The Devastating Impact Of Wildfires: Record High In Global Forest Loss
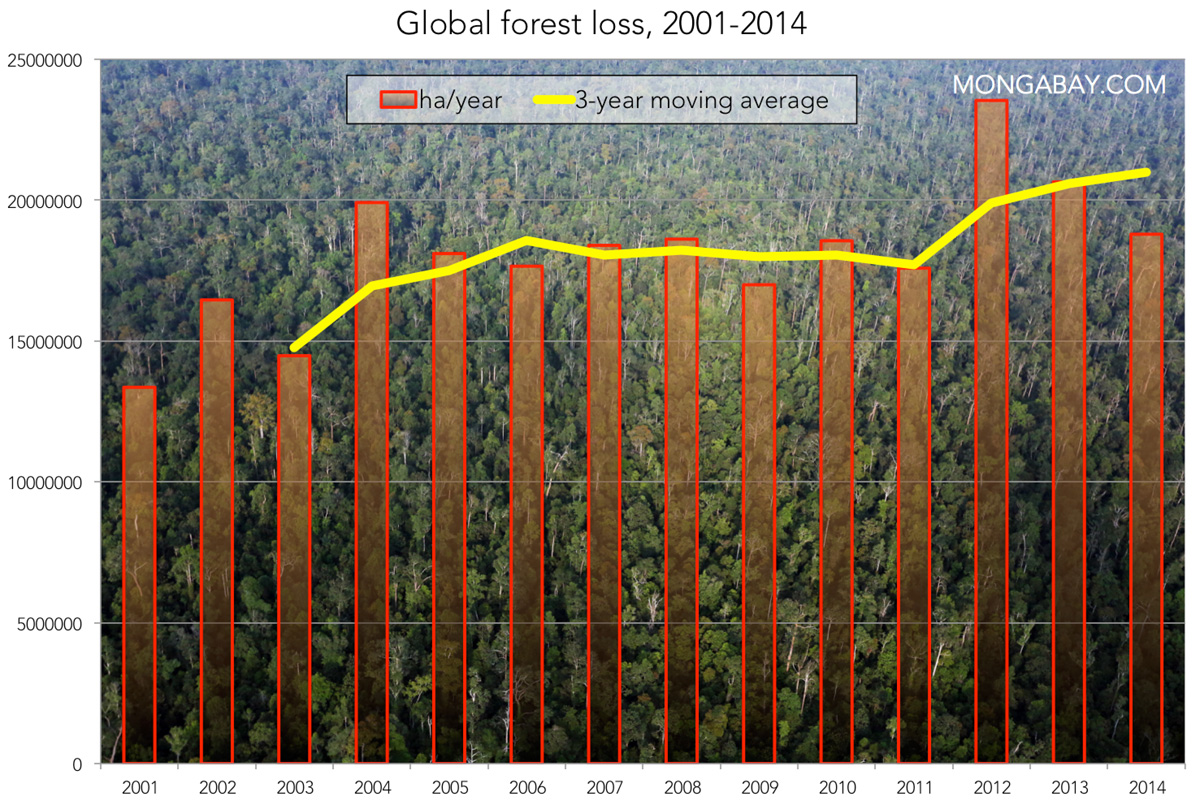
Table of Contents
Environmental Consequences of Wildfires
The environmental consequences of wildfires are catastrophic and far-reaching, impacting ecosystems for decades to come. The sheer destructive power of these forest fires leads to significant and long-lasting damage.
Loss of Biodiversity
Wildfires cause immense biodiversity loss, leading to the extinction of countless plant and animal species. Habitat destruction on a massive scale leaves many creatures with nowhere to live and breed.
- Examples of endangered species affected: The koala population in Australia has been decimated by repeated wildfire events. Many bird species reliant on specific forest habitats experience population crashes. Numerous insect and plant species are lost, disrupting delicate ecosystems.
- Loss of unique ecosystems: Wildfires can completely obliterate unique and irreplaceable ecosystems, like old-growth forests and peatlands, which take centuries to regenerate.
- Disruption of food chains: The loss of plant and animal life disrupts intricate food chains, leading to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem. Predators may lose their prey, and herbivores may lose their food sources. This instability can take years, even decades, to recover. Keyword integration: "biodiversity loss," "habitat destruction," "endangered species," "ecosystem damage".
Air and Water Pollution
The smoke and ash produced by wildfires severely impact air and water quality. The resulting air pollution poses significant risks to human and animal health.
- Health effects of wildfire smoke: Smoke inhalation can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and eye irritation. Long-term exposure can lead to chronic respiratory diseases.
- Water contamination affecting drinking supplies and aquatic life: Ash and debris contaminate water sources, affecting drinking water supplies and harming aquatic life. This can lead to water shortages and the spread of waterborne diseases.
- Long-term effects on soil fertility: Wildfires can damage soil structure, reducing fertility and making it more susceptible to erosion. This can hinder the regeneration of vegetation and impact long-term ecosystem health. Keyword integration: "air pollution," "water contamination," "smoke inhalation," "soil degradation."
Carbon Emissions and Climate Change
Wildfires contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change. The burning of vast tracts of forests releases massive amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere.
- Release of stored carbon: Trees and other vegetation store significant amounts of carbon. Wildfires release this stored carbon as carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Contribution to global warming: The increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere contributes to global warming and climate change.
- Feedback loop between climate change and wildfire frequency: Climate change, with its increased temperatures and droughts, creates conditions that are more favorable for wildfires, creating a dangerous feedback loop. Keyword integration: "carbon emissions," "greenhouse gases," "climate change," "global warming," "carbon cycle."
Socioeconomic Impacts of Wildfires
Beyond the environmental devastation, wildfires have profound socioeconomic impacts, affecting communities and economies on a massive scale.
Loss of Human Life and Displacement
Wildfires tragically claim human lives, cause injuries, and lead to the displacement of entire communities.
- Statistics on human casualties: Each year, wildfires result in numerous deaths and injuries, both directly from the fires and indirectly from smoke inhalation or other related causes.
- Economic costs of rebuilding: The cost of rebuilding homes, businesses, and infrastructure after a wildfire can be astronomical, placing a significant burden on individuals, communities, and governments.
- Psychological trauma on survivors: The experience of losing homes, loved ones, or entire communities can cause profound psychological trauma, impacting mental health for years to come. Keyword integration: "wildfire victims," "humanitarian crisis," "economic impact," "displacement," "community recovery."
Damage to Infrastructure and Property
Wildfires cause widespread destruction to homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure, disrupting daily life and the economy.
- Cost of property damage: The economic losses from property damage caused by wildfires are immense, impacting insurance companies, homeowners, and businesses.
- Disruption of essential services (power, water, transportation): Wildfires can damage power lines, water pipes, and transportation networks, disrupting essential services for extended periods.
- Insurance challenges: Insurance companies face significant challenges in managing claims following widespread wildfire damage, often leading to increased premiums and limited coverage. Keyword integration: "property damage," "infrastructure damage," "economic losses," "insurance claims."
Impact on Agriculture and Forestry
Wildfires devastate agricultural lands and forests, impacting livelihoods and food security.
- Loss of agricultural land: Wildfires can destroy crops, livestock, and agricultural infrastructure, leading to food shortages and economic hardship for farmers.
- Impact on timber industry: Wildfires can decimate forests, impacting the timber industry and affecting jobs and economic activity in forestry-dependent regions.
- Food price increases: The destruction of crops and livestock can lead to increased food prices, impacting consumers and those already facing food insecurity. Keyword integration: "agricultural losses," "forestry industry," "food security," "livelihoods."
Combating the Growing Threat of Wildfires
Addressing the escalating threat of wildfires requires a multi-pronged approach involving prevention, improved response mechanisms, and international cooperation.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Proactive measures are crucial in preventing wildfires and mitigating their impact.
- Importance of firebreaks: Creating firebreaks—gaps in vegetation—can help contain wildfires and prevent their spread.
- Responsible land management: Implementing responsible forest management practices, such as controlled burns and thinning, can reduce the risk of large-scale wildfires.
- Educating the public on fire safety: Public awareness campaigns are essential in educating the public about fire safety and responsible outdoor behavior. Keyword integration: "wildfire prevention," "fire management," "forest management," "public awareness," "fire safety."
Improved Wildfire Detection and Response
Technology and early warning systems are essential in mitigating wildfire damage.
- Use of satellite imagery: Satellite imagery allows for early detection of wildfires, enabling faster response times.
- Early warning systems: Developing and implementing effective early warning systems can provide communities with crucial time to evacuate and prepare.
- Improved firefighting techniques: Investing in advanced firefighting techniques, equipment, and training is crucial for effective wildfire suppression. Keyword integration: "wildfire detection," "early warning systems," "firefighting technology," "disaster response."
International Cooperation and Policy
International collaboration and effective policies are essential to address the global wildfire crisis.
- Sharing best practices: Sharing best practices and knowledge among countries can improve wildfire prevention and response strategies worldwide.
- International aid and support: Providing international aid and support to countries affected by wildfires is crucial for disaster relief and recovery efforts.
- Strengthening environmental regulations: Strengthening environmental regulations and promoting sustainable land management practices are essential for long-term wildfire prevention. Keyword integration: "international cooperation," "climate policy," "environmental regulations," "global response."
Conclusion
The record-high number of wildfires and the resulting global forest loss highlight the devastating environmental, socioeconomic, and climatic impacts of this escalating crisis. Combating the devastating impact of wildfires requires collective action, from improved forest management and fire prevention strategies to the development of effective early warning systems and international cooperation. Learn more about wildfire prevention and how you can help by supporting organizations dedicated to wildfire mitigation and advocating for stronger environmental policies. Take action today to protect our forests from the devastating effects of wildfires and build a more resilient future.

Featured Posts
-
 Euronext Amsterdam Stocks Surge 8 After Trump Tariff Pause
May 24, 2025
Euronext Amsterdam Stocks Surge 8 After Trump Tariff Pause
May 24, 2025 -
 Microsoft Email Controversy Palestine Keyword Filtering Sparks Outrage
May 24, 2025
Microsoft Email Controversy Palestine Keyword Filtering Sparks Outrage
May 24, 2025 -
 Trumps Private Warning Putins Unreadiness To End War Say European Officials
May 24, 2025
Trumps Private Warning Putins Unreadiness To End War Say European Officials
May 24, 2025 -
 Rio Tinto Responds To Forrests Pilbara Concerns Addressing Environmental Impacts
May 24, 2025
Rio Tinto Responds To Forrests Pilbara Concerns Addressing Environmental Impacts
May 24, 2025 -
 How To Get Tickets For Bbc Radio 1s Big Weekend
May 24, 2025
How To Get Tickets For Bbc Radio 1s Big Weekend
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Rising Costs And The Implications For Auto Security In Canada
May 24, 2025
Rising Costs And The Implications For Auto Security In Canada
May 24, 2025 -
 Hangi Burc 16 Mart Dogum Tarihlilerin Burc Yorumu
May 24, 2025
Hangi Burc 16 Mart Dogum Tarihlilerin Burc Yorumu
May 24, 2025 -
 Budget Cuts Force Canadians To Reconsider Vehicle Theft Prevention
May 24, 2025
Budget Cuts Force Canadians To Reconsider Vehicle Theft Prevention
May 24, 2025 -
 16 Mart Doganlarin Burcu Ve Kisilik Oezellikleri
May 24, 2025
16 Mart Doganlarin Burcu Ve Kisilik Oezellikleri
May 24, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Inflation On Car Security Measures In Canada
May 24, 2025
The Impact Of Inflation On Car Security Measures In Canada
May 24, 2025
