The Stigma Of Mental Illness In Violent Crime: Why We Fail
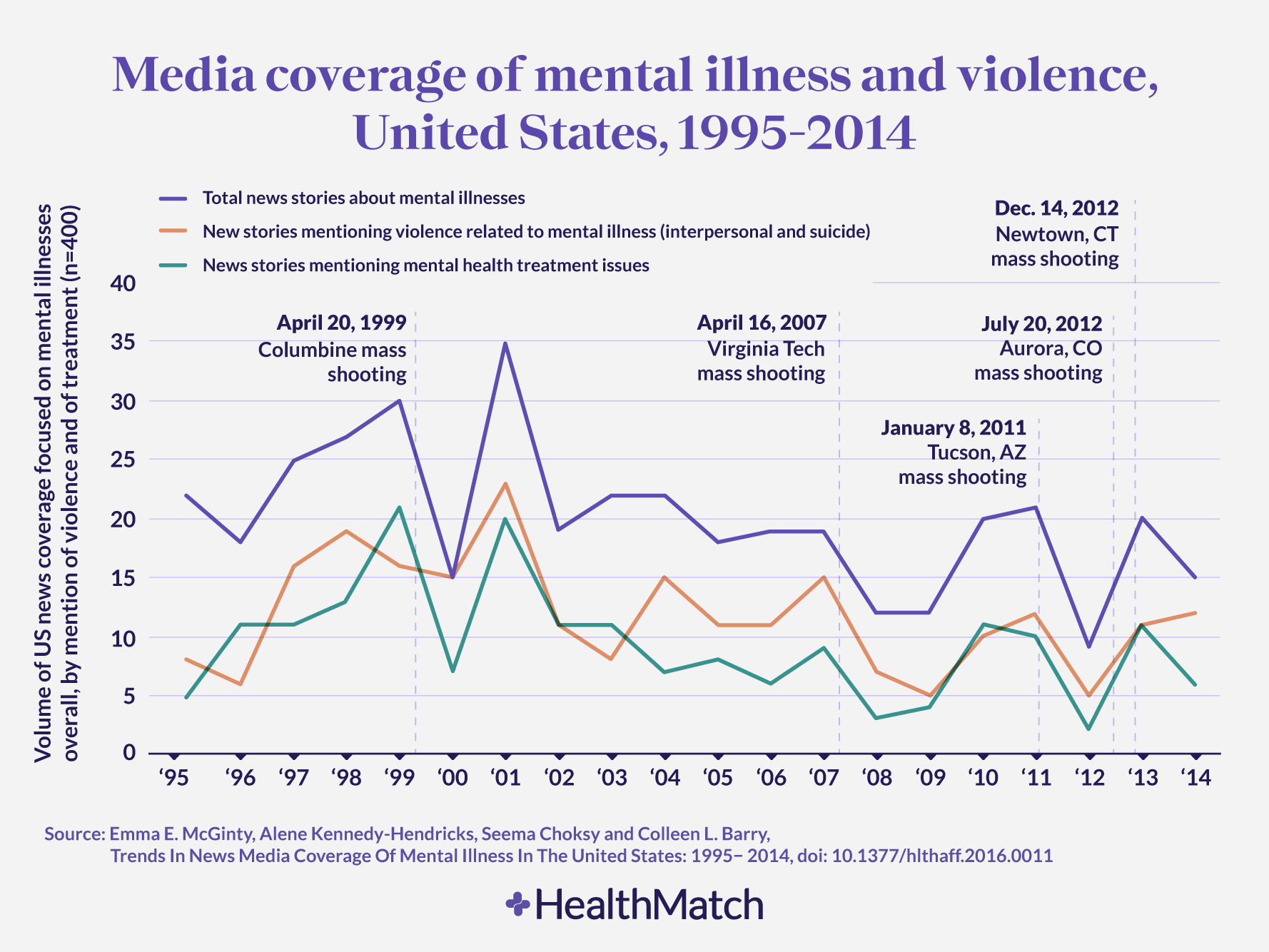
Table of Contents
The Persistent Stigma Surrounding Mental Illness
The pervasive stigma associated with mental illness is a major obstacle to addressing its connection to violent crime. This stigma manifests in several ways, hindering individuals from seeking help and creating a cycle of misunderstanding and inaction.
Misconceptions and Media Portrayals: Negative stereotypes perpetuated by media often portray individuals with mental illness as violent and unpredictable.
- Examples of harmful media representations: Movies and television shows frequently depict mentally ill characters as villains or unstable individuals, reinforcing harmful stereotypes.
- Impact on public perception: These portrayals create fear and misunderstanding among the public, making it difficult for individuals to openly discuss their mental health struggles.
- Difficulty in seeking help due to fear of judgment: The fear of being stigmatized prevents many from seeking professional help, leading to untreated conditions that can potentially contribute to violent behavior.
Lack of Public Awareness and Education: A critical gap exists in public understanding of mental health conditions. Increased education and awareness are crucial to combatting the stigma.
- Statistics on public knowledge of mental health: Surveys consistently reveal a lack of awareness about mental health issues, including symptoms, treatment options, and available resources.
- Suggestions for improving public education campaigns: Public health campaigns should focus on dispelling myths, promoting early intervention, and reducing the stigma associated with mental health treatment.
- Role of schools and community programs: Schools and community organizations play a vital role in educating young people about mental health and promoting help-seeking behaviors.
Systemic Barriers to Accessing Mental Healthcare: Even for those who recognize the need for help, accessing timely and appropriate care remains a significant challenge.
- Long waitlists: Many individuals face excessively long wait times to access mental healthcare services, delaying crucial treatment.
- High cost of treatment: The expense of mental health treatment, including therapy and medication, can be prohibitive for many, especially those with limited financial resources.
- Limited access to specialized care: Access to specialized mental healthcare services, such as inpatient treatment or specific therapies, may be geographically limited or unavailable.
- Geographical disparities: Individuals living in rural or underserved areas often face greater challenges in accessing adequate mental healthcare.
Failures in the Criminal Justice System
The criminal justice system plays a critical role in addressing individuals involved in violent crime, but significant failures exist in how it handles those with mental illness.
Inadequate Mental Health Screening and Assessment: Comprehensive mental health evaluations are often lacking within the justice system.
- Insufficient training for law enforcement: Law enforcement officers require specialized training to identify and appropriately respond to individuals experiencing a mental health crisis.
- Lack of resources for mental health screenings in jails and prisons: Jails and prisons often lack adequate resources and trained personnel to conduct thorough mental health screenings and assessments.
- Difficulties in identifying and addressing co-occurring disorders (substance abuse, etc.): Individuals with mental illness often also struggle with substance abuse or other co-occurring disorders, which require integrated treatment approaches.
Insufficient Diversion Programs and Alternatives to Incarceration: Robust diversion programs are essential to steer individuals with mental illness away from incarceration.
- Examples of successful diversion programs: Mental health courts and specialized pre-trial diversion programs have proven effective in reducing recidivism and improving outcomes for individuals with mental illness.
- Challenges in implementing these programs: Limited funding, lack of resources, and insufficient coordination between mental health and criminal justice systems hinder the widespread implementation of these programs.
- Need for increased funding and resources: Significant investment is needed to expand and improve diversion programs and provide the necessary resources for their effective operation.
Lack of Access to Mental Healthcare Within the Prison System: Correctional facilities often fail to provide adequate mental health services to incarcerated individuals.
- Staffing shortages: Prisons often suffer from severe staffing shortages, including a lack of qualified mental health professionals.
- Limited treatment options: The range of mental health services offered in prisons is often limited, hindering effective treatment.
- High rates of suicide and self-harm in prisons: The lack of adequate mental health care contributes to high rates of suicide and self-harm among incarcerated individuals with mental illness.
The Role of Societal Factors and Systemic Inequality
Societal factors and systemic inequalities significantly influence the link between mental illness and violent crime.
Socioeconomic Disparities and Access to Care: Poverty and lack of access to resources exacerbate mental health challenges and increase the risk of involvement in violent crime.
- Correlation between poverty and mental illness: Poverty is strongly correlated with increased rates of mental illness, due to factors like stress, lack of access to healthcare, and exposure to trauma.
- Limited access to healthcare in underserved communities: Underserved communities often lack access to adequate mental health services, exacerbating existing inequalities.
- Impact of trauma and adverse childhood experiences: Exposure to trauma and adverse childhood experiences significantly increases the risk of developing mental health issues, which can potentially contribute to violent behavior.
Racism and Discrimination in the Mental Healthcare System: Racial bias within the mental healthcare system further complicates the issue.
- Examples of racial bias in diagnosis and treatment: Studies have shown evidence of racial bias in the diagnosis and treatment of mental illness, leading to disparities in care.
- Disproportionate incarceration rates for minority groups with mental illness: Minority groups with mental illness are disproportionately incarcerated compared to their white counterparts, reflecting systemic biases within the criminal justice system.
- Need for culturally competent care: Culturally competent care that considers the unique experiences and needs of diverse populations is crucial to addressing the disparities in mental healthcare access.
Conclusion
The persistent stigma surrounding mental illness, coupled with failures within the criminal justice system and broader societal inequalities, perpetuates the link between mental illness and violent crime. Addressing this complex issue requires a multifaceted approach. We need systemic changes to improve access to mental healthcare, increase funding for diversion programs, and launch comprehensive public awareness campaigns to combat the stigma of mental illness. By confronting the stigma of mental illness and reforming our systems, we can break the cycle and create a safer, more just society for everyone. Let's work together to overcome these challenges and find effective solutions to address the complex relationship between mental illness and violent crime, promoting mental well-being and reducing violent crime through effective mental health strategies.

Featured Posts
-
 Did Us Economic Conditions Affect Elon Musks Net Worth And Tesla
May 10, 2025
Did Us Economic Conditions Affect Elon Musks Net Worth And Tesla
May 10, 2025 -
 Documents On Epstein Diddy Jfk And Mlk Pam Bondi Announces Forthcoming Release
May 10, 2025
Documents On Epstein Diddy Jfk And Mlk Pam Bondi Announces Forthcoming Release
May 10, 2025 -
 Seattle Welcomes Canadian Sports Fans Par Exchange For Canadian Dollars
May 10, 2025
Seattle Welcomes Canadian Sports Fans Par Exchange For Canadian Dollars
May 10, 2025 -
 Bangkok Post The Fight For Transgender Equality Continues
May 10, 2025
Bangkok Post The Fight For Transgender Equality Continues
May 10, 2025 -
 Sensex Today 700 Point Surge Nifty Reclaims 23 800 Live Updates
May 10, 2025
Sensex Today 700 Point Surge Nifty Reclaims 23 800 Live Updates
May 10, 2025
