Anti-Fungal Resistance: Why Deadly Fungi Pose A Serious Threat
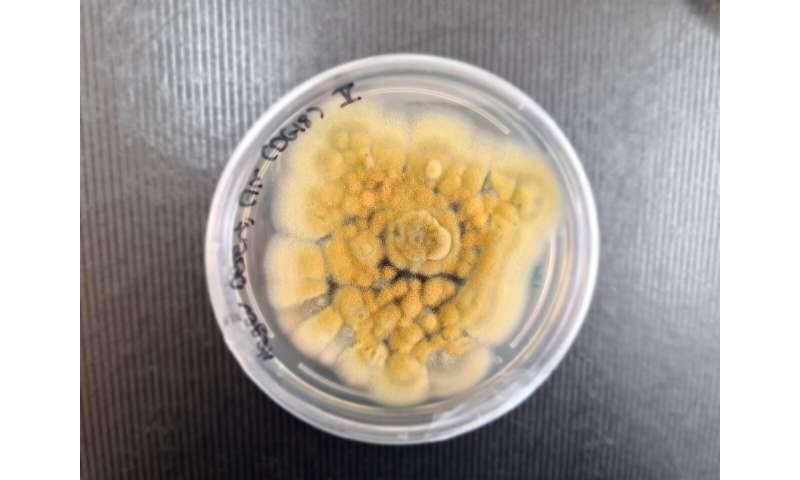
Table of Contents
The Rising Threat of Antifungal-Resistant Fungi
The emergence of antifungal-resistant fungi poses a significant threat to global health. These resistant strains are becoming increasingly prevalent, making infections harder to treat and increasing morbidity and mortality rates.
Mechanisms of Antifungal Resistance: Fungi develop resistance through several mechanisms:
- Target Modification: Fungi alter the target site of the antifungal drug, making it ineffective. For example, Candida albicans can modify its ergosterol biosynthesis pathway, reducing the effectiveness of azoles.
- Efflux Pumps: Fungi utilize efflux pumps to actively expel antifungal drugs from their cells, preventing them from reaching their target. This mechanism is common in Candida species and Aspergillus fumigatus.
- Altered Cell Wall Synthesis: Changes in cell wall composition can reduce the effectiveness of antifungal drugs targeting the cell wall, such as echinocandins. This is observed in some Candida and Aspergillus species.
Examples of fungi developing significant resistance include Candida auris, a particularly concerning multi-drug resistant species, and increasingly azole-resistant strains of Aspergillus fumigatus.
Factors Contributing to the Rise of Antifungal Resistance: Several factors contribute to the rise of antifungal resistance:
- Overuse and Misuse of Antifungals: Overprescription of antifungals in human medicine and their widespread use in agriculture (e.g., in animal feed) contribute to the selection and proliferation of resistant strains.
- Inadequate Infection Control Measures: Poor hygiene practices in healthcare settings and a lack of stringent infection control protocols facilitate the spread of resistant fungi.
- Lack of New Drug Development: The pipeline of new antifungal drugs is limited, leaving few options for treating resistant infections. The high cost and long development time for new antifungals are significant barriers.
Impact of Antifungal Resistance on Human Health
The consequences of antifungal resistance are severe, impacting both individual patients and healthcare systems globally.
Increased Morbidity and Mortality: Infections caused by resistant fungi are often more severe and have higher mortality rates compared to their susceptible counterparts. For example, Candida auris infections are associated with high mortality rates, especially in immunocompromised individuals. Similarly, treatment failures in Aspergillus fumigatus infections due to azole resistance significantly increase mortality risk.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosing antifungal-resistant infections can be challenging, requiring specialized laboratory testing that may not be readily available in all settings. Treatment options are limited, often involving prolonged courses of therapy with potentially toxic drugs, leading to increased treatment costs and lengths of hospital stays.
Strategies to Combat Antifungal Resistance
Combating antifungal resistance requires a multi-pronged approach involving responsible use of antifungals, development of new therapies, and strengthening infection control measures.
Responsible Antifungal Use: Appropriate prescribing practices by healthcare professionals and adherence to treatment regimens by patients are crucial. This includes:
- Only using antifungals when necessary and selecting the most appropriate drug and dose.
- Completing the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve.
- Implementing stewardship programs to optimize antifungal use within healthcare institutions.
Developing New Antifungal Drugs and Therapies: Intensified research and development are essential for discovering and developing new antifungal agents with novel mechanisms of action. This includes exploring:
- New drug targets within fungi.
- Repurposing existing drugs.
- Investigating alternative therapies such as immunotherapy and phage therapy.
Strengthening Infection Prevention and Control: Robust infection prevention and control measures in healthcare settings are critical to prevent the spread of resistant fungi. This involves:
- Strict adherence to hand hygiene protocols.
- Appropriate use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Environmental cleaning and disinfection.
Conclusion
The rise of antifungal resistance presents a significant and growing threat to global health. The limited treatment options, high mortality rates associated with resistant fungal infections, and the challenges in diagnosis underscore the urgency of the situation. Combating this challenge necessitates a concerted effort involving responsible antifungal use, investment in research and development of new antifungal drugs and therapies, and the implementation of robust infection prevention and control measures. Understanding and addressing antifungal resistance is crucial. Learn more about this growing threat and support initiatives promoting responsible antifungal use and the development of new treatments. Let's work together to prevent this deadly threat from becoming even more widespread.

Featured Posts
-
 New Superman Movie Clip Features Krypto
May 08, 2025
New Superman Movie Clip Features Krypto
May 08, 2025 -
 Forza Horizon 5 Ps 5 Release Date When Does It Unlock
May 08, 2025
Forza Horizon 5 Ps 5 Release Date When Does It Unlock
May 08, 2025 -
 Black Rock Etf Poised For 110 Growth Why Billionaires Are Investing
May 08, 2025
Black Rock Etf Poised For 110 Growth Why Billionaires Are Investing
May 08, 2025 -
 Analyzing Ethereums Price Wyckoff Accumulation And The Road To 2 700
May 08, 2025
Analyzing Ethereums Price Wyckoff Accumulation And The Road To 2 700
May 08, 2025 -
 Spk Aciklamasi Kripto Piyasalarinda Yeni Bir Doenem
May 08, 2025
Spk Aciklamasi Kripto Piyasalarinda Yeni Bir Doenem
May 08, 2025
