Analysis: 0.2% Contraction Of The U.S. Economy - Spending And Tariff Factors
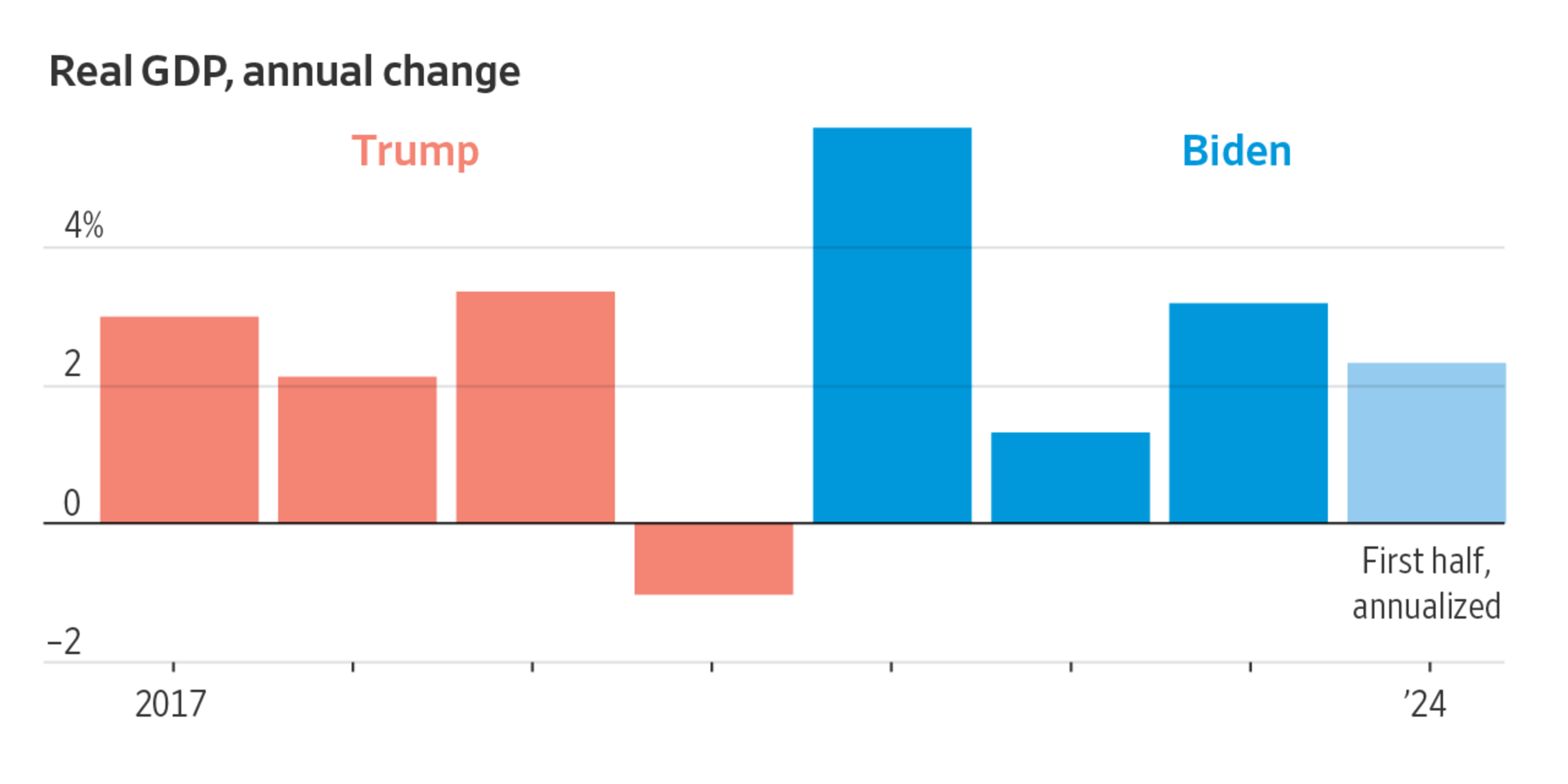
Table of Contents
The Role of Consumer Spending in the Economic Contraction
Consumer spending is the backbone of the U.S. economy, accounting for roughly 70% of economic activity. Any significant decline in consumer spending directly impacts overall economic growth. The recent slowdown is, in part, attributable to a weakening in consumer confidence and shifts in spending patterns.
Decreased Consumer Confidence
Several factors have contributed to a decline in consumer confidence, leading to reduced spending.
- High Inflation: Persistently high inflation has eroded purchasing power, leaving consumers with less disposable income. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) consistently exceeding expectations throughout 2023 points to this persistent pressure.
- Rising Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve's aggressive interest rate hikes, aimed at combating inflation, have increased borrowing costs for consumers. This makes it more expensive to finance purchases like homes and cars, dampening demand. The prime rate increase directly impacts consumer loan rates.
- Negative Consumer Sentiment Indices: Surveys such as the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index and the Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index have shown a consistent decline in consumer optimism, reflecting anxieties about the economy.
Shift in Consumer Spending Patterns
Beyond decreased confidence, consumers have also altered their spending habits.
- Reduced Discretionary Spending: Consumers are cutting back on non-essential goods and services, impacting sectors like retail and hospitality. Restaurants and entertainment venues have reported decreased sales.
- Increased Savings Rate: Faced with economic uncertainty, many consumers are increasing their savings rate, reducing their spending on both necessities and discretionary items.
- Supply Chain Issues: Ongoing supply chain disruptions continue to affect the availability and pricing of goods, further impacting consumer spending decisions. This uncertainty leads to delayed purchases or reduced spending.
The Impact of Tariffs on Economic Activity
Tariffs, taxes imposed on imported goods, play a significant role in shaping economic activity. Their impact on the recent U.S. economy slowdown is multifaceted.
Increased Import Costs
Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers and businesses.
- Examples of Tariff-Affected Goods: Numerous goods, ranging from agricultural products to manufactured goods, have faced increased costs due to tariffs. This includes specific examples like steel and aluminum.
- Ripple Effect on Businesses and Consumers: Higher import costs are passed down the supply chain, affecting businesses' production costs and reducing consumer purchasing power.
- Contribution to Inflation: Increased import costs contribute to overall inflation, further eroding consumer purchasing power and dampening economic growth.
Trade Wars and Retaliatory Measures
Trade disputes and retaliatory tariffs exacerbate the negative impact on economic activity.
- Trade Conflicts Affecting the U.S. Economy: Ongoing trade tensions with various countries have resulted in retaliatory tariffs, further disrupting global trade flows and increasing costs.
- Impact on International Trade Relationships: The imposition of tariffs damages international trade relationships, harming both exporting and importing nations.
- Effect on Specific Industries: Industries like agriculture and manufacturing have been disproportionately affected by trade wars and tariffs, leading to job losses and reduced output.
Other Contributing Factors to the U.S. Economy Slowdown
While consumer spending and tariffs are significant factors, other elements also contributed to the recent economic contraction.
Inventory Adjustments
Businesses reducing inventories to align with slowing demand contributed to the decline in GDP. This reduction in inventory investment directly impacts economic output.
Government Spending
Changes in government spending, both at the federal and state levels, can influence economic growth. Reductions in government spending can contribute to a slowdown.
Global Economic Uncertainty
Global factors, such as geopolitical instability and high energy prices, contribute to uncertainty and negatively impact economic growth. These external pressures add complexity to the domestic economic picture.
Understanding the 0.2% Contraction and its Implications for the Future of the U.S. Economy
The 0.2% contraction in the U.S. economy is a result of a confluence of factors, with decreased consumer spending and the impact of tariffs playing significant roles. The outlook for the future depends heavily on the trajectory of inflation, consumer confidence, and international trade relations. A sustained period of high inflation, weak consumer sentiment, and ongoing trade tensions could further impede economic growth. Conversely, a decline in inflation, improved consumer confidence, and a de-escalation of trade disputes could foster a recovery.
Stay tuned for further analysis of the U.S. economy slowdown and its implications. Understanding the interplay of these factors is critical for navigating the current economic challenges and ensuring a strong and stable future for the U.S. economy. Continue to monitor the evolving situation regarding the U.S. economy contraction and tariff impacts for a comprehensive understanding.
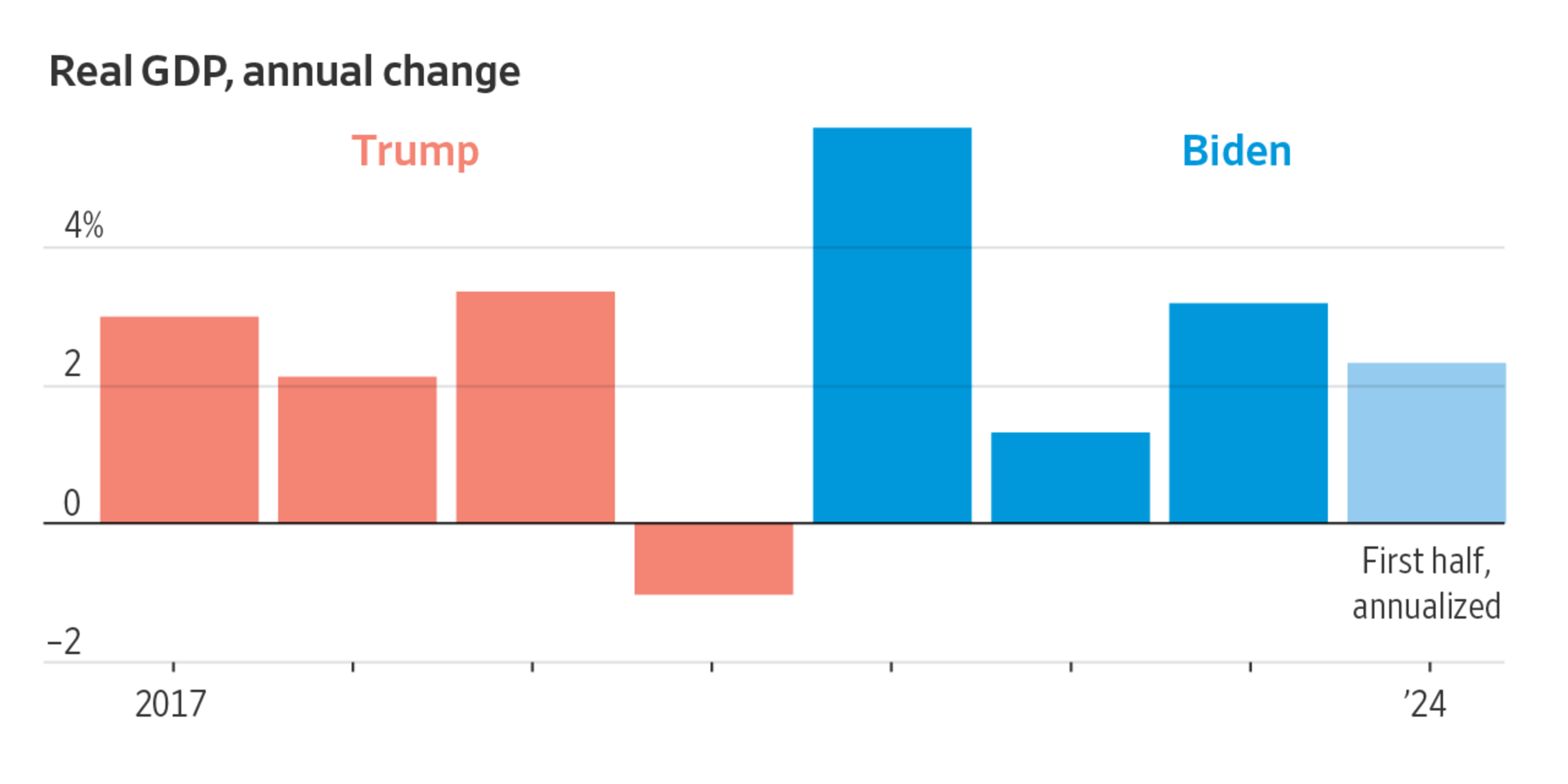
Featured Posts
-
 Rachel Reeves And The Legacy Of Arthur Scargill A Political Comparison
May 31, 2025
Rachel Reeves And The Legacy Of Arthur Scargill A Political Comparison
May 31, 2025 -
 Manitoba Wildfires Crews Fight Deadly Spreading Blazes
May 31, 2025
Manitoba Wildfires Crews Fight Deadly Spreading Blazes
May 31, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers Thursday April 10
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers Thursday April 10
May 31, 2025 -
 Salt Lake City Supercross Your Complete Guide To The Races
May 31, 2025
Salt Lake City Supercross Your Complete Guide To The Races
May 31, 2025 -
 Jack White Joins Detroit Tigers Broadcast Hall Of Fame Discussion And Baseball Talk
May 31, 2025
Jack White Joins Detroit Tigers Broadcast Hall Of Fame Discussion And Baseball Talk
May 31, 2025
