U.S.-China Trade War: Assessing The Economic Consequences Of Tariff Changes
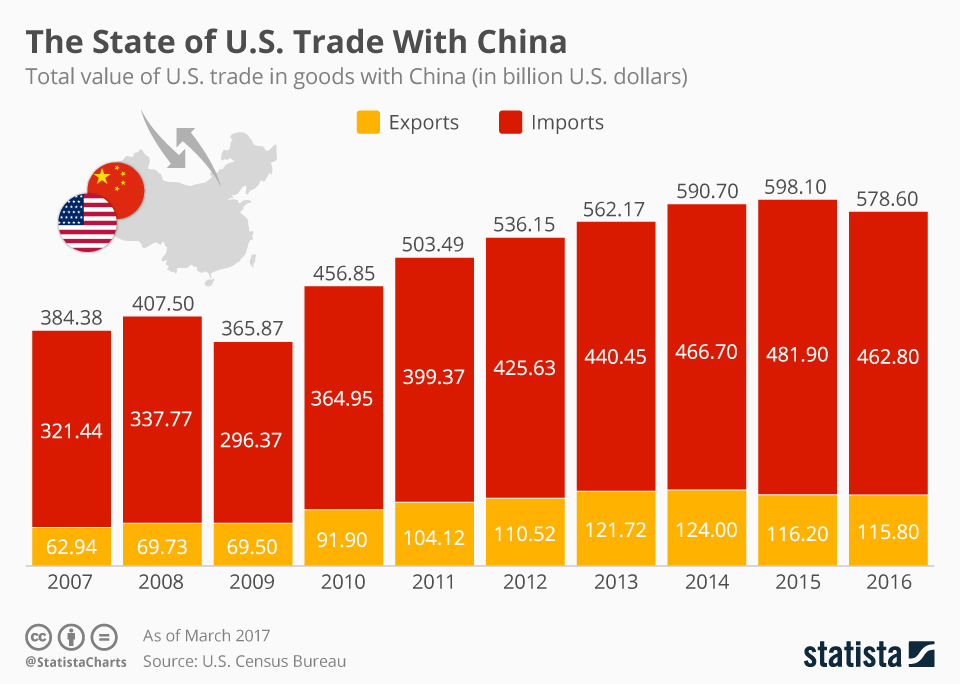
Table of Contents
Impact on U.S. Consumers and Businesses
Increased Prices for Consumers
Tariffs on imported Chinese goods led to higher prices for U.S. consumers. This reduced purchasing power and contributed to inflation. The impact wasn't evenly distributed; low-income households, who spend a larger proportion of their income on necessities, were disproportionately affected.
- Examples: Tariffs increased the cost of everyday items like electronics (phones, laptops), clothing, and furniture.
- Data & Statistics: Studies showed significant price increases in various sectors following the implementation of tariffs. (Note: Specific data and statistics would need to be inserted here, referencing reputable sources like the Bureau of Economic Analysis or academic research papers).
- Impact on Low-Income Households: The increased cost of essential goods reduced disposable income for low-income families, further exacerbating existing economic inequalities.
Challenges for U.S. Businesses
Many U.S. businesses faced significant challenges. Those reliant on imported Chinese goods experienced increased production costs and supply chain disruptions. Companies competing with subsidized Chinese imports also struggled.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The trade war caused delays and uncertainties in global supply chains, impacting production schedules and inventory management.
- Increased Production Costs: Tariffs directly increased the cost of imported raw materials and components, squeezing profit margins.
- Impact on Specific Sectors: The manufacturing and agricultural sectors were particularly hard hit, facing reduced exports to China and higher input costs.
- Protectionism: While tariffs were intended as a tool for protectionism, the downsides included higher consumer prices and reduced competitiveness in some sectors.
Impact on the Chinese Economy
Reduced Chinese Exports and Economic Growth
U.S. tariffs significantly slowed Chinese export growth, impacting its overall economic performance. China responded with retaliatory tariffs, further escalating the conflict and creating a negative feedback loop.
- Decline in Exports to the U.S.: Data (again, specific data and sources needed here) clearly showed a decline in Chinese exports to the U.S. during the trade war period.
- Chinese Government Response: The Chinese government implemented various measures to stimulate domestic demand and support affected industries.
- Impact on Specific Chinese Industries: Industries heavily reliant on exports to the U.S., such as manufacturing and technology, faced the brunt of the negative economic consequences.
Shifting Trade Relationships
To mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs, China actively sought new trade partners, diversifying its export markets and strengthening economic ties with countries like those in the Belt and Road Initiative.
- New Trade Partners: China expanded its trade relationships with countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- Long-Term Implications: The trade war accelerated the shift towards a more multipolar global trading system.
Global Economic Consequences
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
The U.S.-China trade war had significant ripple effects on global supply chains, causing widespread disruptions and uncertainty. The interconnected nature of global trade meant that even businesses not directly involved in U.S.-China trade experienced negative consequences.
- Increased Uncertainty and Volatility: The trade war fueled uncertainty in international trade, making it difficult for businesses to plan for the future.
- Examples of Disruptions: Various industries, from electronics to automotive manufacturing, experienced delays and shortages due to disrupted supply chains.
Increased Uncertainty and Volatility
The trade war injected significant uncertainty and volatility into global financial markets. Investor confidence declined, and investment flows were disrupted, impacting global economic growth.
- Impact on Investor Confidence: The escalating trade conflict created uncertainty, prompting investors to adopt a more cautious stance.
- Potential for Global Recession: The trade war contributed to concerns about a potential global recession.
Long-Term Implications and Lessons Learned
Restructuring of Global Trade
The U.S.-China trade war fundamentally restructured aspects of global trade relationships. It fueled protectionist sentiments worldwide, potentially hindering globalization and free trade.
- Rise of Protectionism: The trade war highlighted the resurgence of protectionist policies in various countries.
- Implications for Globalization: The long-term impact on globalization is still being assessed, with some arguing it has slowed the process of global integration.
Policy Recommendations
Mitigating the negative consequences of future trade disputes requires international cooperation and a renewed commitment to multilateral trade agreements. Emphasis should be placed on resolving disagreements through negotiation and diplomacy rather than escalating trade wars.
- International Cooperation: Strengthening international institutions and promoting dialogue are crucial for managing trade disputes.
- Multilateral Trade Agreements: Reinvigorating and strengthening existing multilateral trade agreements is essential to promote free and fair trade.
Conclusion:
The U.S.-China trade war served as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of global economies and the significant consequences of protectionist policies. The tariff changes resulted in increased prices for consumers, challenges for businesses in both the U.S. and China, and disruptions to global supply chains. Understanding the lasting economic consequences of this trade war is crucial for preventing similar disruptions in the future. Further research into the U.S.-China trade war and its economic impact, focusing on specific sectors and long-term trends, is essential to inform future trade policy. For a deeper dive into the complexities of this global event, explore further resources on the U.S.-China trade war and its multifaceted economic consequences.

Featured Posts
-
 Orange County High School College Sports Results Thursday February 20th
May 13, 2025
Orange County High School College Sports Results Thursday February 20th
May 13, 2025 -
 Ftc V Meta A Deep Dive Into The Antitrust Case
May 13, 2025
Ftc V Meta A Deep Dive Into The Antitrust Case
May 13, 2025 -
 Sabalenka Falls To Ostapenko In Stuttgart Final
May 13, 2025
Sabalenka Falls To Ostapenko In Stuttgart Final
May 13, 2025 -
 Uppgifter Vem Tar Oever Atalanta
May 13, 2025
Uppgifter Vem Tar Oever Atalanta
May 13, 2025 -
 Father Of Gaza Hostage Edan Alexander Hope Remains Urges Us Hamas Talks
May 13, 2025
Father Of Gaza Hostage Edan Alexander Hope Remains Urges Us Hamas Talks
May 13, 2025
