Trump Tariffs: CEOs Sound Alarm On Economic Impact And Consumer Sentiment

Table of Contents
The Direct Economic Impact of Trump Tariffs
The initial goal of the Trump tariffs was to protect American industries, particularly steel and aluminum, from foreign competition. However, the impact extended far beyond these sectors, affecting agriculture, manufacturing, and numerous other industries reliant on global supply chains. The resulting economic repercussions were substantial and far-reaching.
Increased Production Costs
Tariffs directly increased the cost of raw materials for many businesses. These increased import costs were not easily absorbed, leading to a domino effect.
- Industries Hit Hardest: Steel and aluminum manufacturers initially benefitted, but the increased cost of these materials significantly impacted downstream industries like automotive manufacturing, construction, and appliance production.
- Price Increases Passed Onto Consumers: Businesses, facing higher input costs, passed these increased expenses onto consumers through higher prices for finished goods. This led to a noticeable rise in inflation.
- Reduced Competitiveness in Global Markets: American businesses faced a disadvantage in global markets as their production costs rose, making their products less competitive compared to those from countries unaffected by the tariffs.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The complex global supply chains that underpin modern manufacturing were significantly disrupted by the tariffs. The imposition of tariffs forced companies to re-evaluate their sourcing strategies and logistics.
- Delays in Production: The uncertainty surrounding tariffs led to delays in sourcing raw materials and intermediate goods, impacting production schedules and overall efficiency.
- Increased Transportation Costs: Companies had to explore alternative sourcing options, often resulting in longer shipping distances and increased transportation costs.
- Search for Alternative Suppliers: Businesses were forced to invest time and resources searching for alternative suppliers, often at a higher cost and with increased logistical challenges. This particularly affected small businesses with limited resources.
- Impact on Small Businesses: Smaller businesses, lacking the resources of larger corporations, were disproportionately affected by supply chain disruptions, leading to financial strain and, in some cases, closures.
Job Losses and Economic Slowdown
The combination of increased costs, supply chain disruptions, and reduced competitiveness contributed to job losses and a slowdown in economic growth.
- Statistics on Job Losses: While precise figures are debated, studies suggest job losses in sectors heavily impacted by the tariffs. (Note: Insert relevant data and links to reputable sources here. For example, link to studies from the Congressional Budget Office or similar organizations.)
- Reduced Investments: The economic uncertainty created by the tariffs discouraged business investment, as companies hesitated to commit to expansion or new projects.
- Negative Impact on GDP Growth: The combination of job losses and reduced investment negatively impacted overall GDP growth, contributing to a slower economic expansion.
Deteriorating Consumer Sentiment and Spending
The increased prices resulting from the tariffs directly impacted consumers’ purchasing power and confidence. Higher prices for everyday goods squeezed household budgets, leading to a decline in consumer spending.
Reduced Disposable Income
Higher prices for everything from clothing to cars reduced consumer disposable income. This had a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Examples of Everyday Goods Affected: Consumers faced price increases on a wide range of goods, including food, clothing, automobiles, and household appliances.
- Decreased Consumer Confidence Indexes: Consumer confidence indexes, which track consumer optimism about the future, declined during the period of tariff implementation, reflecting increased economic anxiety.
- Reduced Spending on Non-Essential Items: Consumers reacted to higher prices by cutting back on spending, particularly on discretionary or non-essential items.
Shift in Consumer Behavior
Facing higher prices, consumers adapted their behavior to manage their budgets. This shifted spending patterns and affected businesses across various sectors.
- Examples of Changes in Consumer Behavior: Consumers actively sought cheaper alternatives, delayed purchases, or simply bought less.
- Impact on Retail Sales: Retail sales figures reflected the impact of reduced consumer spending, with slower growth or even declines in certain sectors.
- Growth of Discount Retailers: The trend towards value shopping fueled the growth of discount retailers, as consumers prioritized affordability over brand loyalty.
Long-Term Economic Uncertainty
The tariffs' impact extended beyond the immediate consequences, creating long-term economic uncertainty and affecting future investment and growth.
- Investor Uncertainty: The instability caused by the tariffs created uncertainty for investors, making them hesitant to commit capital to new ventures.
- Decreased Business Investment: Reduced investor confidence and fear of further trade disruptions led businesses to postpone or cancel investment plans, hindering future growth.
- Impact on Future Economic Forecasts: Economic forecasters revised their predictions downward, reflecting the dampening effect of the tariffs on long-term economic growth.
Conclusion
The Trump tariffs had a significant and multifaceted negative impact on the US economy. Increased production costs, widespread supply chain disruptions, job losses, and a decline in consumer sentiment all contributed to an economic slowdown. The long-term consequences of these trade policies remain a significant concern for CEOs and economists alike. Understanding the lasting effects of Trump tariffs on the American economy and consumer sentiment is crucial. Further research into the impact of trade policies on different sectors is necessary to mitigate future economic risks. Continue to explore the effects of trade wars and their consequences for a healthy economy. Learn more about the impact of tariffs on businesses and their implications for consumer prices.

Featured Posts
-
 When Does Chelsea Handlers The Feeling Premiere On Netflix
Apr 26, 2025
When Does Chelsea Handlers The Feeling Premiere On Netflix
Apr 26, 2025 -
 How Tariffs Are Slowing Down Big Techs Advertising Revenue
Apr 26, 2025
How Tariffs Are Slowing Down Big Techs Advertising Revenue
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Seven Year Prison Sentence Sought For George Santos In Federal Fraud Case
Apr 26, 2025
Seven Year Prison Sentence Sought For George Santos In Federal Fraud Case
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Chelsea Handlers Whistler Trip Unexpected Star Joins The Fun
Apr 26, 2025
Chelsea Handlers Whistler Trip Unexpected Star Joins The Fun
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Spending Time With Karli Kane Hendrickson Event Occasion
Apr 26, 2025
Spending Time With Karli Kane Hendrickson Event Occasion
Apr 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 100 Days Of Trump How Did It Affect Elon Musks Net Worth
May 10, 2025
100 Days Of Trump How Did It Affect Elon Musks Net Worth
May 10, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Trumps First 100 Days On Elon Musks Financial Status
May 10, 2025
The Impact Of Trumps First 100 Days On Elon Musks Financial Status
May 10, 2025 -
 The Tesla Dogecoin Connection Examining The Influence Of Elon Musk And Market Volatility
May 10, 2025
The Tesla Dogecoin Connection Examining The Influence Of Elon Musk And Market Volatility
May 10, 2025 -
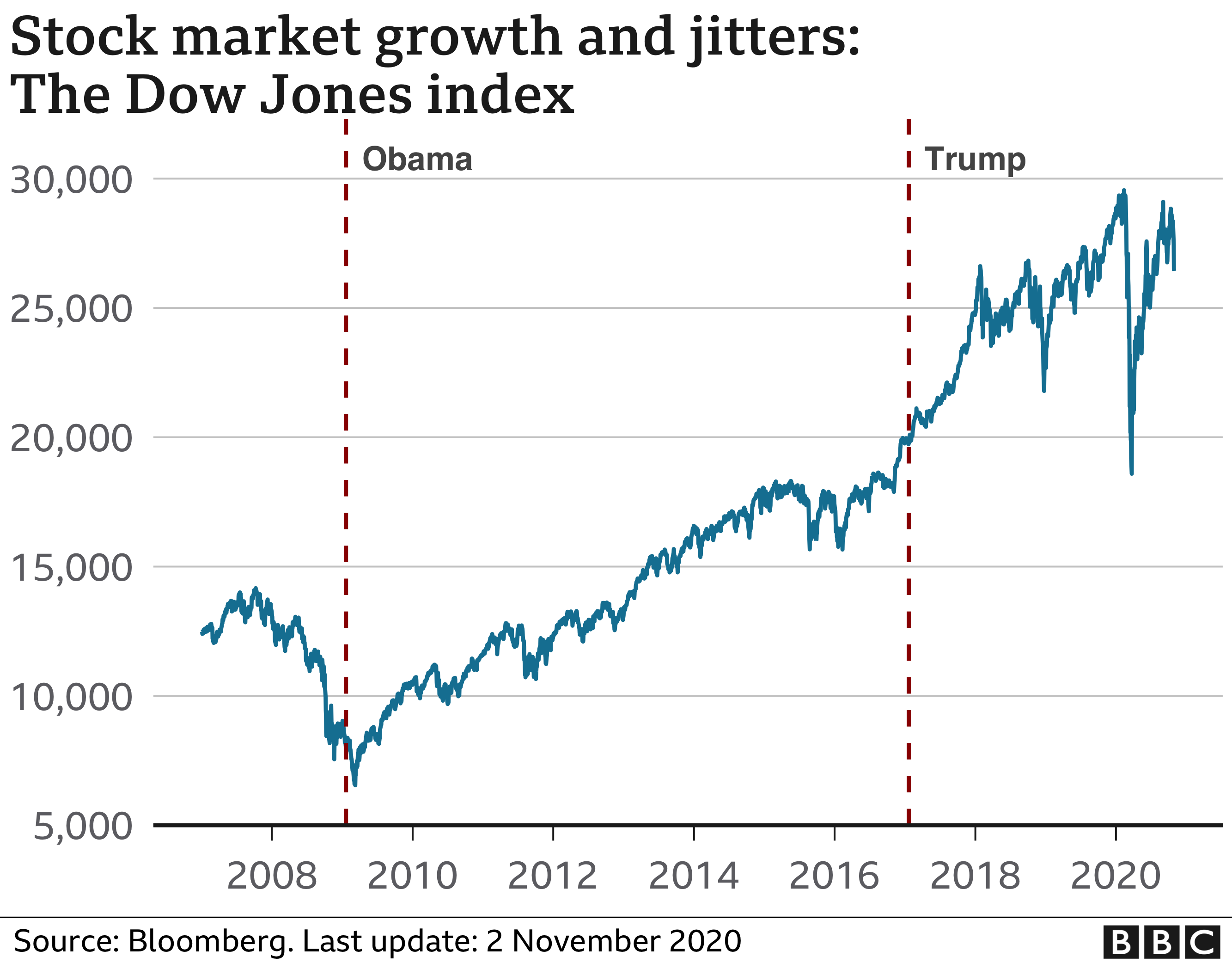 Analyzing The Change In Elon Musks Net Worth The Trump Presidencys First 100 Days
May 10, 2025
Analyzing The Change In Elon Musks Net Worth The Trump Presidencys First 100 Days
May 10, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Impact Of Teslas Stock Performance On Dogecoins Value The Elon Musk Factor
May 10, 2025
Analyzing The Impact Of Teslas Stock Performance On Dogecoins Value The Elon Musk Factor
May 10, 2025
