The Process Of Data Transfer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Table of Contents
Choosing the Right Data Transfer Method
Selecting the appropriate data transfer method is crucial for a successful operation. The best choice depends on factors like the amount of data, the distance between devices, the speed required, and security considerations. Here are some common methods:
Direct Cable Transfer (e.g., USB, Ethernet)
- Pros: High speed, robust security (especially for local transfers), and simplicity. Direct cable transfers offer the fastest speeds for transferring large files between devices in close proximity. Using a USB 3.0 or Thunderbolt cable will significantly improve transfer speeds compared to older USB versions.
- Cons: Limited transfer distance, requiring a physical connection between devices. This method is unsuitable for transferring data over long distances or between devices that are not physically close.
- Best for: Transferring large files (videos, photos, backups) between nearby devices like computers, external hard drives, and smartphones.
Network Transfer (e.g., Wi-Fi, LAN)
- Pros: Convenience, flexibility, and no physical connection needed. Network transfers are ideal for moving files between devices on the same network, eliminating the need for cables.
- Cons: Transfer speed can be significantly affected by network conditions (bandwidth, congestion, Wi-Fi signal strength). Security is also a concern; using a secure network and strong passwords is essential.
- Best for: Transferring files between devices on the same network (e.g., sharing files between computers on a home network), or accessing files remotely from a networked device. File sharing protocols like SMB/CIFS are commonly used for this method.
Cloud-Based Transfer (e.g., Dropbox, Google Drive, OneDrive)
- Pros: Accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, automatic backups, and convenient file sharing capabilities. Cloud-based data transfer solutions provide seamless access to your files from multiple devices.
- Cons: Requires a consistent internet connection, often involves subscription costs for larger storage capacities, and raises potential security concerns related to third-party services. You'll need to trust the security protocols and privacy policies of the chosen cloud provider.
- Best for: Sharing files with multiple users, backing up data regularly, and accessing files from various devices (computers, smartphones, tablets).
External Storage Devices (e.g., Hard Drives, SSDs)
- Pros: High speed, particularly with SSDs, portability, and the ability to access data offline. External drives offer a reliable way to transfer large amounts of data without relying on network connectivity.
- Cons: Requires a physical storage device, which can be lost or damaged. Data stored on these devices is vulnerable if the physical device is lost or stolen.
- Best for: Archiving large amounts of data, transporting files between locations, and creating offline backups.
Preparing for Data Transfer
Proper preparation is essential for a smooth and error-free data transfer. Neglecting this step can lead to data loss or corruption.
Data Backup
Before initiating any data transfer, always create a complete backup of the source data. This precaution safeguards against potential data loss during the transfer process. Use reputable backup software or cloud services to ensure data integrity.
Source and Destination Preparation
Identify the source and destination devices clearly. Verify that the destination device has enough available storage space to accommodate the files being transferred. Insufficient space can interrupt the transfer and cause errors.
Security Considerations
Prioritize data security throughout the data transfer process. Employ strong passwords, consider encrypting sensitive data, and use secure transfer protocols like SFTP for network transfers. Install and regularly update your antivirus software to protect against malware.
Executing the Data Transfer
This section outlines the steps for executing data transfer using the methods described above. Remember to tailor these instructions to your specific software and hardware.
Step-by-step instructions for each method:
(This section would contain detailed, step-by-step instructions with screenshots for each transfer method: direct cable, network, cloud, and external storage. Due to the length constraints of this response, these instructions are omitted here but are crucial for a complete article.)
Monitoring Progress
Monitor the data transfer progress closely. Most transfer utilities provide a progress bar indicating the completion percentage. Address any errors or slowdowns promptly.
Verification
After the transfer completes, verify the data integrity. Compare file sizes and checksums (MD5 or SHA) to ensure all files were transferred correctly and without corruption.
Troubleshooting Common Data Transfer Issues
Despite careful planning, issues can arise during data transfer. Here are some common problems and solutions:
Slow Transfer Speeds
Slow transfer speeds can result from network congestion, hardware limitations (old USB versions, slow hard drives), or excessively large file sizes. Check your network connection, use faster hardware, or consider compressing large files before transfer.
Transfer Errors
Error messages often indicate problems with the source or destination devices, insufficient storage space, or corrupted files. Consult the error message for clues and search online for specific solutions related to the error code.
Data Loss or Corruption
Data loss or corruption can be devastating. Preventing data loss involves regular backups, using reliable transfer methods, and employing error-checking tools. Recovering corrupted files might require specialized data recovery software.
Conclusion
Successfully transferring data requires careful planning and execution. By understanding the various methods available and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure a smooth and efficient data transfer process. Remember to always prioritize data security and back up your information before beginning any data transfer. Mastering the art of effective data transfer will enhance your productivity and safeguard your valuable information. Choose the best data transfer method for your specific needs and enjoy the benefits of seamless data management.

Featured Posts
-
 Krypto The Last Dog Of Krypton A Critical Analysis Of Dcs Latest Film
May 08, 2025
Krypto The Last Dog Of Krypton A Critical Analysis Of Dcs Latest Film
May 08, 2025 -
 Alex Carusos Playoff History Making Performance In Thunder Game 1 Victory
May 08, 2025
Alex Carusos Playoff History Making Performance In Thunder Game 1 Victory
May 08, 2025 -
 Brasileirao De Arrascaeta Brilha Flamengo Vence Gremio Com Atuacao Decisiva
May 08, 2025
Brasileirao De Arrascaeta Brilha Flamengo Vence Gremio Com Atuacao Decisiva
May 08, 2025 -
 Sonys Ps 5 Pro Major Upgrade Details And Release Speculation
May 08, 2025
Sonys Ps 5 Pro Major Upgrade Details And Release Speculation
May 08, 2025 -
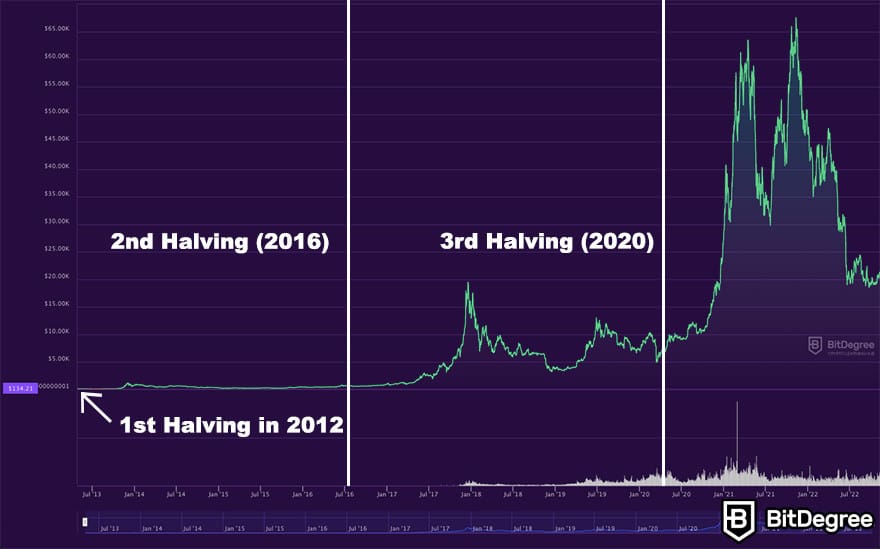 Micro Strategy Stock Vs Bitcoin A 2025 Investment Comparison
May 08, 2025
Micro Strategy Stock Vs Bitcoin A 2025 Investment Comparison
May 08, 2025
