Did Trump's China Tariffs Cause Higher Prices And Product Shortages? An Economic Analysis

Table of Contents
The Mechanism of Tariffs and their Impact on Prices
Trump's tariffs on Chinese goods, ranging from steel and aluminum to consumer electronics and apparel, directly increased the cost of imported goods. This mechanism, fundamental to understanding the economic impact, operates by adding a percentage to the price of imported products at the point of entry into the US. This increased import cost is a form of cost-push inflation, where production costs rise, pushing up prices for consumers. The extent to which this cost is passed on to consumers, however, depends on several factors.
-
Analysis of specific tariff rates imposed on various Chinese goods: The tariff rates varied considerably depending on the product category. Some goods faced tariffs as high as 25%, while others saw lower rates. This variation created a complex and uneven impact across different sectors of the US economy.
-
Examination of data showing changes in consumer prices after tariff implementation: Statistical analysis of consumer price indices (CPI) following the implementation of the tariffs reveals a correlation between increased import costs and higher prices for consumers. However, isolating the precise impact of tariffs from other economic factors requires sophisticated econometric modelling.
-
Discussion of the role of elasticity of demand and supply in influencing price changes: The elasticity of demand and supply for specific goods plays a crucial role in determining how much of the tariff burden is absorbed by consumers versus producers. For goods with inelastic demand (meaning consumers are less responsive to price changes), a larger portion of the tariff is likely to be passed on to consumers.
-
Consideration of alternative explanations for price increases besides tariffs: While tariffs undeniably increased import costs, other factors contributed to price increases. These include global inflation, supply chain disruptions unrelated to tariffs, and increases in energy and commodity prices.
The Impact on Supply Chains and Product Availability
The Trump administration's tariffs disrupted global supply chains, exacerbating existing vulnerabilities and creating new challenges for businesses. The interconnected nature of global manufacturing means that trade restrictions in one area can have ripple effects throughout the entire system. Furthermore, retaliatory tariffs imposed by China in response to US tariffs further complicated the situation, adding another layer of disruption to the flow of goods.
-
Case studies of specific industries affected by supply chain disruptions due to tariffs: Industries heavily reliant on imported Chinese goods, such as electronics manufacturing and apparel, experienced significant disruptions. These disruptions manifested as delays, increased costs, and in some cases, temporary shortages.
-
Analysis of data on import volumes before and after tariff implementation: A decline in import volumes of certain goods from China following the implementation of tariffs supports the claim that these measures restricted the flow of goods into the US market.
-
Discussion of the role of retaliatory tariffs imposed by China: China responded to the US tariffs with its own retaliatory measures, further disrupting global supply chains and creating a "trade war" scenario that negatively impacted both economies.
-
Examination of the impact on small businesses and their reliance on imported goods: Small businesses, often with limited resources and less negotiating power, were disproportionately affected by the disruptions in supply chains and higher import costs.
Alternative Explanations for Price Increases and Shortages
Attributing price increases and shortages solely to the Trump tariffs would be an oversimplification. Several other factors contributed significantly to the economic landscape during that period. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, created unprecedented supply chain shocks, impacting the availability of goods globally and pushing up prices.
-
Analysis of global inflation trends during the period of tariff implementation: Global inflation was already rising prior to the implementation of the tariffs, creating a complex backdrop against which to assess the impact of the trade policies.
-
Discussion of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on supply chains and manufacturing: The pandemic-induced lockdowns and disruptions had a dramatic impact on global supply chains, compounding the effects of the tariffs. Factory shutdowns, port congestion, and transportation bottlenecks all contributed to shortages and price increases.
-
Examination of the role of changes in oil prices and other commodity prices: Fluctuations in oil and other commodity prices also played a role in driving up inflation during this period, independent of the tariffs.
-
Differentiation between demand-pull and cost-push inflation in explaining price changes: While the tariffs primarily contributed to cost-push inflation, demand-pull inflation (due to increased demand exceeding supply) also played a role in driving up prices for certain goods.
Assessing the Overall Economic Impact
Determining the net economic effect of Trump's China tariffs requires careful consideration of both costs and benefits. While proponents argued that the tariffs protected domestic industries and created jobs, critics pointed to higher consumer prices and supply chain disruptions as significant drawbacks.
-
Overview of studies examining the overall economic costs and benefits of the tariffs: Numerous economic studies have attempted to quantify the costs and benefits, with varying conclusions. The lack of consensus underscores the complexity of disentangling the impact of tariffs from other confounding economic factors.
-
Discussion of the impact on the US trade balance with China: The impact on the US trade balance with China was mixed, with some goods seeing decreased imports while others experienced increased imports from other countries.
-
Analysis of the impact on US GDP growth and job creation: The impact on GDP growth and job creation is similarly debated, with some studies suggesting a negative impact and others showing a neutral or even slightly positive effect.
Conclusion
This analysis explored the multifaceted impact of Trump's China tariffs on the US economy, examining their influence on prices, supply chains, and overall economic well-being. While the tariffs aimed to protect certain industries, the evidence suggests a complex interplay of factors affecting consumer prices and product availability. The impact was not solely attributable to tariffs, with global events like the COVID-19 pandemic also playing a significant role. Further research is needed to definitively quantify the specific contribution of the tariffs to the observed economic changes. Understanding the full economic consequences of such policies requires a nuanced approach that considers both the intended and unintended ramifications. To delve deeper into the complexities of this crucial economic issue, further research into the effects of Trump's China tariffs is encouraged.

Featured Posts
-
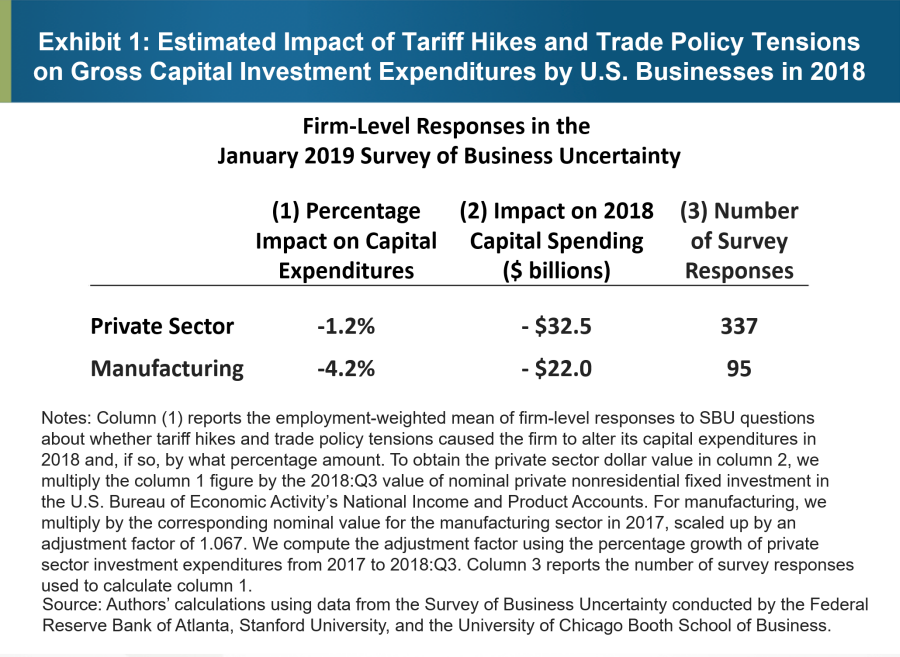 Tariff Uncertainty Drives U S Businesses To Cut Costs
Apr 29, 2025
Tariff Uncertainty Drives U S Businesses To Cut Costs
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Adult Adhd From Suspicion To Support And Management
Apr 29, 2025
Adult Adhd From Suspicion To Support And Management
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Koezuti Porsche F1 Motorral Felszerelve
Apr 29, 2025
Koezuti Porsche F1 Motorral Felszerelve
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Analyzing Tylor Megills Recent Success Key Factors Contributing To His Mets Wins
Apr 29, 2025
Analyzing Tylor Megills Recent Success Key Factors Contributing To His Mets Wins
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Show Canceled Due To Severe Ohio River Flooding
Apr 29, 2025
Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Show Canceled Due To Severe Ohio River Flooding
Apr 29, 2025
