U.S. Federal Reserve Rate Decision: Economic Headwinds And Policy Response
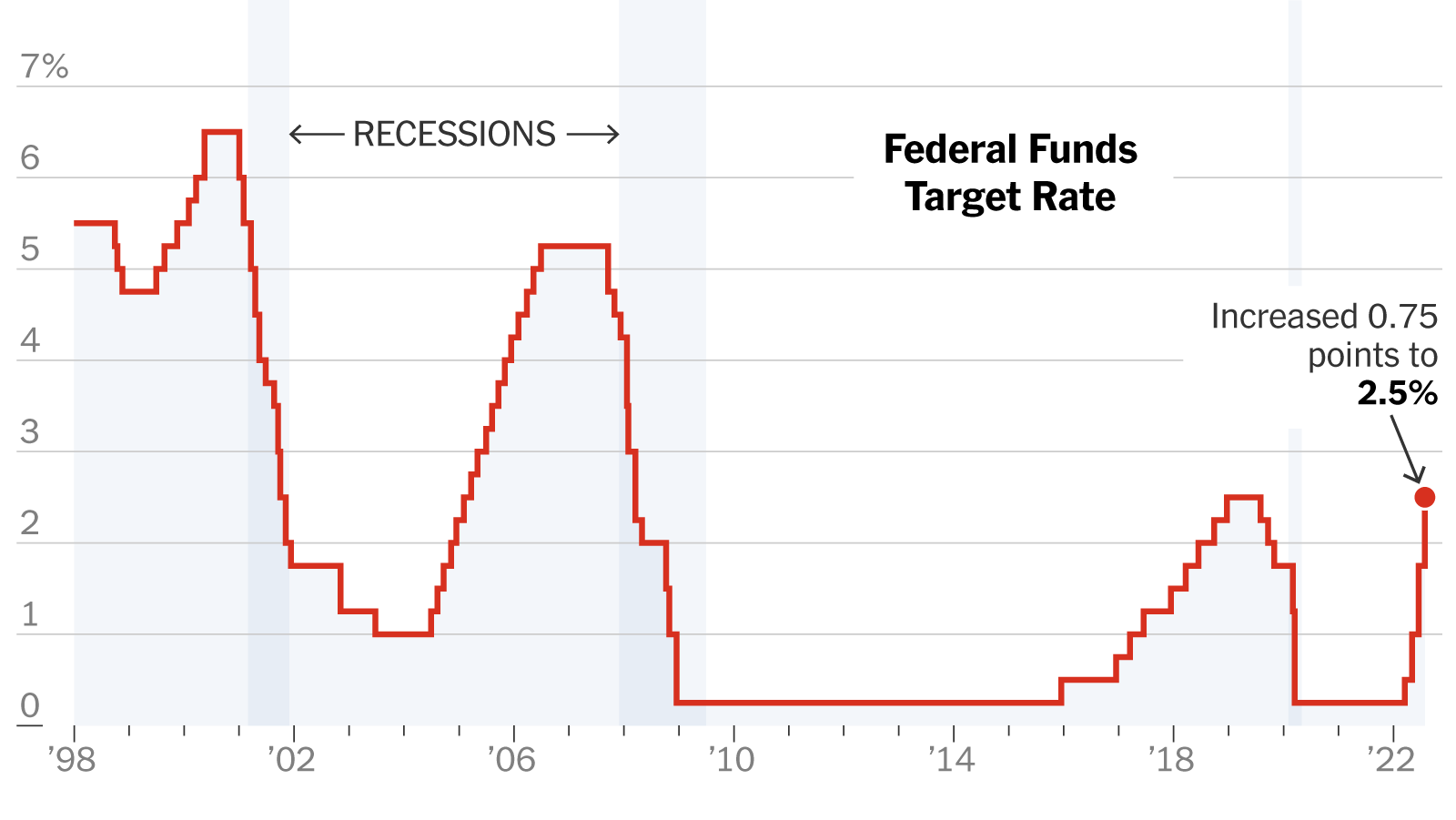
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures and the Fed's Response
Persistent Inflationary Trends
Inflation remains a significant challenge. Current inflation rates, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), are still elevated above the Federal Reserve's target of 2%. Several factors contribute to this persistent inflation:
- Supply chain disruptions: Ongoing global supply chain bottlenecks continue to increase the cost of goods.
- Elevated energy prices: Soaring energy costs, driven by geopolitical factors and increased demand, are a major driver of inflation.
- Strong consumer demand: Robust consumer spending, fueled by pent-up demand and government stimulus, has put upward pressure on prices.
It's important to distinguish between headline inflation (the overall inflation rate) and core inflation (excluding volatile food and energy prices). While headline inflation may fluctuate, persistent core inflation indicates broader inflationary pressures. Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides crucial insights into these trends.
The Fed's Tools for Combating Inflation
The Federal Reserve employs several monetary policy tools to combat inflation:
- Federal Funds Rate: This is the target rate that the Fed wants banks to charge each other for overnight loans. Raising this rate increases borrowing costs for banks, which in turn leads to higher interest rates for consumers and businesses.
- Quantitative Tightening (QT): This involves reducing the Fed's balance sheet by allowing U.S. Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities to mature without reinvestment. This reduces the money supply, curbing inflationary pressures.
The impact of these tools is far-reaching. Higher interest rates affect borrowing costs for mortgages, auto loans, and business investments, potentially slowing down economic growth and consumer spending.
Balancing Inflation Control with Economic Growth
The Fed faces a delicate balancing act: controlling inflation without triggering a recession. Aggressive rate hikes, while effective in curbing inflation, could lead to:
- Job losses: Higher interest rates can lead to reduced business investment and hiring.
- Reduced investment: Businesses may postpone expansion plans due to increased borrowing costs.
- Economic slowdown: A sharp decrease in economic activity could lead to a recession.
Economic Indicators and Outlook
Key Economic Data Points
Several key economic indicators inform the Fed's decision-making:
- GDP Growth: Slowing GDP growth signals a potential economic slowdown.
- Unemployment Rate: Rising unemployment is a key indicator of economic weakness.
- Consumer Confidence Index: Decreased consumer confidence suggests reduced spending and investment.
Analyzing these data points, sourced from reputable organizations like the Federal Reserve and the Bureau of Economic Analysis, provides a clearer picture of the current economic climate.
Assessing Recession Risks
The probability of a recession is a key concern. Economists offer differing perspectives, with some predicting a mild recession while others remain more optimistic. Monitoring these forecasts from reputable sources is vital in understanding the overall economic outlook.
Global Economic Factors
Global events significantly impact the U.S. economy and the Fed's decisions:
- Geopolitical instability: Conflicts and political tensions can disrupt supply chains and impact energy prices.
- Supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain issues continue to contribute to inflationary pressures.
Understanding these global factors is crucial for anticipating the Fed's response.
Market Reactions and Implications
Stock Market Response
The stock market's reaction to previous U.S. Federal Reserve rate decisions provides insights into potential future responses. Rate hikes often lead to short-term market volatility, but the long-term impact depends on various factors, including the pace and magnitude of rate increases and the overall economic outlook.
Impact on Bond Yields
The Fed's decision directly impacts bond yields. Higher interest rates generally lead to higher bond yields, impacting the fixed-income market.
Currency Exchange Rates
Changes in U.S. interest rates influence the value of the U.S. dollar. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investment, strengthening the dollar against other currencies.
Conclusion: Understanding the U.S. Federal Reserve Rate Decision and its Future Implications
The U.S. Federal Reserve rate decision is a complex issue with significant implications for the U.S. and global economies. The Fed faces the challenge of balancing inflation control with economic growth, navigating persistent inflationary pressures, and considering various economic indicators and global factors. The impact of the decision will ripple through the stock market, bond yields, and currency exchange rates. The future path of interest rates remains uncertain, and continuous monitoring of economic data will be critical in understanding the ongoing economic trajectory.
Stay informed about future U.S. Federal Reserve rate decisions to make informed financial decisions. Consult with a financial advisor to discuss how these rate changes may impact your personal financial strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 Epstein Files Pam Bondis Announcement And What It Means
May 09, 2025
Epstein Files Pam Bondis Announcement And What It Means
May 09, 2025 -
 Aeroport Permi Zakryt Iz Za Snegopada Chto Nuzhno Znat Passazhiram
May 09, 2025
Aeroport Permi Zakryt Iz Za Snegopada Chto Nuzhno Znat Passazhiram
May 09, 2025 -
 Daycare Debate Psychologist Sparks Outrage With Harmful Claims
May 09, 2025
Daycare Debate Psychologist Sparks Outrage With Harmful Claims
May 09, 2025 -
 From Wolves To Europes Best The Unlikely Success Story
May 09, 2025
From Wolves To Europes Best The Unlikely Success Story
May 09, 2025 -
 Jeanine Pirros Controversial Remarks On Due Process And El Salvador Prison Transfers
May 09, 2025
Jeanine Pirros Controversial Remarks On Due Process And El Salvador Prison Transfers
May 09, 2025
