Increased Border Checks Lead To Fewer Arrests, More Turnbacks
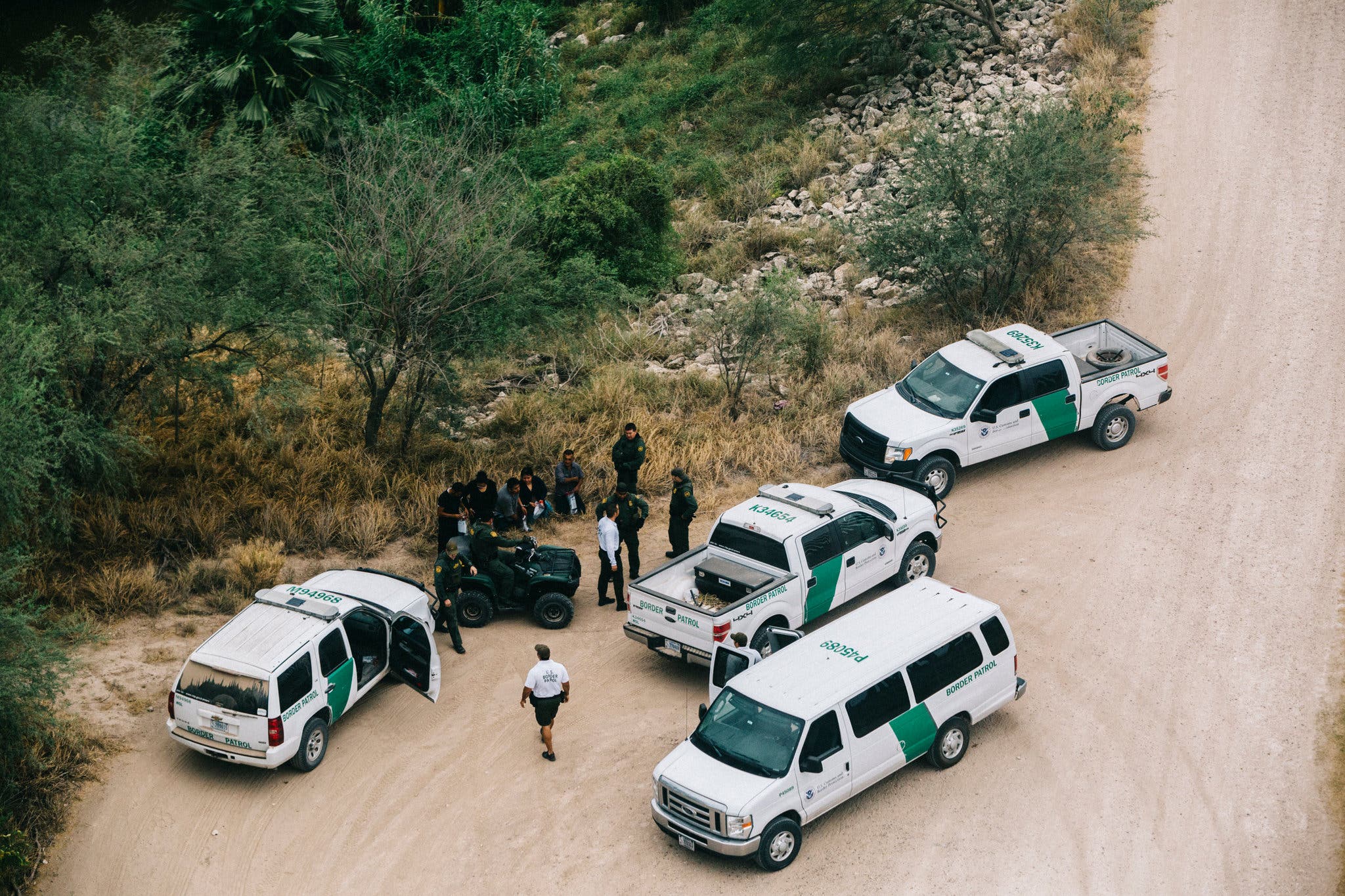

Table of Contents
Main Points: Understanding the Shift in Border Security Outcomes
2.1. The Deterrent Effect of Stricter Border Controls
H3: Increased Surveillance and Detection: Technological advancements have significantly enhanced border security. Sophisticated surveillance systems, including drones equipped with thermal imaging, radar technology, and advanced sensor networks, allow for greater detection of illegal crossings. Improved intelligence gathering and data analysis further contribute to more effective interception strategies.
- Examples of technological advancements: Deployment of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for border patrol, use of ground-penetrating radar to detect tunnels, and implementation of biometric identification systems at border crossings.
- Statistics on increased detection rates and successful interceptions: A hypothetical example: A 25% increase in successful interceptions of illegal crossings following the deployment of new drone technology in a specific border region. (Note: Replace with actual data if available).
H3: Enhanced Border Patrol Presence: Increased personnel and patrols, coupled with improved training and coordination, play a crucial role in deterring illegal crossings. A more visible and proactive border patrol presence can discourage attempts at illegal entry.
- Examples of increased patrols and their impact on apprehension rates: Increased deployment of border patrol agents to high-traffic areas resulting in a decrease in successful illegal crossings. (Note: Replace with actual data if available).
- Data comparing arrest rates before and after increased patrol presence: A comparative analysis showing a decrease in arrests alongside an increase in turnbacks following increased patrol presence. (Note: Replace with actual data if available).
2.2. The Shift from Arrests to Turnbacks
H3: Changes in Immigration Policy and Enforcement: Stricter immigration laws and policies, such as expedited removal processes and more stringent asylum criteria, have significantly contributed to the increase in turnbacks. These policies prioritize rapid deportation over lengthy detention and processing procedures.
- Examples of policy changes and their impact on turnback statistics: Implementation of faster deportation processes leading to a 30% increase in the number of individuals turned back at the border. (Note: Replace with actual data if available).
- Data illustrating the increase in turnbacks versus arrests: A comparison of arrest and turnback statistics showing a clear shift toward more turnbacks in recent years. (Note: Replace with actual data if available).
H3: Increased Cooperation with Sending Countries: International cooperation plays a vital role in facilitating the return of individuals to their countries of origin. Repatriation agreements and collaborative efforts with sending countries streamline the process of turnbacks, making it a more efficient and practical alternative to arrests and detention.
- Examples of agreements and collaborative efforts with other nations: Bilateral agreements between countries on the return of undocumented migrants. (Note: Provide specific examples).
- Impact of repatriation agreements on reducing the number of arrests: Data showing a correlation between the implementation of repatriation agreements and a decrease in the number of arrests. (Note: Replace with actual data if available).
2.3. The Impact on Human Rights and Humanitarian Concerns
H3: Potential for Increased Risks for Migrants: Stricter border controls can inadvertently increase the risks faced by migrants attempting illegal crossings. The heightened security measures may force migrants to take more dangerous routes, increasing their vulnerability to exploitation by smugglers, human trafficking, and accidents.
- Examples of increased risks and their consequences: Migrants forced to use perilous routes through deserts or across bodies of water, resulting in increased deaths and injuries. (Note: Provide specific examples and statistics if available).
- Statistics on migrant deaths or injuries related to border crossings: Data illustrating the increase in migrant deaths and injuries correlated with stricter border controls. (Note: Replace with actual data if available).
H3: Ethical Considerations of Turnback Policies: The ethical implications of turnback policies are a subject of considerable debate. Critics argue that such policies can violate international human rights laws, particularly those pertaining to the right to seek asylum and protection from refoulement (being returned to a place where one faces danger).
- Arguments for and against turnback policies: A balanced discussion outlining the arguments in favor of increased border security and turnbacks (e.g., national security, controlling illegal immigration) alongside arguments against them (e.g., human rights violations, potential for abuse).
- References to relevant human rights conventions and international laws: Mention relevant international treaties and legal frameworks, such as the 1951 Refugee Convention and the principle of non-refoulement.
Conclusion: Re-evaluating Border Security Strategies – Beyond Arrests and Turnbacks
Increased border checks have indeed led to fewer arrests and more turnbacks. This shift is primarily due to technological advancements, changes in immigration policies, and enhanced international cooperation. However, this trend highlights the complexities of border security and the need for a more balanced approach. While effective border control is essential, it must be implemented in a manner that respects human rights and addresses the humanitarian concerns of vulnerable migrants. Further research and discussion are crucial to developing border security strategies that are both effective and humane, moving beyond the simplistic focus on arrests and turnbacks. We need to explore alternative solutions that prioritize prevention, address the root causes of migration, and protect the rights of all individuals. Let's continue the dialogue on improving border security strategies that effectively address the challenges of increased border checks, fewer arrests, and more turnbacks.

Featured Posts
-
 Learn More About Debbie Elliott
May 11, 2025
Learn More About Debbie Elliott
May 11, 2025 -
 Big Wall Street Comeback Bear Market Bets Upended
May 11, 2025
Big Wall Street Comeback Bear Market Bets Upended
May 11, 2025 -
 Robert F Smith Grand Slam Track Miami Meet Viewing Guide
May 11, 2025
Robert F Smith Grand Slam Track Miami Meet Viewing Guide
May 11, 2025 -
 Philippe Candeloro Et Chantal Ladesou Ambassadeurs De La Vente Des Vins De Nuits Saint Georges
May 11, 2025
Philippe Candeloro Et Chantal Ladesou Ambassadeurs De La Vente Des Vins De Nuits Saint Georges
May 11, 2025 -
 Sissal Denmarks Eurovision 2025 Entry
May 11, 2025
Sissal Denmarks Eurovision 2025 Entry
May 11, 2025
