Trump's Tariffs: How They Increased Prices And Emptied Shelves In The US
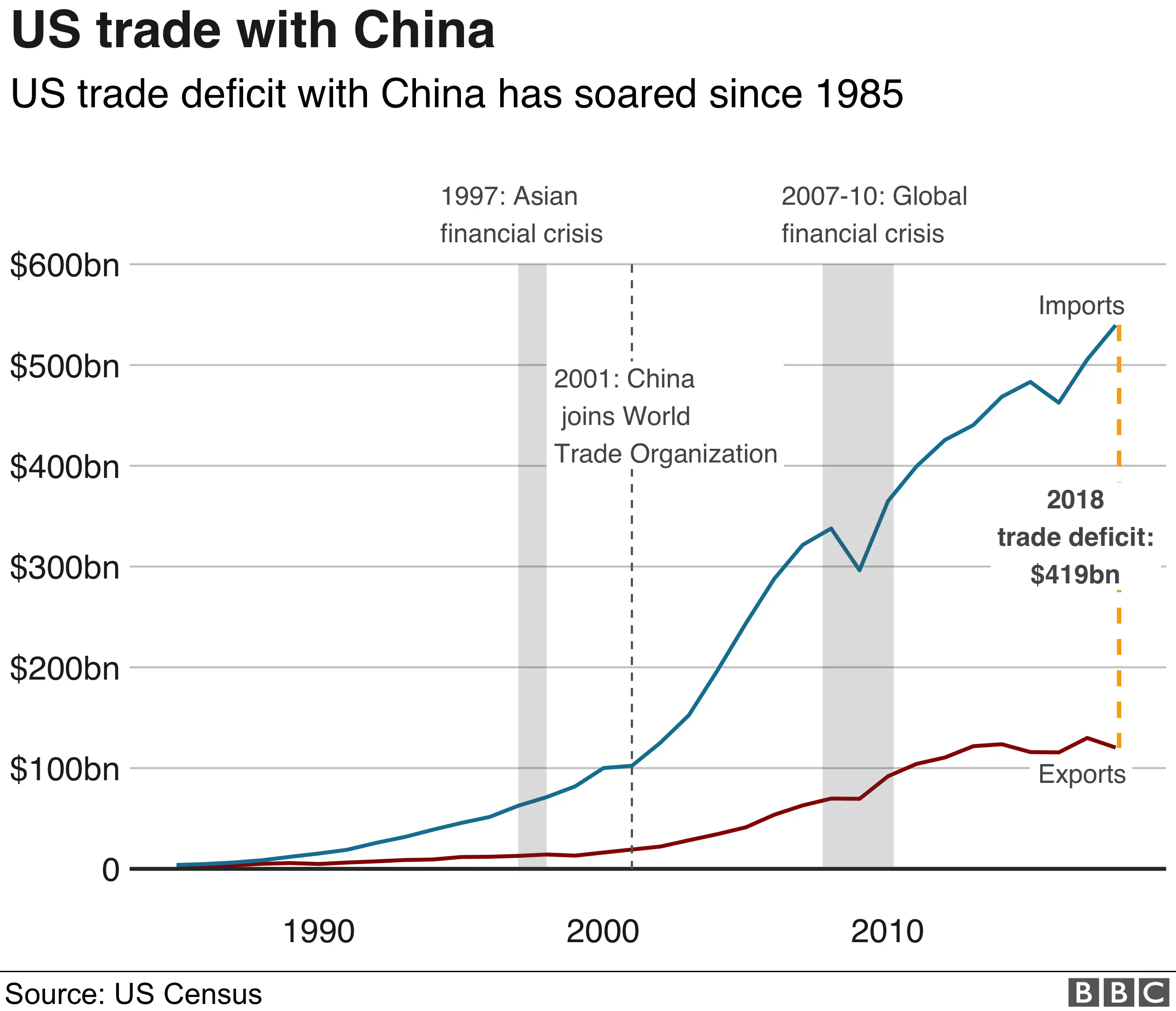
Table of Contents
The Mechanics of Trump's Tariffs
Trump's tariffs were a cornerstone of his "America First" trade policy. They primarily targeted steel and aluminum imports from various countries, aiming to protect domestic industries. However, the most significant tariffs were levied on goods imported from China, escalating into a protracted trade war. These tariffs weren't uniform; they varied significantly depending on the product. The intended consequence was to bolster American manufacturing and reduce the trade deficit. However, the unintended consequences proved far-reaching and detrimental.
- Specific examples of targeted goods and their tariff rates: Steel and aluminum faced tariffs of 25% and 10%, respectively. Chinese goods faced tariffs ranging from 10% to 25%, affecting a wide array of products from consumer electronics to furniture.
- Explanation of the "trade war" context: The tariffs triggered retaliatory tariffs from China and other countries, creating a trade war that disrupted global supply chains and impacted multiple economies.
- Mention of retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries: China retaliated with tariffs on American agricultural products like soybeans and pork, hurting American farmers significantly. The EU and other trading partners also imposed tariffs on American goods.
Increased Prices for Consumers
Tariffs directly increased the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for American consumers. This contributed to a rise in inflation, measurable through the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The increased costs weren't evenly distributed, disproportionately affecting low-income families who spend a larger percentage of their income on essential goods.
- Examples of specific goods whose prices increased significantly: The price of steel and aluminum increased, leading to higher prices for automobiles, construction materials, and many manufactured goods. Consumer electronics and furniture also saw price increases due to tariffs on Chinese imports.
- Statistics illustrating the rise in prices: While precise figures attributing price increases solely to tariffs are debated, studies by organizations like the Peterson Institute for International Economics showed significant price increases across various sectors.
- Discussion of the burden on low-income families: Low-income households faced a heavier burden as they had less disposable income to absorb the increased prices, impacting their ability to afford necessities.
The Impact on Specific Industries
The automotive industry, construction sector, and manufacturing were among the hardest hit. Increased input costs from tariffs forced businesses to either absorb losses, raise prices, or reduce production, leading to job losses and economic slowdown in some areas.
- Case studies of businesses affected by tariffs: Many small and medium-sized businesses, particularly those reliant on imported materials, faced severe financial strain. Case studies highlighted closures and bankruptcies directly linked to increased costs from tariffs.
- Statistics showing job losses or production slowdowns: Although quantifying job losses directly attributable to tariffs is complex, various reports suggest slowed production and job losses in certain manufacturing sectors.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Empty Shelves
Trump's tariffs significantly disrupted global supply chains. Businesses struggled to source materials and components, leading to delays and shortages of various goods. The added complexity and cost of navigating tariffs further exacerbated the situation.
- Examples of products that became scarce due to tariffs: Certain types of steel, aluminum products, and consumer goods imported from China experienced shortages.
- Discussion of the role of logistics and transportation: Increased shipping costs and logistical hurdles further contributed to delays and shortages.
- Mention of increased shipping costs: Companies faced higher transportation costs due to the complexities of navigating tariff regulations and increased demand for alternative sources of goods.
The Role of Trade Wars
The retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries in response to Trump's tariffs created a trade war, compounding the negative economic impacts. This "tit-for-tat" escalation disrupted trade flows globally, creating uncertainty and further escalating costs.
Conclusion
Trump's tariffs ultimately led to increased prices for consumers, disrupted supply chains, and contributed to economic uncertainty. The unintended consequences, including retaliatory tariffs and supply chain disruptions, overshadowed any potential benefits. The long-term economic impacts of these policies are still being assessed, but it's clear that they placed a significant burden on American businesses and consumers. Understanding the effects of trade protectionism like Trump's tariffs is crucial for informed economic decision-making. Further research into the impact of tariffs on the US economy will provide a clearer understanding of their long-term effects. Learn more about the unintended consequences of tariffs and how they can impact your wallet and your access to goods.

Featured Posts
-
 Community Mourns Details Emerge From Canadian Filipino Car Ramming
Apr 29, 2025
Community Mourns Details Emerge From Canadian Filipino Car Ramming
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Diamond Johnson From Norfolk State To Minnesota Lynx Wnba Camp
Apr 29, 2025
Diamond Johnson From Norfolk State To Minnesota Lynx Wnba Camp
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Oh What A Beautiful World Album A Deep Dive Into Willie Nelsons Latest
Apr 29, 2025
The Oh What A Beautiful World Album A Deep Dive Into Willie Nelsons Latest
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Covid 19 Test Fraud Lab Owner Admits To Faking Results
Apr 29, 2025
Covid 19 Test Fraud Lab Owner Admits To Faking Results
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Convicted Cardinals Eligibility For Papal Conclave Participation
Apr 29, 2025
Convicted Cardinals Eligibility For Papal Conclave Participation
Apr 29, 2025
