U.S. Penny Phase-Out: No More Pennies In Circulation By Early 2026

Table of Contents
The Economic Case for Eliminating the Penny
Rising Production Costs
The cost to produce a penny currently exceeds its face value, making its continued circulation economically unsustainable. The U.S. Mint's production costs are a significant factor in this debate.
- Current Cost: Reports suggest the cost to produce a single penny is significantly higher than one cent. Precise figures vary depending on the source and year, but it's consistently above the penny's value. (Source citations needed here – e.g., "U.S. Mint Annual Report 2023," relevant news articles).
- Material Costs: Pennies are primarily composed of zinc, with a small amount of copper plating. Fluctuations in the price of these metals directly impact production costs.
- Environmental Impact: The extraction, processing, and transportation of these materials contribute to environmental concerns, adding another layer to the cost analysis beyond the purely monetary.
Inefficiency in Transactions
Pennies slow down transactions, particularly in cash-based systems, leading to lost productivity and increased labor costs.
- Time Consumption: Handling and counting pennies adds considerable time to transactions, especially for businesses processing large volumes of cash. This inefficiency translates to lost employee time and reduced productivity.
- Labor Costs: The time spent handling pennies directly increases labor costs for businesses. This hidden cost is often overlooked in the broader economic discussion surrounding penny elimination.
- Reduced Efficiency: A pennyless system could significantly streamline transactions, improving efficiency for both businesses and consumers. Studies focusing on transaction speeds in countries without low-value coins could provide further data.
Public Perception and Support
Gauging public opinion on the penny's elimination is crucial. Analyzing polls, surveys, and news articles reveals a mixed but evolving public perspective.
- Polling Data: While initial reactions often show resistance to change, recent polls may reflect a shift in public opinion. (Cite specific polls and surveys here, noting the methodologies and dates).
- Addressing Concerns: Many concerns revolve around price increases and potential rounding disadvantages. Addressing these anxieties through transparent communication is vital for gaining public acceptance.
- Nostalgia Factor: The sentimental value attached to the penny shouldn't be underestimated. Addressing this emotional aspect in any public communication strategy is essential.
Potential Challenges and Concerns of a Pennyless Future
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
A pennyless system necessitates adjustments for businesses and consumers.
- Pricing Strategies: Businesses will need to adjust their pricing strategies, potentially leading to price rounding. This could affect both consumer purchasing decisions and business profitability.
- Consumer Adaptation: Consumers will need to adapt to a system without pennies, potentially leading to some initial confusion or adjustment period. Clear communication about rounding practices is crucial for a smooth transition.
- Potential for Price Increases: While some argue a pennyless system will lead to cost savings, concerns remain about businesses using the transition as an opportunity to round up prices, effectively creating a hidden price increase.
Transitioning to a Pennyless System
Removing pennies from circulation poses significant logistical challenges.
- Collection and Removal: A comprehensive plan is needed for collecting and removing billions of pennies from circulation. This might involve encouraging banks and other financial institutions to participate in the collection process.
- Public Awareness Campaign: A large-scale public awareness campaign is essential to inform the public about the change and the new rounding practices. This campaign must address concerns and provide clear, easily understandable information.
- Timeline and Implementation: A phased approach might be more feasible than an immediate, complete elimination, allowing for gradual adaptation and mitigating potential disruptions.
Alternative Rounding Methods
Various rounding methods could be employed.
- Rounding to the Nearest Nickel: This is a common method in other countries without low-value coins. It's relatively simple to understand and implement.
- Rounding Up or Down: This method requires clear guidelines to ensure fairness and avoid potential bias toward price increases.
- Impact Assessment: A thorough cost-benefit analysis of each rounding method is necessary to determine the most equitable and efficient solution for all stakeholders.
The Proposed 2026 Timeline and its Feasibility
Legislative and Regulatory Hurdles
Implementing a penny phase-out by 2026 faces significant legislative and regulatory hurdles.
- Congressional Action: Legislative approval is necessary to authorize the elimination of the penny. This requires navigating political processes and potential opposition from various stakeholders.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes to existing regulations governing currency and financial transactions will be necessary.
- Lobbying Efforts: Expect lobbying efforts from various interest groups, potentially delaying or influencing the legislative process.
Public Awareness Campaigns
A successful public awareness campaign is crucial.
- Key Messages: The campaign should clearly communicate the economic benefits, the planned transition timeline, and the chosen rounding method. Addressing public concerns directly and transparently is vital.
- Effective Communication Channels: Utilize a multi-channel approach, leveraging print, broadcast, and digital media to reach diverse audiences.
- Targeted Messaging: Tailor messaging to specific demographics, addressing their unique concerns and needs effectively.
Conclusion
The potential phase-out of the U.S. penny by early 2026 presents a complex scenario with both economic advantages and logistical challenges. While eliminating the penny could streamline transactions and save money on production costs, careful planning and public education are vital for a smooth transition. Understanding the economic arguments for and against a pennyless future is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. Stay informed about the progress of this ongoing debate to prepare for the potential end of the penny in circulation. Continue to research the implications of the penny phase-out and prepare for a pennyless future.

Featured Posts
-
 Sistema Frontal Y Vaguada Causaran Lluvias Este Sabado
May 23, 2025
Sistema Frontal Y Vaguada Causaran Lluvias Este Sabado
May 23, 2025 -
 Vybz Kartel Sold Out Brooklyn Shows Impress Fans
May 23, 2025
Vybz Kartel Sold Out Brooklyn Shows Impress Fans
May 23, 2025 -
 Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Essential Rock 101 Information
May 23, 2025
Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 Essential Rock 101 Information
May 23, 2025 -
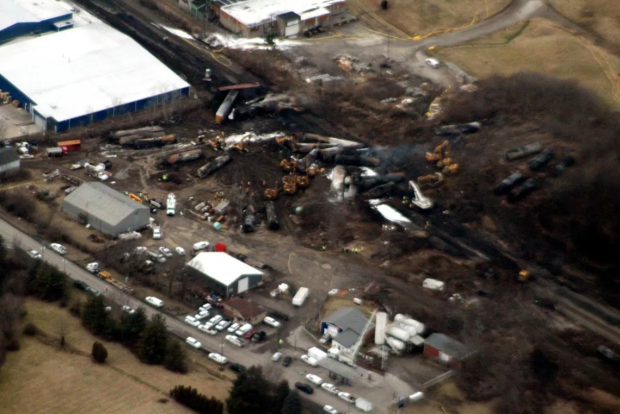 Ohio Train Derailment The Prolonged Presence Of Toxic Chemicals In Structures
May 23, 2025
Ohio Train Derailment The Prolonged Presence Of Toxic Chemicals In Structures
May 23, 2025 -
 From Bishop To Viral Tik Tok Star Womans Unforgettable Story
May 23, 2025
From Bishop To Viral Tik Tok Star Womans Unforgettable Story
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Bjk Cup Kazakhstan Wins Australia Eliminated
May 23, 2025
Bjk Cup Kazakhstan Wins Australia Eliminated
May 23, 2025 -
 Smotret Onlayn Rybakina Srazhaetsya Za 4 Milliarda Na Turnire
May 23, 2025
Smotret Onlayn Rybakina Srazhaetsya Za 4 Milliarda Na Turnire
May 23, 2025 -
 Australias Bjk Cup Run Ends Kazakhstan Reaches Finals
May 23, 2025
Australias Bjk Cup Run Ends Kazakhstan Reaches Finals
May 23, 2025 -
 Pryamaya Translyatsiya Rybakina Protiv Eks Tretey Raketki Mira Za 4 Milliarda
May 23, 2025
Pryamaya Translyatsiya Rybakina Protiv Eks Tretey Raketki Mira Za 4 Milliarda
May 23, 2025 -
 Final Kubka Billi Dzhin King Kazakhstan Prodolzhaet Pobednuyu Seriyu
May 23, 2025
Final Kubka Billi Dzhin King Kazakhstan Prodolzhaet Pobednuyu Seriyu
May 23, 2025
