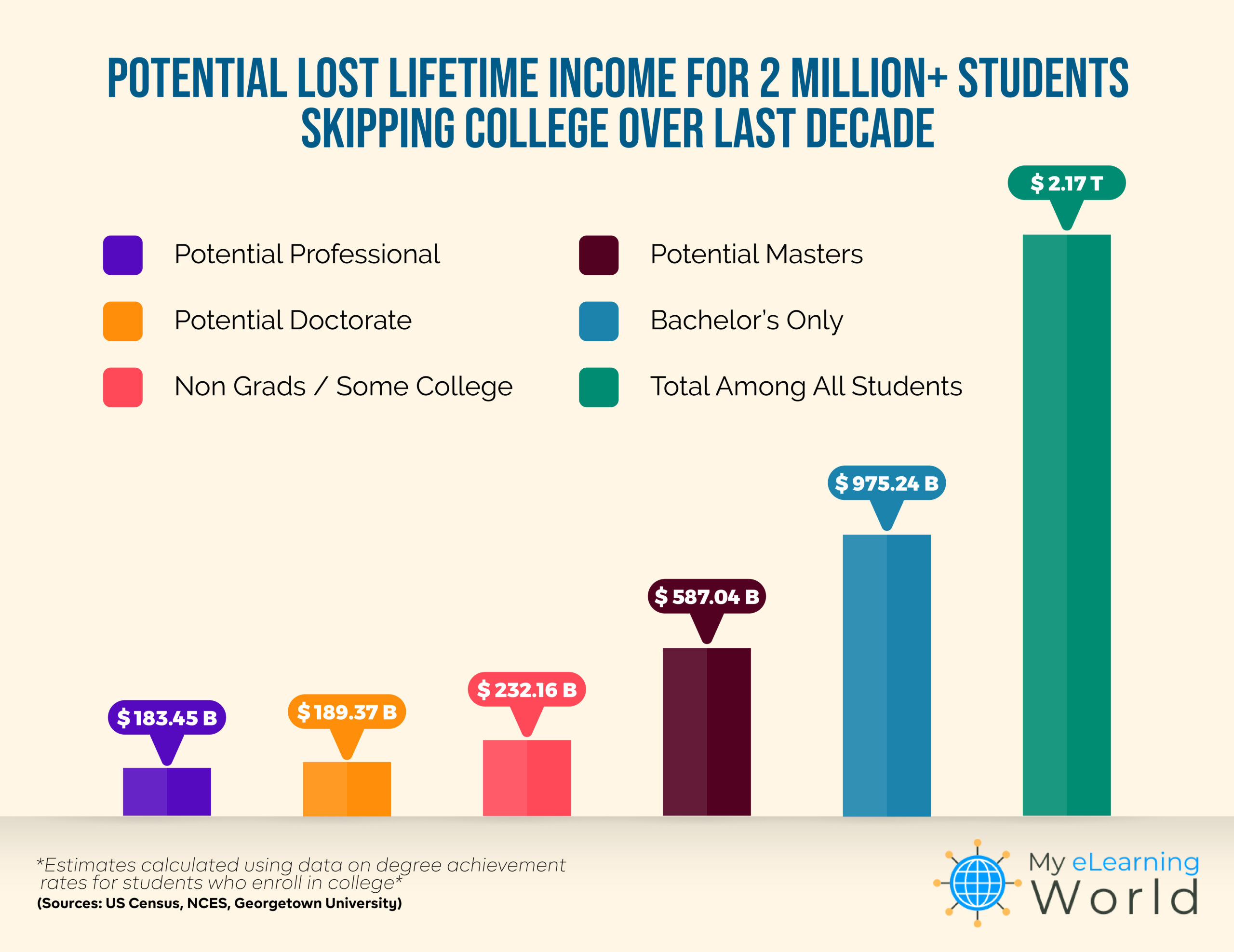 College Enrollment Decline A Deep Dive Into The Economic Hardship Facing Boom Towns
May 21, 2025
College Enrollment Decline A Deep Dive Into The Economic Hardship Facing Boom Towns
May 21, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Answers And Hints For April 26 2025
May 21, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Answers And Hints For April 26 2025
May 21, 2025
