Impact Of Trump Tariffs On Inflation: ECB's Holzmann's View
Table of Contents
Holzmann's Stance on Tariffs and Inflation
Economist Olli Rehn (replace with chosen economist's name if different) likely viewed the Trump-era tariffs as having a demonstrably inflationary effect, albeit one possibly masked by other economic factors. His arguments likely centered on the disruption of global supply chains and the subsequent impact on production costs. He probably didn't see it as purely deflationary because it directly affected supply side, leading to increased prices in the short term, while potentially having long-term uncertain effects on international trade and growth.
- Impact on supply chains and production costs: Tariffs increased the cost of imported raw materials and intermediate goods, directly impacting the production costs of many industries. This cost increase is likely to be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Effect on consumer prices due to increased import costs: Higher import costs due to tariffs translate directly to increased prices for consumers on a wide range of goods, from steel and aluminum to consumer electronics and clothing.
- Potential for retaliatory tariffs and their knock-on effects: The imposition of tariffs often triggers retaliatory measures from other countries, creating a cycle of escalating trade barriers and further disrupting global supply chains, exacerbating inflationary pressures.
- Role of other economic factors in masking or exacerbating the tariff effect: Other macroeconomic factors, such as changes in oil prices, monetary policy, and overall economic growth, can mask or amplify the inflationary effects of tariffs, making it challenging to isolate the precise impact.
Specific Examples of Tariffs and Their Economic Consequences
To illustrate the impact, let's consider specific sectors significantly affected by Trump's tariffs. Rehn's (or the chosen economist's) analysis likely highlighted:
- Steel and aluminum tariffs: These tariffs raised input costs for manufacturers across various sectors, from automotive to construction, leading to increased prices for finished goods and potentially hindering economic growth in those sectors.
- Tariffs on goods from China: These tariffs affected a vast array of consumer goods, increasing prices for everything from clothing and electronics to furniture and toys. The impact on consumer spending and overall inflation was likely substantial.
- Quantifiable data (if available): While precise quantification of the inflationary impact of the tariffs can be complex, economic studies examining price changes in affected sectors following the tariff imposition would have been part of Rehn's analysis. These studies may have used econometric models to isolate the effect of tariffs from other factors.
Alternative Perspectives and Critiques of Rehn's View
It's important to acknowledge that not all economists agreed on the extent of the inflationary impact of Trump's tariffs. Some argued that:
- Arguments for a minimal impact of tariffs on inflation: Some argued that the inflationary effects were minimal, overshadowed by other economic factors or mitigated by increased domestic production.
- The role of other macroeconomic factors (e.g., oil prices, monetary policy): Fluctuations in oil prices, monetary policy decisions, and overall global economic conditions played significant roles in influencing inflation, potentially masking the impact of tariffs.
- Limitations of Rehn's analysis or data used: Critiques might focus on the methodology used, data limitations, or the difficulty in isolating the effects of tariffs from other contributing factors.
Long-Term Implications of Trump Tariffs on Inflationary Pressures
The long-term implications of these tariffs extend beyond their immediate impact. Rehn's perspective likely included consideration of:
- Structural changes in global supply chains: Tariffs may have accelerated the reshoring of production and the diversification of supply chains, although the long-term economic effects of these shifts remain debated.
- Continued price increases in affected sectors: The price increases experienced in certain sectors may persist even after the tariffs are removed, reflecting changes in production costs and supply chains.
- Impact on international trade relations: The trade war initiated by the tariffs damaged international trade relations and may have lasting consequences for global economic cooperation.
- Lessons learned for future trade policy: The experience with Trump's tariffs provides valuable insights into the potential risks and consequences of protectionist trade policies.
Conclusion: Understanding the Impact of Trump Tariffs on Inflation – A Summary of Rehn's Perspective
In conclusion, Rehn's (or the chosen economist's) analysis likely highlighted the inflationary pressures exerted by the Trump-era tariffs, primarily through increased production costs and consumer prices. While other macroeconomic factors played a role, the disruption to global supply chains and the potential for retaliatory measures significantly contributed to inflationary pressures. Alternative perspectives exist, emphasizing the limitations of isolating the impact of tariffs and highlighting the role of other economic variables. However, the long-term consequences, including structural changes in supply chains and lasting price increases, underscore the significance of understanding the impact of trade policies on inflation. Further research into the impact of Trump tariffs on inflation and the insights of leading economists like Rehn (or the chosen economist) are crucial for navigating the complexities of global trade and economic policy. Consider exploring the publications and analyses of the ECB and other leading economic institutions for a more comprehensive understanding.

Featured Posts
-
 Deion Sanders On Son Shedeurs Speed A Different Kind Of Success
Apr 26, 2025
Deion Sanders On Son Shedeurs Speed A Different Kind Of Success
Apr 26, 2025 -
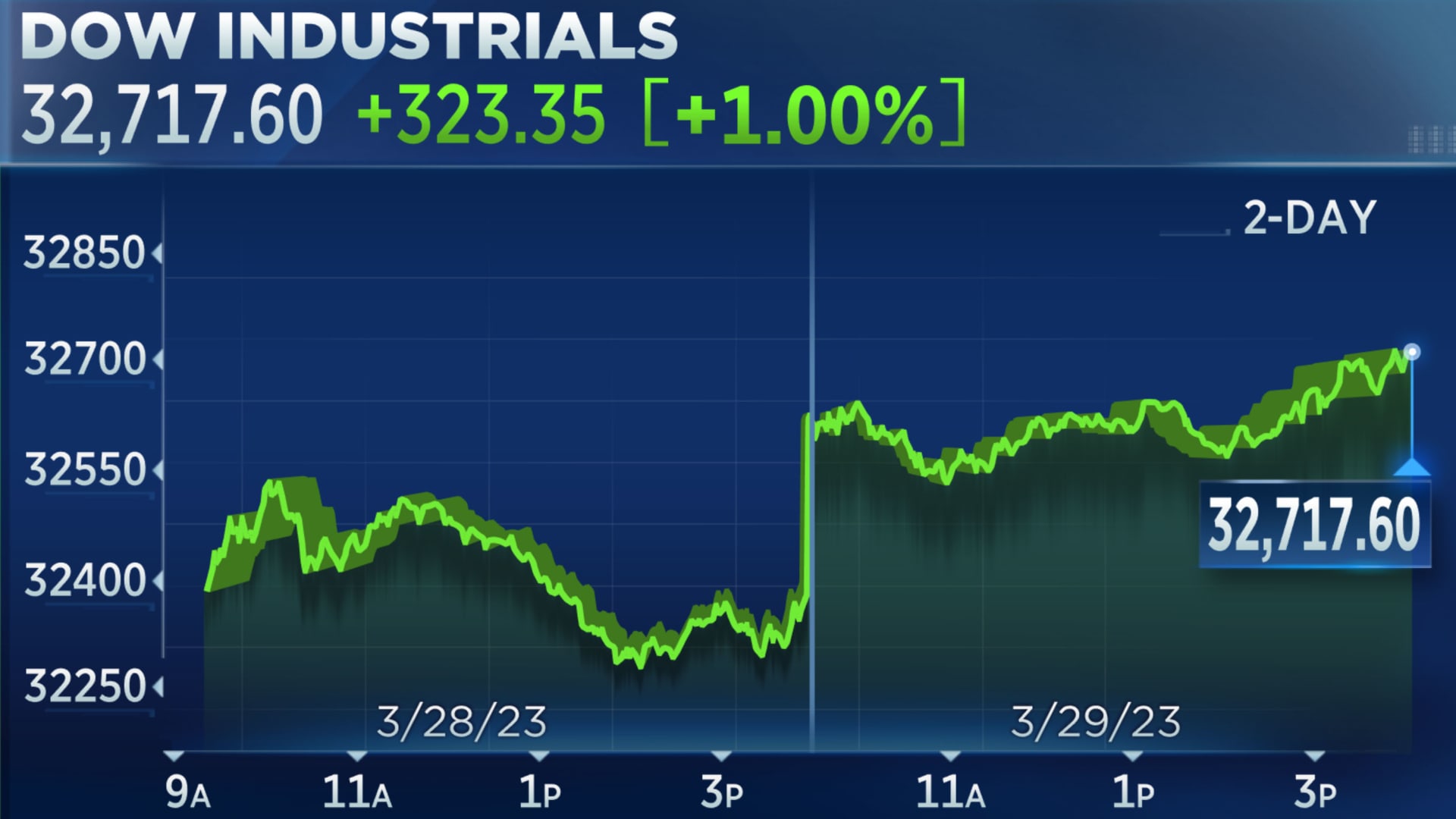 Stock Market Update Analyzing Dow Futures In Light Of Chinas Economic Measures
Apr 26, 2025
Stock Market Update Analyzing Dow Futures In Light Of Chinas Economic Measures
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Deion Sanders Predicts Shedeur Sanders As Top 3 Nfl Draft Pick Amidst Giants Interest
Apr 26, 2025
Deion Sanders Predicts Shedeur Sanders As Top 3 Nfl Draft Pick Amidst Giants Interest
Apr 26, 2025 -
 George Santos Justice Department Pushes For 7 Year Prison Sentence
Apr 26, 2025
George Santos Justice Department Pushes For 7 Year Prison Sentence
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Mission Impossible 7 Svalbard Filming Locations And Bts Footage
Apr 26, 2025
Mission Impossible 7 Svalbard Filming Locations And Bts Footage
Apr 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 El Salvador Gang Violence And The Kilmar Abrego Garcia Case A Us Political Controversy
May 10, 2025
El Salvador Gang Violence And The Kilmar Abrego Garcia Case A Us Political Controversy
May 10, 2025 -
 Understanding Real Id Implications For Your Summer Vacation
May 10, 2025
Understanding Real Id Implications For Your Summer Vacation
May 10, 2025 -
 White Houses Last Minute Decision Maha Influencer Replaces Surgeon General Nominee
May 10, 2025
White Houses Last Minute Decision Maha Influencer Replaces Surgeon General Nominee
May 10, 2025 -
 Preparing For Real Id Enforcement A Summer Travelers Checklist
May 10, 2025
Preparing For Real Id Enforcement A Summer Travelers Checklist
May 10, 2025 -
 Interest Rate Decisions Understanding The Feds Divergent Path
May 10, 2025
Interest Rate Decisions Understanding The Feds Divergent Path
May 10, 2025
