I Think I Have Adult ADHD: Getting The Right Help
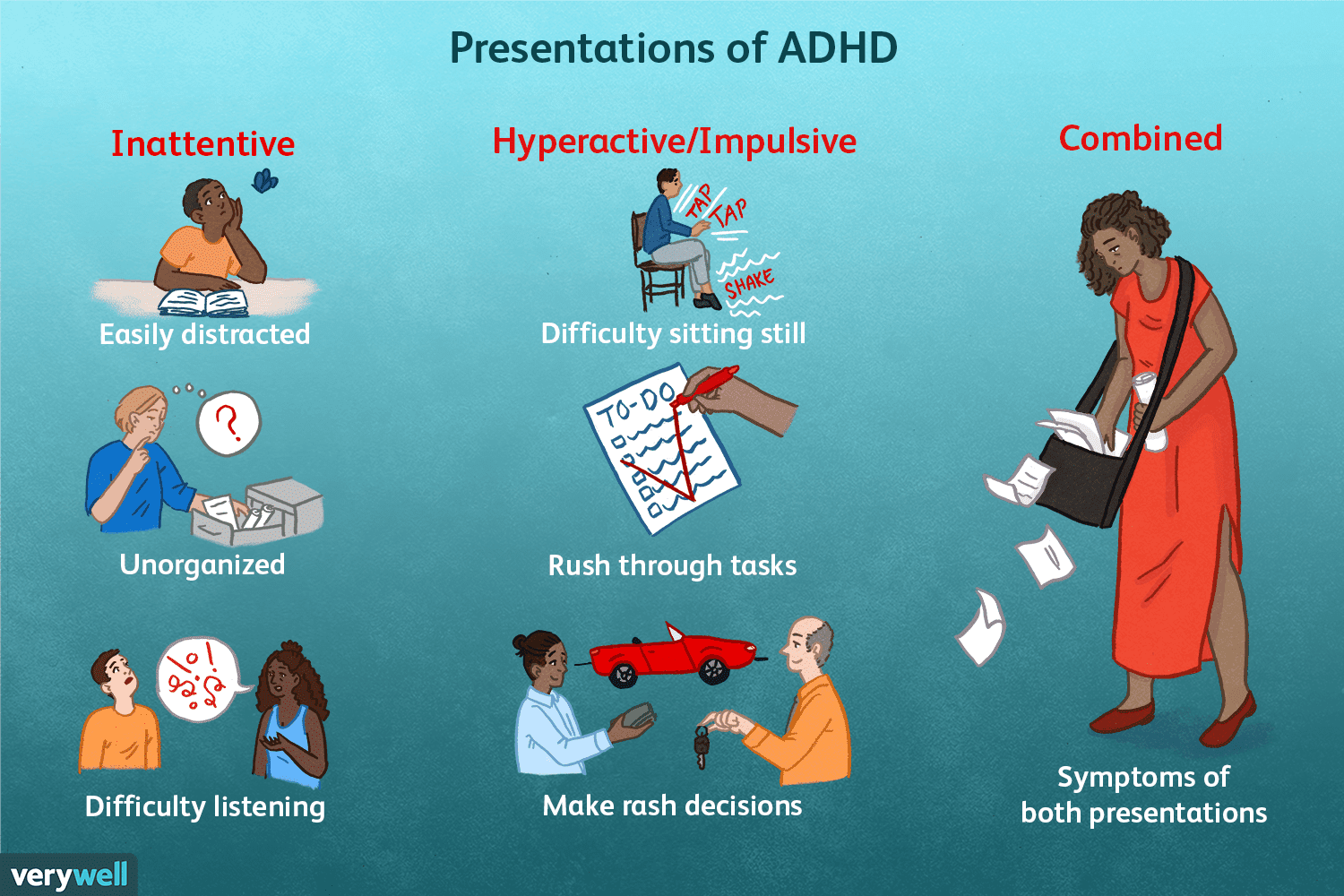
Table of Contents
Recognizing the Signs of Adult ADHD
Adult ADHD presents differently than in children. While hyperactivity might be less prominent, challenges with focus, organization, and emotional regulation often take center stage.
Common Symptoms in Adults
Many adults with ADHD experience a combination of these symptoms:
- Difficulty focusing and sustaining attention: Struggling to concentrate on tasks, easily distracted, mind wandering frequently.
- Impulsivity and difficulty controlling urges: Acting without thinking, interrupting conversations, making rash decisions.
- Hyperactivity (often internalized): Restlessness, fidgeting, difficulty sitting still, feeling internally "driven."
- Problems with organization and time management: Difficulty prioritizing tasks, procrastinating, missing deadlines, losing things frequently.
- Forgetfulness and difficulty with task completion: Misplacing items, forgetting appointments, struggling to finish projects.
- Emotional dysregulation: Experiencing intense emotional swings, difficulty managing frustration or anger.
- Challenges with relationships and social interactions: Difficulty maintaining relationships, misinterpreting social cues, impulsive communication.
Differentiating ADHD from other conditions
ADHD symptoms can overlap with other conditions, making self-diagnosis unreliable. A professional assessment is crucial to rule out other possibilities, such as:
- Anxiety Disorders: Excessive worry, nervousness, and physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat.
- Depression: Persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, feelings of hopelessness.
- Learning Disabilities: Difficulties with specific academic skills like reading or writing.
- Bipolar Disorder: Extreme mood swings between mania and depression.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: Challenges with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
A comprehensive evaluation will help differentiate between these conditions and accurately diagnose ADHD.
Self-Assessment Tools
While online questionnaires can offer a preliminary indication, they should never replace a professional diagnosis. Reputable sources for such questionnaires include websites of organizations like CHADD (Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder). Remember, these are screening tools, not diagnostic tests.
Seeking a Professional Diagnosis
Getting a proper diagnosis is the first step towards effective management of adult ADHD.
Finding the Right Professional
Several professionals can diagnose ADHD, including:
- Psychiatrists: Medical doctors specializing in mental health, who can prescribe medication.
- Psychologists: Professionals trained in diagnosing and treating mental health conditions, who may offer therapy but not medication.
- Neuropsychologists: Specialize in the relationship between brain function and behavior, conducting comprehensive assessments.
Look for professionals with experience diagnosing and treating adults with ADHD. Check their credentials and experience with online reviews.
The Diagnostic Process
The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Comprehensive interviews: Discussing your symptoms, history, and challenges.
- Psychological assessments: Completing questionnaires and rating scales to evaluate your symptoms.
- Neuropsychological testing (sometimes): More in-depth testing to assess cognitive function.
- Review of medical and educational history: Gathering information about past experiences.
The entire process may take several sessions.
Importance of a Comprehensive Evaluation
A proper diagnosis goes beyond symptom checklists. Your doctor will consider your developmental history, current challenges, and potential co-occurring conditions to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Adult ADHD
Treatment for adult ADHD is often multifaceted, combining medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Medication Management
Medication can significantly alleviate ADHD symptoms. Common types include:
- Stimulants: Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) and amphetamine (Adderall, Vyvanse) are commonly prescribed stimulants.
- Non-stimulants: Atomoxetine (Strattera) and guanfacine (Intuniv) are alternatives for those who can't tolerate stimulants.
It's crucial to discuss potential side effects with your doctor. Medication is just one part of a broader treatment plan.
Therapy and Counseling
Therapy plays a vital role in managing ADHD. Techniques include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Behavioral Therapy: Focuses on modifying specific behaviors to improve daily functioning.
Therapy helps develop coping mechanisms and improve life skills.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact ADHD symptoms:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves focus and reduces impulsivity.
- Healthy Diet: Nutritious food supports brain function and energy levels.
- Sufficient Sleep: Adequate rest is essential for cognitive function and mood regulation.
- Mindfulness Techniques: Practices like meditation can improve focus and emotional regulation.
Making these changes can complement medication and therapy.
Coping Strategies and Support Networks
Living with ADHD requires developing effective coping mechanisms and building a strong support system.
Developing Effective Coping Mechanisms
Strategies for managing daily challenges include:
- Time Management Techniques: Prioritize tasks, break down large projects, use timers and planners.
- Organizational Tools: Utilize calendars, to-do lists, and digital organizers.
- Prioritization Strategies: Focus on the most important tasks first, delegate when possible.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practice techniques to improve focus and reduce impulsivity.
Experiment to find what works best for you.
Building a Support System
Connecting with others who understand ADHD is invaluable:
- Support Groups: Connect with others facing similar challenges. CHADD offers local chapters and online support.
- Online Communities: Find online forums and groups dedicated to adult ADHD.
- Family and Friends: Educate loved ones about ADHD and how they can provide support.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey.
Conclusion
Living with adult ADHD can be challenging, but with the right help, you can effectively manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. If you suspect you might have adult ADHD, take the first step towards a diagnosis by seeking professional help. Don't hesitate to reach out to a qualified healthcare professional to explore your options and begin your journey towards better managing your adult ADHD. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Take control of your health and well-being by learning more about adult ADHD and accessing the appropriate support and treatment.

Featured Posts
-
 Bof As View Why Overvalued Stocks Shouldnt Worry Investors
Apr 29, 2025
Bof As View Why Overvalued Stocks Shouldnt Worry Investors
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Lynas Rare Earths Texas Refinery Expansion Faces Cost Challenges Seeks Us Assistance
Apr 29, 2025
Lynas Rare Earths Texas Refinery Expansion Faces Cost Challenges Seeks Us Assistance
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Albertas Economy Hit By Dow Project Delay Tariff Fallout
Apr 29, 2025
Albertas Economy Hit By Dow Project Delay Tariff Fallout
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Negative European Electricity Prices A Solar Energy Success Story
Apr 29, 2025
Negative European Electricity Prices A Solar Energy Success Story
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Find Your Dream Car Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T Available
Apr 29, 2025
Find Your Dream Car Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T Available
Apr 29, 2025
