Inflation's Persistence: The Role Of Post-Pandemic Fiscal Measures, According To The ECB
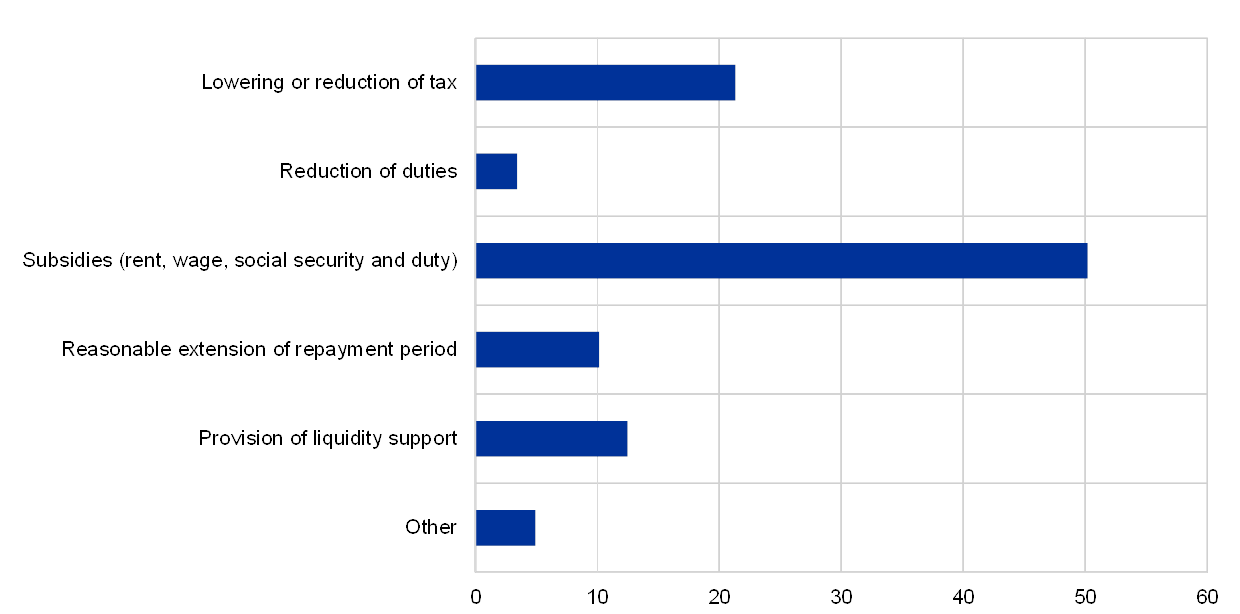
Table of Contents
The ECB's Assessment of Post-Pandemic Fiscal Stimulus
The ECB acknowledges that the substantial fiscal stimulus packages implemented across Europe to mitigate the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic played a significant role in the current inflationary environment. These measures, while necessary to prevent a deeper economic crisis, inadvertently contributed to inflation's persistence.
Increased Aggregate Demand
Massive fiscal stimulus packages injected significant liquidity into the economy, leading to a surge in aggregate demand.
- Examples of fiscal measures: These included extensive wage subsidy programs (like Kurzarbeit in Germany), direct cash payments to citizens, and large-scale investments in infrastructure projects.
- Demand exceeding supply: This rapid increase in demand significantly outpaced the capacity of supply chains to meet it, creating upward pressure on prices. The increased purchasing power, coupled with constrained supply, was a key driver of inflation.
- Sector-specific impact: The ECB's analysis highlights the uneven impact across sectors. For example, the energy sector experienced significant price increases due to both increased demand and supply chain disruptions.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Fiscal Policy Interaction
The interaction between expansive fiscal policies and pre-existing supply chain disruptions further exacerbated inflationary pressures. The increased demand fueled by fiscal stimulus collided with constrained supply, leading to even higher price increases.
- Demand colliding with constrained supply: The surge in demand amplified the existing bottlenecks in global supply chains, which were already struggling to recover from the pandemic's initial shock.
- Specific supply chain bottlenecks: Examples include shortages of semiconductors impacting the automotive industry, disruptions in energy supplies causing soaring energy prices, and logistical challenges leading to delays and higher transportation costs.
- Fiscal measures amplifying bottlenecks: While not the sole cause, the increased demand generated by fiscal measures arguably amplified these existing bottlenecks, contributing to the severity and persistence of inflation.
The ECB's Monetary Policy Response to Inflation's Persistence
Faced with persistent inflation, the ECB has implemented a series of monetary policy measures aimed at cooling down the economy and curbing inflationary pressures.
Interest Rate Hikes
A key element of the ECB's response has been a series of significant interest rate hikes. This is a classic tool to combat inflation by making borrowing more expensive, thus reducing investment and consumer spending.
- Timing and magnitude: The ECB has progressively increased its key interest rates, beginning in July 2022 and continuing throughout 2023. The magnitude of these hikes has been substantial, reflecting the severity of the inflationary challenge.
- Mechanism of impact: Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers, leading to reduced investment, lower consumption, and ultimately, decreased aggregate demand. This helps to alleviate inflationary pressures.
- Potential side effects: While necessary, interest rate hikes carry the risk of slowing economic growth, potentially leading to a recession or increased unemployment. The ECB is carefully navigating this delicate balancing act.
Quantitative Tightening
Alongside interest rate hikes, the ECB has engaged in quantitative tightening (QT), reducing its asset purchase program and allowing its balance sheet to shrink.
- Reducing the money supply: By reducing the amount of money circulating in the economy, QT aims to curb inflationary pressures. This complements the effects of higher interest rates.
- Impact on financial markets: QT can influence financial markets, impacting bond yields and potentially impacting credit conditions for businesses and consumers.
- Potential risks: QT carries the risk of causing financial market instability if implemented too aggressively. The ECB is monitoring the impact closely and adjusting its approach as needed.
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook on Inflation's Persistence
The pandemic and the subsequent fiscal and monetary responses have likely created lasting structural changes in the economy that will continue to influence inflation's trajectory for some time.
Structural Changes in the Economy
The pandemic has spurred shifts in labor markets, supply chains, and global geopolitical dynamics that are likely to impact inflation in the long term.
- Shifts in labor markets: Changes in labor supply and demand, remote work trends, and worker expectations regarding wages are all potential factors influencing inflation.
- Geopolitical events and supply chains: The war in Ukraine, for example, has significantly disrupted global energy markets and supply chains, exacerbating inflationary pressures.
- ECB inflation forecasts: The ECB regularly publishes inflation forecasts, which are crucial for understanding the future outlook and guiding policy decisions. These forecasts consider various factors, including the ongoing impact of the war in Ukraine and supply chain dynamics.
The Role of Fiscal Sustainability
Maintaining price stability over the long term requires fiscal sustainability. Excessive government debt can contribute to inflation, particularly if it leads to increased money creation by central banks.
- Government debt and inflation: High levels of government debt can put upward pressure on inflation if not managed effectively.
- ECB recommendations for fiscal policy: The ECB advocates for responsible fiscal policy, including measures to control government spending and reduce debt levels.
- Balancing fiscal support and inflation control: The challenge lies in balancing the need for fiscal support to stimulate economic growth with the need to control inflation. This requires careful coordination between monetary and fiscal authorities.
Conclusion
The ECB's analysis highlights the significant role post-pandemic fiscal measures played in contributing to inflation's persistence. While necessary to mitigate the immediate economic fallout of the pandemic, these measures, combined with supply chain disruptions, created a perfect storm for increased inflationary pressures. The ECB's subsequent monetary policy response, including interest rate hikes and quantitative tightening, aims to address this challenge. However, navigating the complexities of managing inflation while fostering economic growth requires careful consideration of both monetary and fiscal policies. Understanding the interplay between these two forces is crucial for long-term economic stability. To stay informed about the ongoing debate on inflation's persistence and the ECB's policy responses, continue following reputable financial news sources and the ECB's official publications. Understanding the dynamics of inflation persistence is critical for making informed economic decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Minnesota Lynx Wnba Camp Invites Norfolk States Diamond Johnson
Apr 29, 2025
Minnesota Lynx Wnba Camp Invites Norfolk States Diamond Johnson
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Examining The Russian Militarys Activities And Their European Implications
Apr 29, 2025
Examining The Russian Militarys Activities And Their European Implications
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Securing Your Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets A Practical Approach
Apr 29, 2025
Securing Your Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets A Practical Approach
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Fn Abwzby Antlaq Fealyath Fy 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025
Fn Abwzby Antlaq Fealyath Fy 19 Nwfmbr
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Xs Financial Transformation Insights From Musks Recent Debt Sale
Apr 29, 2025
Xs Financial Transformation Insights From Musks Recent Debt Sale
Apr 29, 2025
