The Frequency Of Airplane Accidents And Near Misses: A Data-Driven Perspective

Table of Contents
Understanding the Data on Airplane Accidents
Reliable data is crucial for understanding the true frequency of airplane accidents. Several organizations meticulously collect and analyze this information, providing valuable insights into aviation safety trends.
Sources of Data
Several reputable sources provide comprehensive data on airplane accidents and incidents. These include:
- International Air Transport Association (IATA): IATA compiles global data on airline safety performance, offering valuable insights into accident rates and contributing factors.
- Aviation Safety Network (ASN): ASN maintains a comprehensive database of aviation accidents and incidents, providing detailed information on each event.
- National Aviation Authorities: Individual countries maintain their own detailed records of accidents and incidents within their airspace, often providing granular data on specific causes and contributing factors. Examples include the NTSB (USA) and the AAIB (UK).
Global Accident Rates
Despite the perception of frequent incidents, airplane accidents are remarkably rare compared to other modes of transport. When considering passenger miles flown, air travel boasts a significantly lower accident rate than car travel or even train travel.
[Insert Graph/Chart showing comparative accident rates of different modes of transportation]
- Yearly accident rates over the past decade: While fluctuating slightly year-to-year, the overall trend shows a consistent decrease in global commercial airline accidents over the past decade.
- Accident rates per passenger mile flown: This metric consistently demonstrates the remarkable safety of air travel, highlighting the significant improvements in safety protocols and technology.
- Types of accidents: Accidents are categorized into various types, including runway incidents (e.g., runway excursions), mid-air collisions (rare but serious), and mechanical failures. Understanding the breakdown allows for targeted safety improvements.
The Significance of Near Misses in Aviation Safety
Near misses, also known as incidents, are events that could have resulted in an accident but did not. These seemingly minor events offer invaluable insights into potential safety vulnerabilities.
Defining a Near Miss
A near miss in aviation is defined as an unplanned event that could have resulted in an accident but did not, typically due to timely intervention or fortunate circumstances. These events often involve close calls, such as near collisions or equipment malfunctions averted at the last minute.
Reporting and Investigation of Near Misses
Robust reporting systems are critical for identifying and addressing potential hazards. Pilots, air traffic controllers, and maintenance personnel are encouraged to report near misses without fear of reprisal. These reports are then thoroughly investigated to understand the root causes and implement corrective actions.
- The number of near misses reported annually: The number of reported near misses significantly exceeds the number of accidents, highlighting the importance of proactive safety measures.
- Common causes of near misses: Common causes include pilot error (e.g., loss of situational awareness), air traffic control issues (e.g., communication breakdowns), and weather conditions (e.g., low visibility).
- The role of technology in preventing near misses: Technologies like Traffic Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) and Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) play a critical role in preventing near misses by providing pilots with real-time information and alerts.
Factors Contributing to Airplane Accidents and Near Misses
Airplane accidents and near misses result from a complex interplay of factors, often involving a combination of human, technical, and environmental elements.
Human Factors
Human error remains a significant contributor to aviation incidents. This includes:
- Pilot fatigue: Long flights and irregular schedules can lead to reduced performance and increased risk.
- Training deficiencies: Inadequate training can leave pilots unprepared for unexpected situations.
- Communication breakdowns: Poor communication between pilots, air traffic control, and maintenance personnel can lead to errors.
Technical Factors
Technical malfunctions contribute to a smaller percentage of accidents, but their consequences can be severe. These include:
- Mechanical failures: Engine failure, hydraulic system problems, and other mechanical issues.
- Maintenance issues: Inadequate maintenance or overlooked issues during inspections can lead to malfunctions.
- Technological malfunctions: Problems with onboard computers, navigation systems, and other technologies.
Environmental Factors
Weather conditions and geographical limitations play a role in some accidents and near misses:
- Weather conditions: Turbulence, icing, low visibility, and severe weather events significantly impact flight safety.
- Geographical limitations: Terrain challenges, airport infrastructure limitations, and other geographical factors can increase risk.
Improving Aviation Safety: Technologies and Strategies
Continuous improvement in aviation safety relies on technological advancements, enhanced training, and robust regulations.
Advanced Technologies
Technological advancements are at the forefront of enhancing aviation safety:
- Automation: Automating various aspects of flight operations reduces human error.
- Improved navigation systems: More precise and reliable navigation systems reduce the risk of collisions and improve situational awareness.
- Predictive maintenance: Using data analytics to predict potential maintenance needs reduces the likelihood of mechanical failures.
Enhanced Training and Regulations
Stringent training and regulations are vital for maintaining high safety standards:
- Changes in training standards: Simulators and advanced training programs enhance pilots' skills and preparedness.
- Robust safety regulations: International standards and regulations ensure consistent safety protocols worldwide.
- Effective oversight: Regular audits and inspections ensure compliance with safety standards.
Conclusion: A Data-Driven Look at Airplane Accidents and Near Misses
This data-driven analysis of airplane accidents and near misses demonstrates the remarkable safety of air travel. While accidents and near misses remain a possibility, continuous improvements in technology, training, and regulations are reducing their frequency. The importance of robust reporting systems, thorough investigations, and a commitment to learning from incidents is crucial for maintaining the highest levels of aviation safety. Continue learning about aviation safety and the ongoing efforts to reduce the frequency of airplane accidents and near misses by exploring further resources [link to relevant resources].

Featured Posts
-
 How To Understand The Net Asset Value Of The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average Ucits Etf
May 24, 2025
How To Understand The Net Asset Value Of The Amundi Dow Jones Industrial Average Ucits Etf
May 24, 2025 -
 Glastonbury 2025 Lineup Leak Confirmed Artists And Ticket Information
May 24, 2025
Glastonbury 2025 Lineup Leak Confirmed Artists And Ticket Information
May 24, 2025 -
 Gear Essentials For Ferrari Owners A Comprehensive Guide
May 24, 2025
Gear Essentials For Ferrari Owners A Comprehensive Guide
May 24, 2025 -
 Sundays Demonstration Assessing The National Rallys Show Of Support For Le Pen
May 24, 2025
Sundays Demonstration Assessing The National Rallys Show Of Support For Le Pen
May 24, 2025 -
 90 Let Sergeyu Yurskomu Pamyat O Genii Paradoksov
May 24, 2025
90 Let Sergeyu Yurskomu Pamyat O Genii Paradoksov
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Memorial Day Gas Prices A Decade Low Forecast
May 24, 2025
Memorial Day Gas Prices A Decade Low Forecast
May 24, 2025 -
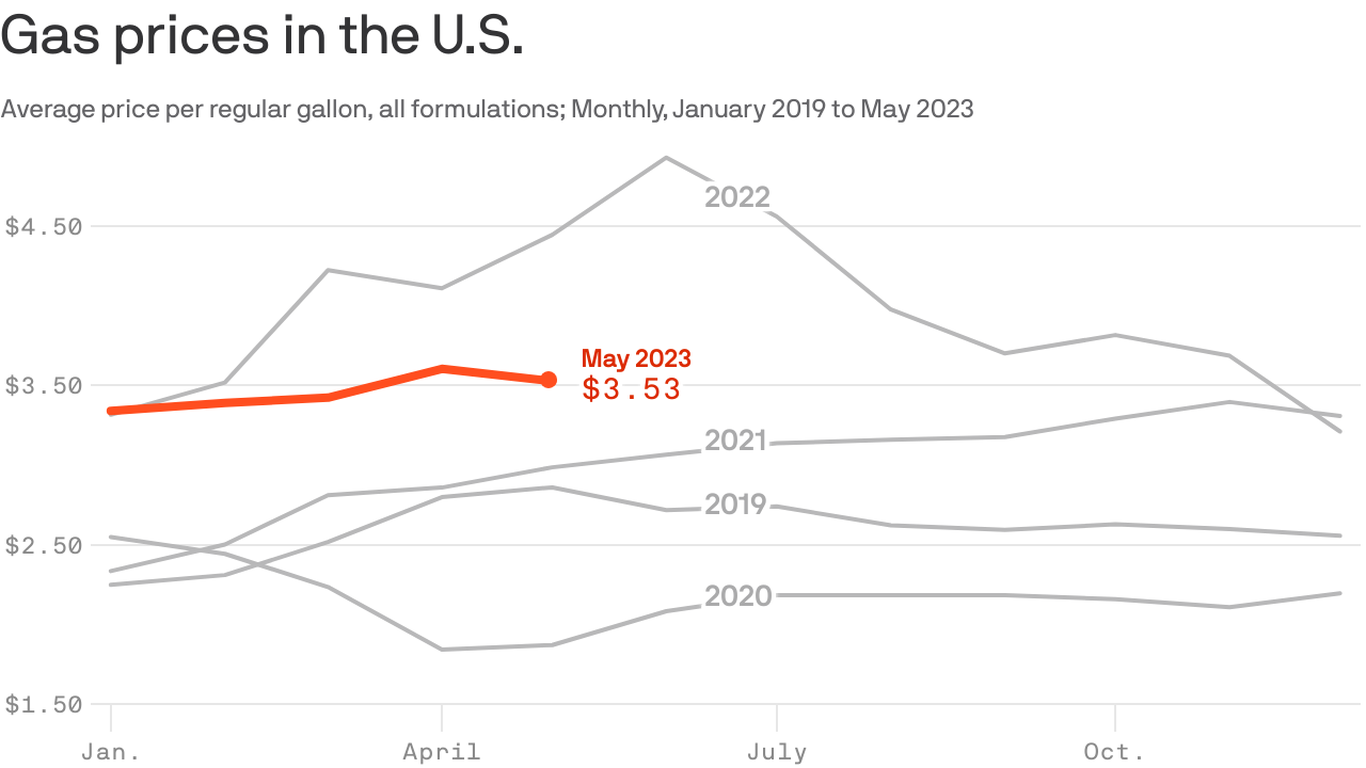 Record Low Gas Prices Predicted For Memorial Day Weekend
May 24, 2025
Record Low Gas Prices Predicted For Memorial Day Weekend
May 24, 2025 -
 Sandy Point Rehoboth Ocean City Beaches Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Weather Prediction
May 24, 2025
Sandy Point Rehoboth Ocean City Beaches Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Weather Prediction
May 24, 2025 -
 2025 Memorial Day Weekend Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 24, 2025
2025 Memorial Day Weekend Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 24, 2025 -
 Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 24, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 24, 2025
